Reference no: EM131183187
1. Comparison of marginal revenue to marginal cost
(i)reveals the contribution of the last unit of production to total profit.
(ii)is helpful in making profit-maximizing production decisions.
(iii)tells a firm whether its fixed costs are too high.
a.(ii) and (iii) only
b.(i) only
c.(i) and (iii) only
d.(i) and (ii) only
2. National defense is a classic example of a public good because
a.there are no private firms willing to supply defense goods such as tanks and weapons.
b.it is difficult to exclude people from receiving the benefits from national defense once it is provided.
c.everyone agrees that some level of national defense is important, but only the government knows the optimal amount.
d.there is no market for private security services.
3. When demand is inelastic, a decrease in price will cause
a.no change in total revenue, but a decrease in quantity demanded.
b.a decrease in total revenue.
c.no change in total revenue, but an increase in quantity demanded.
d.an increase in total revenue.
4. The value and cost of goods are easiest to determine when the goods are
a.common resources.
b.public goods.
c.natural monopolies.
d.private goods.
5. If the demand for donuts is elastic, then a decrease in the price of donuts will
a.decrease total revenue of donut sellers.
b.increase total revenue of donut sellers.
c.not change total revenue of donut sellers.
d.There is not enough information to answer this question.
6. Profit is defined as
a.average revenue minus average total cost.
b.total revenue minus total cost.
c.net revenue minus depreciation.
d.marginal revenue minus marginal cost.
7. To determine whether a good is considered normal or inferior, one could examine the value of the
a.cross-price elasticity of demand for that good.
b.price elasticity of supply for that good.
c.price elasticity of demand for that good.
d.income elasticity of demand for that good.
8. Suppose that demand for a good increases and, at the same time, supply of the good decreases. What would happen in the market for the good?
a.Both equilibrium price and quantity would increase.
b.Equilibrium price would increase, but the impact on equilibrium quantity would be ambiguous.
c.Equilibrium price would decrease, but the impact on equilibrium quantity would be ambiguous.
d.Both equilibrium price and quantity would decrease.
9. Which of the following statements about a well-maintained yard best conveys the general nature of the externality?
a.A well-maintained yard conveys a positive externality because it increases the home's market value.
b.A well-maintained yard conveys a negative externality because it increases the property tax liability of the owner.
c.A well-maintained yard cannot provide any type of externality.
d.A well-maintained yard conveys a positive externality because it increases the value of adjacent properties in the neighborhood.
10. The market demand curve for a monopolist is typically
a.downward sloping.
b.unitary elastic at the point of profit maximization.
c.horizontal.
d.vertical.
11. Patent and copyright laws are major sources of
a.government-created monopolies.
b.resource monopolies.
c.natural monopolies.
d.antitrust regulation.
12. An advance in production technology will
a.shift the supply curve to the right and shift the demand curve to the right.
b.shift the supply curve to the right, but the demand curve will be unaffected.
c.allow firms to raise the price of their product.
d.increase a firm's costs.
13. Total revenue minus explicit and implicit costs is called
a.fixed expenses
b.accounting profit
c.economic profit
d.average total cost
14. When a firm has little ability to influence market prices it is said to be in
a.a competitive market.
b.a thin market.
c.a power market.
d.a strategic market.
Figure 4-1
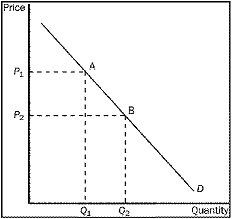
15. Refer to Figure 4-1. The movement from point A to point B on the graph shows
a.an increase in quantity demanded.
b.a decrease in quantity demanded.
c.an increase in demand.
d.a decrease in demand.
16. Elasticity improves our understanding of supply and demand by adding
a.measures of equity.
b.measures of efficiency.
c.a qualitative element to our analysis.
d.a quantitative element to our analysis.
17. If the supply of a product decreases, we would expect
a.equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity both to decrease.
b.equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity both to increase.
c.equilibrium price to decrease and equilibrium quantity to increase.
d.equilibrium price to increase and equilibrium quantity to decrease.
18. The amount of money that a firm receives from the sale of its output is called
a.total gross profit.
b.net revenue.
c.total revenue.
d.total net profit.
19. The greater the price elasticity of demand, the
a.greater the responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in price.
b.greater the percentage change in price over the percentage change in quantity demanded.
c.smaller the responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in price.
d.more likely the product is a necessity.
