Reference no: EM131011016
1. If Weiskamp T-shirt Co. lowers its price from $6 to $5 and finds that students increase their quantity demanded from 400 to 600 T-shirts, demand is
a. price inelastic
b. price elastic
c. unit elastic
d. cross elastic
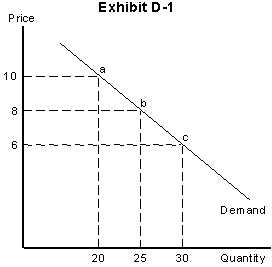
2. In Exhibit D-1, price elasticity of demand within the price range $8 and $6 is
a. 4.27
b. 1.5
c. 1.6
d. 0.64
3. In Exhibit D-1, price elasticity of demand within the price range $10 and $8 is
a. 1.0
b. 0.7
c. 1.5
d. 2.0
4. The cross elasticity of demand for substitute goods must
a. Be greater than one
b. Be less than one
c. Be zero
d. exceed zero
5. The cross elasticity of demand for complementary goods must
a. Be less than one
b. Be greater than one
c. exceed zero
d. Be negative
6. If Herbert the hair stylist raises the price of his cuts from $13 to $15 and the quantity demanded for his cuts falls from 300 to 260, demand is
a. price inelastic
b. price elastic
c. unit elastic
d. cross elastic
Exhibits E-2
| Quantity |
Marginal Utillities(Utils) |
| Brownies |
Ice cream |
Ple |
| 1 |
20 |
18 |
16 |
| 2 |
18 |
17 |
13 |
| 3 |
15 |
14 |
9 |
| 4 |
12 |
11 |
7 |
| 5 |
10 |
8 |
5 |
7. Refer to Exhibit E-2. Each dessert is priced at $1. If you had $10 to spend on desserts, which of the following combinations of goods would you buy?
a. 5 units of brownies, 4 units of ice cream, and 1 unit of pie
b. 4 units of brownies, 5 units of ice cream, and 1 unit of pie
c. 4 units of brownies, 4 units of ice cream, and 2 units of pie
d. 4 units of brownies, 3 units of ice cream, and 3 units of pie
Exhibit E-3
| Quantity |
Marginal Utillities(Utils) |
| Clothes |
Amusement |
| 1 |
15 |
20 |
| 2 |
13 |
18 |
| 3 |
10 |
15 |
| 4 |
8 |
12 |
| 5 |
6 |
10 |
8. Refer to Exhibit E-3. Clothes and amusements are priced at $10 each. If you had a budget of $50, which of the following combinations of goods would you buy?
a. 4 units of clothes and 1 unit of amusement
b. 3 units of clothes and 3 units of amusement
c. 2 units of clothes and 3 units of amusement
d. 1 unit of clothes and 4 units of amusement
9. Refer to Exhibit E-3. Clothes and amusements are priced at $10 each. The marginal utility per dollar for the first unit of amusement is
a. 0.5
b. 1.5
c. 2.0
d. 5.0
10. Refer to Exhibit E-3. Your budget is $50. The price of amusement goods is $10. If the price of clothes falls to $4, which of the following statements is true?
a. The marginal-utility-to-price ratio for clothes will decrease.
b. The marginal-utility-to-price ratio for clothes will increase.
c. The quantity demanded of clothes will decrease.
d. There will be no change in the quantity demanded of clothes or amusements.
11. Given whatever income they have, consumers make consumption choices to maximize the
a. total utility of the goods they consume
b. marginal utility of the goods they consume
c. average utility of each good they consume
d. number of goods they buy
12. According to the law of diminishing marginal utility, the fifth pair of gloves that Mary receives for Christmas makes her
a. as happy as she was while receiving the first pair
b. less happy than she was while receiving the first pair
c. more happy than she was while receiving the first pair
d. consider that fifth pair as having zero marginal utility
13. If the total utility Jack receives from 10 gallons of gasoline is 16, and the total utility Jack receives from 11 gallons of gasoline is 20, the marginal utility of the 11th gallon of gasoline is
a. 1
b. 4
c. 7
d. 20
14. If income increases from $100 to $150 and demand increases from 1 to 2, then income elasticity is
a. -1.1
b. 1.67
c. -1.5
d. 2.0
15. If income decreases from $150 to $100 and demand increases from 3 to 5, then income elasticity is
a. -1.25
b. 1.33
c. -1.5
d. 2.0
16. If the price of apples rises from $2 to $2.50 per pound, and the demand for bananas increases from 3 to 6 lbs per week, cross prices elasticity is
a. -2
b. 1.5
c. -1.75
d. 3
17. If the price of gasoline rises from $1.50 to $2 per pound and the demand for automobiles falls from 2.5 to 1.5 million, cross prices elasticity is
a. -2
b. 1.5
c. -1.75
d. 1.6
18. When demand is inelastic, a decrease in price will cause
a. no change in total revenue.
b. an increase in total revenue.
c. a decrease in total revenue.
d. There is insufficient information to answer this question.
