Reference no: EM131649273
Assignment
1. Water is considered a scarce good because:
A) not enough of it is available for all needs.
B) it does not have any uses.
C) scarce goods are less expensive.
D) not enough of it is available for all needs and because it is less expensive.
2. You can spend $100 on either a new economics textbook or a new CD player. If you choose to buy the new economics textbook, the opportunity cost is:
A) $100.
B) your enjoyment of the new CD player.
C) both the $100 and the your enjoyment of the new CD player.
D) impossible to determine.
3. A choice made ________ is a choice whether to do a little more or a little less of something.
A) at the front end
B) in the beginning
C) at the margin
D) ceteris paribus
4. Which of the following is an example of marginal analysis?
A) What additional output does a family business produce when it hires one more worker?
B) How do tax cuts change the growth rate of median income?
C) When a large corporation lays off workers, how do profits change if sales remain constant?
D) Should a commuter take the bus to work rather than driving.
5. If disequilibrium exists in a market:
A) it will continue unless there is government intervention.
B) no individual will be better off doing something different.
C) there will be opportunities available to people to make themselves better off.
D) it must be because the government has intervened in the market, resulting in the market's failure to reach equilibrium.
6. If all of the opportunities to make someone better off (without making someone else worse off) have been exploited, an economy is
A) equitable.
B) inefficient.
C) marginally optimal.
D) efficient.
7. An increase in efficiency means that an economy has:
A) reduced its opportunity costs.
B) increased the equity of its distribution of goods and services.
C) made some people better off without making others worse off.
D) increased the incentives for its citizens to follow their own self-interest.
8. Which of the following principles underlies the interaction of individual choices?
A) Resources are scarce.
B) There are gains from trade.
C) Marginal analysis is used for "how much" decisions.
D) People usually exploit opportunities to make themselves better off.
9. When building a model, economists:
A) simplify reality in order to highlight what really matters.
B) attempt to duplicate reality in all of its complexity.
C) ignore the facts and instead try to determine what the facts should be.
D) are careful to avoid the scientific method.
Use the following to answer questions 10-11:
Figure: Guns and Butter
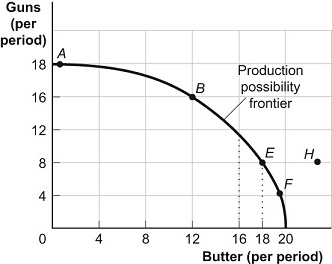
10. (Figure: Guns and Butter) Look at the figure Guns and Butter. On this figure, points A, B, E, and F:
A) indicate combinations of guns and butter that society can produce using all of its factors efficiently.
B) show that the opportunity cost of more guns increases but that of more butter decreases.
C) indicate that society wants butter more than it wants guns.
D) indicate constant costs for guns and increasing costs for butter.
11. (Figure: Guns and Butter) Look at the figure Guns and Butter. If the economy were operating at point B, producing 16 guns and 12 pounds of butter per period, a decision to move to point E and produce 18 pounds of butter:
A) indicates you can have more butter and guns simultaneously.
B) makes it clear that this economy experiences decreasing opportunity costs.
C) involves a loss of 8 guns per period.
D) involves a loss of 4 guns per period.
12. If an economy is producing a level of output that is on its production possibility frontier, the economy has:
A) idle resources.
B) idle resources but is using resources efficiently.
C) no idle resources but is using resources inefficiently.
D) no idle resources and is using resources efficiently.
13. Technological improvements will:
A) leave the production possibility frontier unchanged.
B) shift the production possibility frontier inward.
C) shift the production possibility frontier outward.
D) necessarily lead to increased unemployment.
14. The effect of a tremendous natural disaster can be shown by:
A) a point inside of the production possibility frontier.
B) an outward shift of the production possibility frontier.
C) a movement from one point to another along the production possibility frontier.
D) an inward shift of the production possibility frontier.
15. Assume an economy is operating on its production possibility frontier, which shows the production of military and civilian goods. If the output of military goods is increased, the output of civilian goods:
A) will increase, too.
B) will not change.
C) must decrease.
D) may increase or decrease.
16. Statements that make value judgments are:
A) pecuniary.
B) positive.
C) nominal.
D) normative.
17. An example of a positive statement is:
A) the rate of unemployment is 4%.
B) a high rate of economic growth is good for the country.
C) everyone in the country should be covered by national health insurance.
D) baseball players should not be paid higher salaries than the president of the United States.
18. Which of the following is a normative economic statement?
A) Government has grown too large and should be reduced.
B) There has been an increase in the rate of inflation.
C) Government is subject to the same rules as all other institutions.
D) The money supply grew by 3% last year.
19. Unemployment of 5% is too high. This is an example of:
A) a normative statement.
