Reference no: EM132430036
Question 1.
Please search case study "Orange County Bankruptcy" in Google. First, do some self-learning, and then write an essay to give me some directions on:
Who is Robert Citron?
What was the Orange County Governance Structure?
What was the political and economic background before the bankruptcy?
What was the Orange County Investment Pool and balance sheet (1994)?
What was Citrons Strategy?
How the Fed action affects the interest rate in 1994?
Describe the crisis following the Fed action.
Describe the outcomes.
Finally what are the lessons to learn?
Please list all the references.
The essay should be within three pages including tables and references. The font is Times New Roman, size 12pt, 1.5 line space, and each of the nine questions to be answered in their own paragraphis preferred.
Question 2.
Background:Metallgesells chaft AG was formerly one of Germany's largest industrial conglomerates based in Frankfurt. It had over 20,000 employees and revenues in excess of 10 billion US dollars. It had over 250 subsidiaries specializing in mining, specialty chemicals (Chemetall), commodity trading, financial services, and engineering (Lurgi). In 1993, the company lost 1.3 billion dollars suffering from flawed long hedge strategy in near term futures contracts that was meant to protect against forward sales commitments. A fall in spot prices forced margin calls for the company and the contracts were closed at a loss. Subsequently, the spot price increased and the company suffered even greater losses covering its customer commitments.It is debated whether the company was speculating after unwinding the long futures hedge since they became essentially exposed or naked against their forward customer commitments.
The following illustrates how important it is to consider tailing factor in taking a correct hedge strategy. 0.5 marks for filling each blank>
Suppose the current spot price is $3. With 50 percent of the probability, the spot price will increase or decrease by 1 dollar for first year and then remain the same as shown in the graph below.
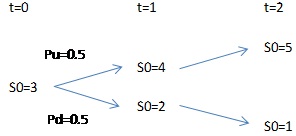
Please answer the following questions.
If the annual discrete compounding risk-free rate is 10%, and the cost of carry offsets the convenience yield exactly, then the future price is equal to the spot price. Please explain.
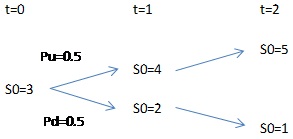
Assume hedger takes hedge ratio as h*, i.e, if the risk exposure is a long position of 100 units of spot commodity, to hedge the risk, hedger will short 100h*futures underlying on that commodity.Please answer the questions in the right panel in analogy to the left panel, by filling the blanks in j) -r) below:If the stock price falls from 3 to 2, then
a) the future price falls from 3 to 2;
b) hedger makes profit (3-2)×100h*=100h* from the future, at t=1;
c) by investing the profit from t=1till t=2, 100h* dollars profit becomes (1+0.1)×100h*=110 h*;
d) meanwhile, hedger makes a loss of 100×(2-3)= -100 from the stock at t=1;
e) hedger doesn't make further loss on stock from t=1 to t=2;
f) net profit/loss is [110h*-100] dollars;
g) stock price is 2 at t=2, hence the value of stock at t=2 is 2×100=200;
h) the value of futures is its gain and loss, hence, at t=2, its value is 110h*;
i) the value of the portfolio is the sum of the value of stock and the value of futures, which is [200+110h*].
If the stock price rises from 3 to 4, then
j) the future price____________________;
k) hedger makes_________________from the future, at t=1;
l) ___________________from t=1 till t=2, _______________becomes _______________________________;
m) meanwhile, hedger makes a profit _______________from the stock at t=1;
n) hedger doesn't make further _____________on stock from t=1 to t=2;
o) net profit/loss is___________________;
p) stock price is_____ at t=2, hence the value of stock at t=2 is______________;
q) the value of futures is its gain and loss, hence, at t=2, its value is____________;
r) the value of the portfolio is the sum of the value of stock and the value of futures, which is___________________.
To make the hedge portfolio risk-free, the value of the portfolio should not vary no matter stock price rises or falls (or, equivalently, the hedge portfolio should not make profit in one state and make loss in the other, where the state means stock price rises or falls). Please based on the above fact, solve the optimal hedge ratio h*.
To make the hedge portfolio risk-free, the hedge portfolio should not make profit in one state and make loss in the other, where the state means stock price rises or falls. Please use the optimal hedge ratio solved in (c) to verify this fact.
Question 3.
The following webpage discusses 10 trading strategies
If you anticipate that stock price will rise, which strategies should you take?
If you anticipate that stock price will drop, which strategies should you take?
If you anticipate that stock price will roughly stay, which strategies should you take?
If you anticipate that stock price will move a lot (either risk or decline), which strategies should you take?
Please summarize on how to choose a trading strategy.
Question 4.
Two companies have investments which pay the following rates of interest:
|
|
Fixed
|
Float
|
|
Firm A
|
6%
|
Libor
|
|
Firm B
|
8%
|
Libor+0.5%
|
Assume A prefers a fixed rate and B prefers a floating rate. Show how these two firms can both benefit by entering into a swap agreement. If an intermediary charges both parties equally a 0.1% fee and any benefits are spread equally between Firm A and Firm B, what rates could A and B receive on their preferred interest rate? Please draw the cash flow chart.
|
Fixed Rate |
Floating Rate |
| Firm A |
6% |
LIBOR |
| Firm B |
8% |
LIBOR+0.5% |
| Difference |
Δfixed = 2% |
Δfloating = 0.5% |
| Total gain to all three parties (Firms A,B&Intermediary) |
Δfixed - Δfloating = 1.5% |
|
|
= 1.5% |
|
| Individual gain to X and Y each |
(1.5% - 0.1%x2)/2 = 0.65% |
|
Since Firm A prefers investment with fixed rate,
Firm A's fixed rate of interest= 6% + 0.65% = 6.65%
Since Firm B prefers investment with floating rate,
Firm B's floating rate of interest= LIBOR+0.5%+0.65% = LIBOR+1.15%
By entering a swap agreement, Firm A will receive 6.65%, Firm B will receive LIBOR +1.15%, and the intermediary will benefit 0.2%.
