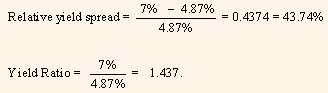A yield spread between any two bond issues can be easily computed when the maturity date for both these issues is same.
The yield spread between these two bond issues, say bond A and bond B, is calculated as follows:
Yield Spread = Yield on bond A - Yield on bond B
Here, bond B is considered to be a benchmark against which bond A is measured.
When a yield spread is calculated by applying the above formula, it is referred to as an absolute yield spread. It is measured in basis points. For example, on the basis of Table 1, as on 03.07.2007, the yield on a 5-year on-the-run treasury issue was 4.87% and the yield on a single A-rated 5-year industrial bond was 7%. If bond A is the 10-year industrial bond and bond B is the 10-year on-the-run treasury issue, the absolute yield spread is:
Yield Spread = 7% - 4.87% = 2.13% or 213 basis points.
Unless otherwise specified, yield spreads are measured by applying the
above-mentioned formula. Yield spread may also be computed on a relative basis by taking the ratio of the yield spread to the yield of the reference bond. This is called a relative yield spread.

Sometimes, bonds are compared in terms of a yield ratio, the quotient of two bond yields, as shown below:
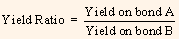
Let us assume that Bond B is the benchmark Treasury issue; then the equations for the yield spread measures are as follows:
Absolute yield spread = Yield on bond A - Yield of on-the run treasury
Relative yield spread = 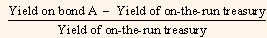
Yield Ratio = 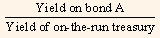
Considering the above example, let us compare the yields on the 5-year single A-rated industrial bond and the 5-year on-the-run treasury; the relative yield spread and yield ratio are computed below:
Absolute yield spread = 7% - 4.87% = 2.13% = 213 basis points