19. When demand is elastic, an increase in price will cause
a. no change in total revenue.
b. an increase in total revenue.
c. a decrease in total revenue.
d. There is insufficient information to answer this question.
Exhibit I-1
| Price |
Quantity |
| $20 |
10 |
| 19 |
11 |
| 18 |
12 |
| 17 |
13 |
| 16 |
14 |
20. In Exhibit I-1, the marginal revenue of the twelfth unit equals
a. $7
b. $18
c. $216
d. $1
21. At P = $20, AVC = $10, AFC = $10, & Q = 20, the result is a
a. loss of $10
b. profit of $10
c. loss of $20
d. normal economic profit
22. If at Q = 12, MC of the twelfth unit = $84 & MR of that unit = $70, the firm should
a. shut down
b. increase output
c. remain at Q = 12
d. reduce output
23. In the short run, a firm should shut down if price is less than
a. ATC
b. AR
c. MC
d. AVC
24. When the firm's output level is zero, profit equals
a. Zero
b. fixed cost
c. variable cost
d. marginal revenue
25. At P = $20, AVC = $10, AFC = $8 & Q = 20, the result is a
a. loss of $10
b. normal economic profit
c. profit of $20
d. profit of $40
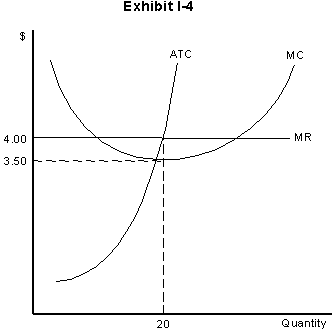
26. In Exhibit I-4, if this firm is currently producing 20 units of output, this firm
a. is earning a profit of $10
b. is earning a profit of $.50
c. is losing $10
d. should shut down
27. In Exhibit I-4, if this firm is currently producing 20 units of output, this firm
a. is at its profit-maximizing point
b. could increase profits by increasing output
c. could increase profits by decreasing price
d. should shut down
28. At P = $24, Q = 200, MC = MR, AFC = $6, AVC = $25, the firm should
a. increase output.
b. decrease output.
c. shut down.
d. stay at the current output level, although profit = -$1,400.
29. The firm's supply curve is
a. the same as the industry's supply curve
b. the average total cost curve
c. perfectly horizontal
d. the marginal cost curve above AVC
30. At P = $24, AVC = $22 & ATC = $26, in the long run this firm should
a. continue to operate at a loss
b. earn a positive profit
c. go out of business
d. increase output
31. At P = $20, AVC = $10, AFC = $12, & Q = 20, the result is a
a. loss of $20
b. profit of $0
c. profit of $40
d. loss of $40
32. Market power refers to the
a. firm's ability to control the industry's supply and demand
b. joining of firms into a cartel
c. firm's ability to influence market price
d. market's ability to control a firm's price
Exhibit I-2
| Unit QuantityMarginal CostMarginal revenue |
| 12 |
$5 |
$9 |
| $13 |
6 |
9 |
| 14 |
7 |
9 |
| 15 |
8 |
9 |
| 16 |
9 |
9 |
| 17 |
10 |
9 |
33. In Exhibit I-2, at what quantity does the firm maximize profit?
a. 13 units
b. 14 units
c. 15 units
d. 16 units
34. Which of the following is NOT possible when a firm is maximizing its profits?
a. MC = MR
b. AVC is at its minimum point
c. AFC < AVC
d. MC = MR and TR is increasing
35 The marginal product of labor can be defined as (where d denotes "change")
a. d profit/d labor.
b. d output/d labor.
c. d labor/d total cost.
d. d labor/d output.
36. Diminishing marginal product of labor would arise when
a. workers are discouraged about the lack of help from other workers.
b. only new workers are trained in using the most productive capital.
c. crowded office space reduces the productivity of new workers.
d. union workers are told to reduce their work effort in preparation for a new round of
collective bargaining talks.
37. The cost to produce an additional unit of output is the firm's
a. average variable cost.
b. marginal cost.
c. average opportunity cost.
d. total productivity cost.
38. Average total cost equals
a. (fixed costs + variable costs)/quantity produced.
b. (fixed costs + variable costs)/change in quantity produced.
c. change in total costs/quantity produced.
d. change in total costs/change in quantity produced.
39. If we assume that marginal product of labor is initially increasing but always decreasing thereafter, average total cost
a. and average fixed cost are always falling.
b. and average fixed cost are always U-shaped.
c. and average fixed cost are always rising.
d. is U-shaped and average fixed cost is always falling.
40. If marginal cost is rising
a. average total cost must be falling.
b. average fixed cost must be rising.
c. marginal product must be rising.
d. marginal product must be falling.