Reference no: EM132381532
Collecting and Analyzing Your Own Prints
You will make a fingerprint impression of each of your 10 fingers:
Materials:
• Your fingers
• Charcoal/Soft Pencil
• Transparent tape
• Magnifying Glass
• Paper
Procedure:
1. Color a dark square of charcoal/pencil on scrap paper. Roll the "pad" portion of a finger over the square from one side of your finger to the other side of your finger. You can roll/smear your finger around. This is like "dusting" your fingerprint.
2. Carefully tear off about 2" of clear tape and lay it on your dusted finger. Press the tape down evenly and then peel it off slowly. This is like "lifting" a latent fingerprint. If you have a good print, stick the tape with your print on a piece of paper and label which finger it is. Otherwise, try again.
3. Repeat steps 1 - 2 (keep coloring over your original dark square) for your remaining fingers and stick the tapes to your paper.
4. Using a magnifying glass, record the type of fingerprint under each of your 10 fingerprints.
Choices for types of fingerprints:
• Radial Loop
• Ulnar Loop
• Whorl
• Central Pocket Loop Whorl
• Double Loop Whorl
• Accidental Whorl
• Plain arch
• Tented arch
5. Don't submit your actual fingerprints with your lab!!! They are considered your personal data. Just record how many fingers you have of each type above.
Determining your Henry-FBI Classification Number
Edward Henry developed a method of classifying all sets of 10 fingerprints into 1,024 groups. This is done so that when an unknown set of prints is submitted to the FBI for comparison, most of the millions of sets on file can be weeded out, leaving only a few dozens of sets of prints that have to be compared by hand. Even with computer programs to help with comparisons, sometimes forensic scientists still need to compare by hand.
Each person's 10 fingerprints are assigned a number, which is called the Henry-FBI classification number:
Step 1: Identify the presence of any whorl patterns on your fingers. In the table below, write a yes or no in rows 1 and 4 if you have whorls on the each of the fingers listed:
|
ROW
|
Finger
|
Right Index
|
Right Ring
|
Left Thumb
|
Left Middle
|
Left Pinky
|
|
Primary Classification
|
|
1
|
Does this
finger have a whorl?
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2
|
Classification
Number
|
|
|
|
|
|
1
|
|
|
3
|
Finger
|
Right Thumb
|
Right Middle
|
Right Pinky
|
Left Index
|
Left Ring
|
|
Primary Classification
|
|
4
|
Does this finger have a
whorl?
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5
|
Classification Number
|
|
|
|
|
|
1
|
|
Step 2: Each finger is given a different number. Examine the diagram below.
• If your finger DOES NOT have a whorl pattern, write a ZERO in rows 2 and 5 in the table above for the classification number.
• If your finger DOES have a whorl pattern write the corresponding number from the diagram below (attached) in rows 2 and 5.
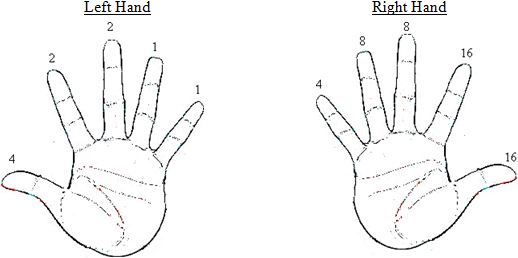
Step 3: Add up the numbers in rows 2 and 5, including the "1" that is in the 2nd to last column. Write the total in the last column of the table. This number (written as a fraction) is your Henry - FBI classification.
Your fraction: Numerator (Last column in row 2) = / Denominator (Last Column in row 5) =
1. Were all your fingerprints the same type of pattern? What patterns were they? Provide a possible explanation as to why they may vary:
2. Examine this table, which shows the frequency of each type of fingerprint in the population as a whole.
|
Frequency of Fingerprint Patterns
|
|
Loops
|
Whorls
|
Arches
|
|
Radial
|
Ulnar
|
Plain
|
Other
|
Plain
|
Tented
|
|
5%
|
60%
|
20%
|
10%
|
4%
|
1%
|
If 60% of the population has ulnar loops, why are fingerprints considered to be individual evidence?