20. When supply and demand both increase, equilibrium
a.quantity may increase, decrease, or remain unchanged.
b.price will increase.
c.price may increase, decrease, or remain unchanged.
d.price will decrease.
21. Private markets fail to account for externalities because
a.the government cannot easily estimate the optimal quantity of pollution.
b.sellers include costs associated with externalities in the price of their product.
c.decisionmakers in the market fail to include the costs of their behavior to third parties.
d.externalitiesdon't occur in private markets.
22. Which of the following is an example of an externality?
a.cigarette smoke that permeates an entire restaurant
b.a flu shot that prevents a student from transmitting the virus to her roommate
c.a beautiful flower garden outside of the local post office
d.All of the above are correct.
23. Economists assume that monopolists behave as
a.cost minimizers.
b.pricemaximizers.
c.maximizers of social welfare.
d.profitmaximizers.
24. According to the law of supply,
a.the quantity supplied of a good is negatively related to the price of the good.
b.when the price of a good falls, the quantity supplied of the good rises.
c.the supply curve for a good is upward-sloping.
d.All of the above are correct.
25. If the demand for a product decreases, we would expect
a.equilibrium price to decrease and equilibrium quantity to increase.
b.equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity to both increase.
c.equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity to both decrease.
d.equilibrium price to increase and equilibrium quantity to decrease.
26. Two goods are complements if a decrease in the price of one good
a.decreases the demand for the other good.
b.increases the demand for the other good.
c.increases the quantity demanded of the other good.
d.decreases the quantity demanded of the other good.
27. Demand is said to be inelastic if the
a.quantity demanded changes proportionately more than price.
b.quantity demanded changes proportionately the same as price.
c.quantity demanded changes proportionately less than price.
d.price changes proportionately more than income.
28. An externality exists whenever
a.the economy can benefit from government intervention.
b.a person engages in an activity that influences the well-being of a bystander and yet neither pays nor receives payment for that effect.
c.a firm sells its product in a foreign market.
d.markets are not able to reach equilibrium.
29. Explicit costs
a.require an outlay of money by the firm.
b.include all of the firm's opportunity costs.
c.include income that is forgone by the firm's owners.
d.Both b and c are correct.
30. If, at the current price, there is a shortage of a good,
a.quantity demanded equals quantity supplied.
b.the price is below the equilibrium price.
c.sellers are producing more than buyers wish to buy.
d.the market must be in equilibrium.
31. A positive externality
a.causes the product to be overproduced.
b.is a benefit to a market bystander.
c.benefits consumers because it results in a lower equilibrium price.
d.provides an additional benefit to market participants.
32. When a negative externality exists in a market, the cost to producers
a.will differ from the cost to society, regardless of whether an externality is present.
b.is greater than the cost to society.
c.will be the same as the cost to society.
d.will be less than the cost to society.
33. The amount by which total cost rises when the firm produces one additional unit of output is called
a.variable cost.
b.marginal cost.
c.average cost.
d.fixed cost.
34. Marginal revenue can become negative for
a.monopoly firms, but not for competitive firms.
b.competitive firms, but not for monopoly firms.
c.neither competitive nor monopoly firms.
d.both competitive and monopoly firms.
35. Which of the following statements is correct?
a.A competitive firm is a price maker and a monopoly is a price taker.
b.Both competitive firms and monopolies are price makers.
c.A competitive firm is a price taker and a monopoly is a price maker.
d.Both competitive firms and monopolies are price takers.
36. Quantity demanded falls as the price rises and rises as the price falls, so we say that
a.quantity demanded is a function of demand.
b.quantity demanded is determined by quantity supplied.
c.quantity demanded is negatively related to the price.
d.price is determined by quantity demanded.
37. When goods do not have a price, which of the following primarily ensures that the good is produced?
a.charities
b.entrepreneurs
c.the market
d.the government
38. An increase in demand is represented by
a.a movement upward and to the left along a demand curve.
b.a rightward shift of a demand curve.
c.a leftward shift of a demand curve.
d.a movement downward and to the right along a demand curve.
39. The signals that guide the allocation of resources in a market economy are
a.prices.
b.quantities.
c.surpluses and shortages.
d.property rights.
40. Diminishing marginal product suggests that the marginal
a.product of an extra worker is greater than the previous worker's marginal product.
b.cost of an extra worker is unchanged.
c.product of an extra worker is less than the previous worker's marginal product.
d.cost of an extra worker is less than the previous worker's marginal cost.