B) a positive statement.
C) the circular-flow model.
D) comparative advantage.
20. The law of demand implies that:
A) consumers are not responsive to price changes.
B) consumers will buy more at lower prices.
C) sellers will offer more on the market at higher prices.
D) sellers will offer less on the market at lower prices.
21. In much of the country, homeowners choose to heat their houses with either natural gas or home heating oil. Which of the following would cause a change in the demand for natural gas?
A) a change in the price of home heating oil
B) a change in income
C) an increase in consumer tastes for natural gas as an energy source
D) all of the above
22. If goods A and Z are complements, an increase in the price of good Z will:
A) increase the demand for good A.
B) decrease the demand for good A.
C) decrease the demand for good Z.
D) decrease the demand for both good A and good Z.
23. A good is inferior if which of the following is true?
A) When income increases, the demand remains unchanged.
B) When income increases, the demand decreases.
C) When income increases, the demand increases.
D) Income and the demand are unrelated.
24. Pizza is a normal good. If students' incomes at your college increase, the effect on pizza would be:
A) an increase in the demand.
B) an increase in the quantity demanded.
C) a decrease in the demand.
D) no change in the demand.
25. Which of the following is not a determinant of supply?
A) expectations regarding future prices
B) the technology of production
C) the cost of production
D) consumer tastes
26. A decrease in supply means:
A) a shift to the left of the entire supply curve.
B) a movement down the supply curve as prices go down.
C) that less will be demanded at every price.
D) that more will be supplied at every price.
27. In the local market for coffee, what would happen if Joyce's Java and Everyday Joe's coffee shops go out of business?
A) The supply curve shifts to the right.
B) The demand curve shifts to the left.
C) The supply curve shifts to the left.
D) The demand curve shifts to the right.
28. A technological advance in the production of automobiles will:
A) increase the demand for automobiles.
B) increase the supply of automobiles.
C) decrease the demand for automobiles.
D) decrease the supply of automobiles.
29. A shift to the left of a supply curve is caused by:
A) an increase in the number of sellers.
B) a technological improvement in production.
C) an increase in the cost of an input.
D) an increase in the number of buyers.
30. Excess supply occurs when:
A) the price is above the equilibrium price.
B) the quantity demanded exceeds the quantity supplied.
C) the price is below the equilibrium price.
D) the quantity demanded exceeds the quantity supplied and when the price is below the equilibrium price.
Use the following to answer questions 31-32:
Figure: The Demand and Supply of Wheat
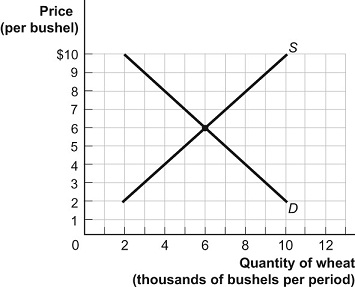
31. (Figure: The Demand and Supply of Wheat) Look at the figure The Demand and Supply of Wheat. If there were a decrease in supply of 2,000 bushels at each price, the equilibrium price and quantity would be ________ and ________ bushels, respectively.
A) $5; 5,000
B) $7; 5,000
C) $6; 4,000
D) $8; 6,000
32. (Figure: The Demand and Supply of Wheat) Look at the figure The Demand and Supply of Wheat. A temporary price of $2 in this market would result in:
A) a surplus of 4,000 bushels.
B) a shortage of 8,000 bushels.
C) a shortage of 10,000 bushels.
D) a surplus of 10,000 bushels.
Use the following to answer questions 33-35:
Figure: Four Markets for DVDs
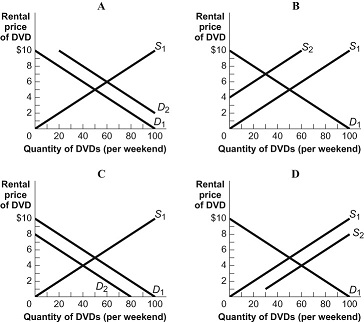
33. (Figure: Four Markets for DVDs) Look at the figure Four Markets for DVDs. If D1 or S1 is the original curve and D2 or S2 is the new curve, which of the graphs shows a change that results in an increase in the quantity demanded of DVDs?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
34. (Figure: Four Markets for DVDs) Look at the figure Four Markets for DVDs. If D1 or S1 is the original curve and D2 or S2 is the new curve, which of the graphs illustrates what may happen in the market for DVDs if there is an increase in the cost of a movie ticket at the local theater?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
35. (Figure: Four Markets for DVDs) Look at the figure Four Markets for DVDs. If D1 or S1 is the original curve and D2 or S2 is the new curve,, which of the graphs illustrates what may happen in the market for DVDs if the cost of producing DVDs falls?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D