3. How do your fingerprints compare to the population as a whole?
4. Why are Henry - FBI classification numbers useful to police officers and forensic scientists?
For each vocabulary word, match the correct definition AND example:
|
DEFINITION
|
|
VOCABULARY WORD
|
|
EXAMPLE
|
|
5. A fingerprint pattern with one or more ridges entering and exiting from the same side.
|
Fingerprint
|
A.
This area
|
|
6. Fingerprint made by the deposit of perspiration or body oils that is invisible to
the naked eye.
|
Dactyloscopy
|
B. Ridge endings, Islands, Bridges, Eye/enclosures, Cicatrix, Bifurcations and Dots.
|
|
7. A fingerprint pattern with at least two deltas and a core.
|
Loop
|
C. ALL of the following:
|
|
8. The fine structure of ridge characteristics in fingerprints.
|
Delta
|
D. Tented & Plain
|
|
9. The study of fingerprints.
|
Whorl
|
E. Fingerprint lifted by dusting or iodine fuming.
|
|
10. An impression made by
ridge patterns on the top of a finger.
|
Arch
|
F. Fingerprint in clay, wax or fresh paint.
|
|
11. A triangular area found on all loop and whorl patterns.
|
Minutiae
|
G. Plain,

Central Pocket, Double Loop & Accidental
|
12. A 3-D print made as an
indentation in soft material. |
________Visible Print________ |
H. People who use fingerprints to help determine who committed a crime are studying this. |
| 13. Fingerprint left by a finger that has touched something to stain it. |
________Latent Print ________ |
I. Fingerprint in blood, ink or
paint. |
| 14. A fingerprint pattern with no delta or core where all ridges enter from one side and exit the other. |
________Plastic Print________ |
J. Ulnar and Radial |
15. List three parts of the body that have ridges and furrows.
16. Why do fingerprints offer an evolutionary advantage?
17. Label the following in the diagram below: Papillae, Dermis, Epidermis, and Ridges
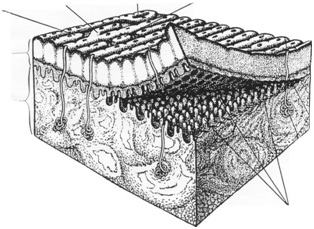
18. For each statement below, identify which part of the skin/fingerprint anatomy is described. (Terms may be used more than once).
Possible Choices: Dermis, Epidermis, Ridges, Furrows, Papillae
________ Raised structures on the tips of fingers
________ Creates the Ridges on the surface
________ Outermost layer of skin
________ Layer of skin that contains papillae
________ Layer of skin that contains sweat glands and nerve cells
________ White space left in fingerprint patterns
________ Black space left in fingerprint patterns
19. List TWO components left by your fingers when you touch something.
20. Why do identical twins NOT have identical fingerprint patterns?
21. Compare and contrast a radial and ulnar loop pattern.
22. What are minutiae and why are they important in classification?
23. In the table below, describe the print and identify TWO objects this type of print could be found on:
|
Type of Print
|
Description
|
Two Objects could be Found on
|
|
Plastic
|
|
|
|
Visible
|
|
|
|
Latent
|
|
|
24. What is the chemical found in superglue that adheres to fingerprint?
25. Describe the technique and the type of surface the technique could be used on to visualize latent prints:
|
Technique
|
Description
|
Type of Surface Used On
|
|
Dusting
|
|
|
|
Iodine Fuming
|
|
|
|
Ninhydrin
|
|
|
|
Silver Nitrate
|
|
|
|
Superglue Fuming
|
|
|
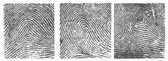
26. For each fingerprint below, identify the PATTERN (Whorl, Loop, or Arch) and SUBCATEGORY of the fingerprint shown (Radial, Plain, etc). Patterns and subcategories may be used more than once.
** Remember that PRINTS are MIRROR IMAGES of what is actually on the FINGER on the BODY !