41. For both public goods and common resources, an externality arises because
a.something of value has no price attached to it.
b.supply exceeds demand.
c.cost-benefit analysis can only measure the cost of the free-rider problem.
d.Both a and b are correct.
42. Which of the following is not a characteristic of a perfectly competitive market?
a.There are many sellers.
b.Sellers must accept the price the market determines.
c.Different sellers sell identical products.
d.All of the above are characteristics of a perfectly competitive market.
43. When a perfectly competitive firm decides to shut down, it is most likely that
a.price is below the firm's average variable cost.
b.fixed costs exceed variable costs.
c.marginal cost is above average total cost.
d.marginal cost is above average variable cost.
44. The amount of money that a wheat farmer could have earned if he had planted barley instead of wheat is
a.an implicit cost.
b.an explicit cost.
c.forgone accounting profit.
d.an accounting cost
45. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of a perfectly competitive market?
a.Firms have difficulty entering the market.
b.Goods offered for sale are largely the same.
c.Firms are price takers.
d.There are many sellers in the market.
46. When a natural monopoly exists, it is
a.never cost effective for one firm to produce the product.
b.always cost effective for government-owned firms to produce the product.
c.never cost effective for two or more private firms to produce the product.
d.always cost effective for two or more private firms to produce the product.
47. Which of the following statements is correct?
a.Buyers determine demand and sellers determine supply.
b.Buyers and sellers as one group determine demand, but only sellers determine supply.
c.Buyers determine supply and sellers determine demand.
d.Buyers and sellers as one group determine supply, but only buyers determine demand.
48. When externalities exist, buyers and sellers
a.neglect the external effects of their actions, but the market equilibrium is still efficient.
b.do not neglect the external effects of their actions, and the market equilibrium is not efficient.
c.neglect the external effects of their actions, and the market equilibrium is not efficient.
d.do not neglect the external effects of their actions, and the market equilibrium is efficient.
49. The unique point at which the supply and demand curves intersect is called
a.cohesion.
b.market harmony.
c.coincidence.
d.equilibrium.
50. In order to sell more of its product, a monopolist must
a.sell to the government.
b.use its market power to force up the price of complementary products.
c.sell in international markets.
d.lower its price.
51. In a perfectly competitive market, the process of entry and exit will end when, for firms in the market,
a.accounting profits are zero.
b.marginal revenue is equal to average variable cost.
c.economic profits are zero.
d.price is equal to average variable cost.
52. The price elasticity of demand measures how much
a.demand responds to a change in supply.
b.quantity demanded responds to a change in income.
c.price responds to a change in demand.
d.quantity demanded responds to a change in price.
53. A free rider is a person who
a.will only purchase a product on sale.
b.receives the benefit of a good but avoids paying for it.
c.takes advantage of tax loop-holes to lower his taxes.
d.can produce a good at no cost.
54. Markets fail to allocate resources efficiently when
a.property rights are not well established.
b.prices fluctuate.
c.the government refuses to intervene in private markets.
d.people who have property rights abuse their privileges.
55. Which of the following events will definitely cause equilibrium quantity to fall?
a.demand decreases and supply increases
b.demand and supply both increase
c.demand and supply both decrease
d.demand increases and supply decreases
56. Which of the following is an example of a barrier to entry?
(i)A key resource is owned by a single firm.
(ii)The costs of production make a single producer more efficient than a large number of producers.
(iii)The government has given the existing monopoly the exclusive right to produce the good.
a.(ii) and (iii)
b.(i) only
c.(i) and (ii)
d.All of the above are examples of barriers to entry.
57. Which of the following costs do not vary with the amount of output a firm produces?
a.average fixed costs
b.fixed costs and average fixed costs
c.marginal costs and average fixed costs
d.fixed costs
58. A fundamental source of monopoly market power arises from
a.perfectly elastic demand.
b.barriers to entry.
c.perfectly inelastic demand.
d.availability of "free" natural resources, such as water or air.
59. The short-run supply curve for a firm in a perfectly competitive market is
a.the portion of its marginal cost curve that lies above its average variable cost.
b.determined by forces external to the firm.
c.horizontal.
d.likely to slope downward.
60. For a firm in a perfectly competitive market, the price of the good is always
a.greater than average revenue.
b.equal to total revenue.
c.equal to marginal revenue.
d.equal to the firm's efficient scale of output.