Reference no: EM132181365
Research Methods & Biostatistics for Food & Nutrition Sciences SPSS Biostatistics Assignment -
Please complete all 3 parts of this assignment.
PART 1 -
Coeliac disease is an autoimmune condition caused by gluten intolerance in those individuals who are genetically susceptible. Coeliac disease affects approximately 1% of the European population and results in damage to the lining of the gut. Symptoms of coeliac disease include diarrhoea, weight loss, pain and vomiting. If a gluten-free diet is not strictly followed, nutrient deficiencies can occur. On a standard gluten-free diet, approximately 80% of overweight coeliac patients will gain weight and 30% of normal weight coeliac patients will become overweight.
A study was carried out to assess the effect of a strict gluten-free diet on nutritional status of coeliac patients and healthy controls. Fifteen coeliac patients and fifteen healthy controls were recruited and followed a 6-month gluten-free diet. Blood samples were taken at baseline (before the diet) and 6-months later (after the diet) and used to assess iron, folate and vitamin B12 status. Body mass index (BMI) was also recorded before and after the diet intervention.
BMI and nutritional status measures of iron, folate and vitamin B12 before and after the diet intervention are given in DATA Assignment 1.0.sav (in Blackboard Learn assignment area) for both the coeliac patients and healthy controls.
1.1 What is the aim of the study? Give the null and alternate hypotheses.
1.2 Using SPSS, assess and comment on the normality of the data.
1.3 Produce a summary table of the baseline BMI and nutritional status data for the coeliac patients and controls, showing any statistical differences between the groups using appropriate statistical tests (assume all data are normal and present as means ± SD).
1.4 Carry out statistical tests to analyse the differences between baseline and post intervention measures and present these data in an appropriate table (assume all data are normal and present as means ± SD).
1.5 Write a short conclusion on the study.
PART 2 -
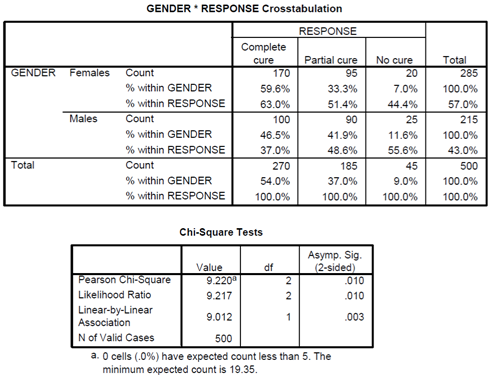
Antibiotics are powerful medicines that fight bacterial infections. In treating a patient, a doctor must know which antibiotics are most effective in either killing the organism or at least inhibiting or retarding its further growth. A study was carried out in which 500 patients admitted to hospital with bacterial infections were given a specific antibiotic and the response to the treatment recorded. The effectiveness of the antibiotic in the 500 patients is presented in the table below.
|
Complete cure
|
Partial cure
|
No cure
|
TOTAL
|
|
Females
|
170
|
95
|
20
|
|
|
Males
|
100
|
90
|
25
|
|
|
TOTAL
|
|
|
|
|
Use the data from the table above to answer the following questions:
2.1 What proportion of females was completely cured?
2.2 What proportion of those who were not cured is male?
2.3 What is the probability of selecting a person, from the sample of 500 subjects, who is female and was partially cured?
2.4 What percentage of the sample of 500 subjects is female?
2.5 The data in the table above were analysed using the chi-square test. The results from SPSS are shown below. What can you conclude from the results of the test?
PART 3 -
A study was carried out to assess maternal factors during pregnancy which influence birth outcomes. A total of 90 pregnant women were recruited at 12 weeks gestation and blood samples and anthropometric measurements were taken. The type of delivery, gestational age at delivery and anthropometric measurements of the baby were recorded at birth.
Using dataset labelled DATA Assignment 3.0.sav (in Blackboard Learn Assignments Area), complete the following questions.
3.1 Given the variables in the database, what is the aim of the study? Give the null and alternate hypotheses
3.2 Produce a summary table of the age, height, weight and BMI data for the pregnant women according to 'Type of Delivery', showing any statistical differences between the 'type of delivery' groups using appropriate statistical tests (assume all data are normally distributed).
3.3 If the data were not normally distributed, what summary statistics would you produce within a table and what statistical tests would you carry out to assess differences between 'type of delivery' groups?
3.4 Write a short conclusion on the study based on your findings from question 3.2.
Attachment:- Assignment Files.rar