Reference no: EM13494620
Case -1:
A 21 year old white male comes to you complaining that his vision in his right eye has been steadily getting worse over the last couple of years. He had a refraction a couple of years ago and felt that the vision was OK, but not quite perfect when compared to the left eye. His history is negative for eye disease, trauma or surgery. He suffers from hay fever for which he takes a Claritin tablet, but uses no other medications. He has worn glasses since age 10 and has not worn contact lenses.
His visual acuity is OD 20/40 and OS 20/20 with his current spectacles; OD 20/800 and OS 20/200 without spectacles. Your refraction is; OD -3.50 DS -3.00DC x 145, 20/40; OS -0.75DS -1.75DC x 135, 20/20-. Pinhole improved OD to 20/25. Keratometry: ~OD 49.00D@135, 53.25D@45 but very difficult to measure due to Grade 4 distortion. OS 45.00D@10 & 46.00D@100, Grade 1 distortion.
Guiding Questions
1. What is the refractive diagnosis? Be prepared to explain myopia, hyperopia and astigmatism.
2. What proportion of total refractive power is contributed by the cornea? Explain.
3. What is the principle of operation for the keratometer? What is the significance of the distorted image and what abnormalities could produce distortion?
4. What is the significance of the pinhole result?
5. What is hay fever? How does Claritin work?
6. Is there any significance to the fact that he has hay fever? (you may not be able to answer this until later in the case)
Case 2:
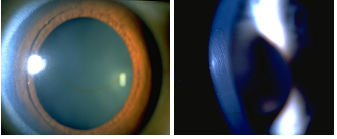
Confrontation and pupil testing is normal. Dilated fundus exam is also normal. Slit -lamp exam suggests some significant variation in corneal thickness; an optic section seems to be thinner inferiorly in the right eye and less pronounced in the left eye. Also you notice some vertical striae in the posterior cornea OS and a "greenish-brown" circular ring (see photos). You order corneal topography analysis.
Guiding Questions
1. What's an optic section?
2. Describe the anatomy and histology of the cornea.
3. What is the function of each layer of the cornea?
4. Why is the cornea transparent?
5. How does the composition of the sclera differ from the cornea? If the sclera is very thin (Stapholomata)
or a piece of it is dried out, it becomes transparent. Explain.
6. What controls the hydration of the cornea? What is the thickness-hydration relationship? Do the thin
areas seen by slit-lamp examination represent a change in hydration?
7. What are corneal striae?
8. What is the colored ring?
Case 3
Topography maps are shown. For comparison a map from two normal patients are shown. The patient is diagnosed as having Keratoconus.
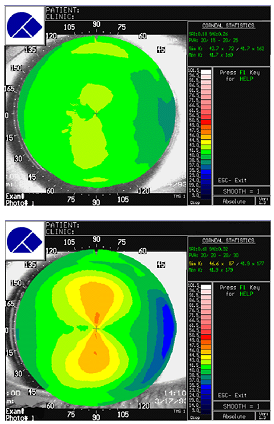
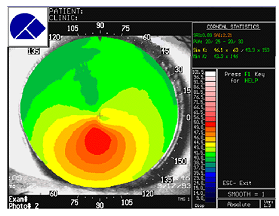
Questions
1. How does topography work?
2. Why does the normal cornea flatten towards the periphery?
3. Where is the apex of the cone?
4. What are the treatment options for keratoconus? Explain how each could improve vision, their limitations, and possible complications.
A few years later, the left eye becomes more astigmatic and shows signs of keratoconus.. The right eye progressed and eventually required a corneal transplant. This worked for about 15 years when signs of ectasia began to appear again.
5. What is the significance of the disease being bilateral in terms of understanding its cause?
6. How could the donor cornea, which was normal, begin to show signs of keratoconus?
7. Describe the current hypotheses for the cause of Keratoconus. (You need to do careful Pubmed searches).