Reference no: EM13809903
1. Pete slides a crate up a ramp at an angle of 21o by exerting a 150 N force parallel to the ramp. The crate moves at a constant speed.
The coefficient of friction is 0.3. How much work did Pete do when the crate was raised a vertical distance of 1.74 m?
2. A particle moving in the xy plane undergoes a displacement s→ = (sx i^ + sy j^), with sx = 1.26 m, sy = 4.98 m, while a constant force F→ = (Fx i^+ Fy j^), with Fx = 6.53 N, Fy = 1.67 N, acts on the particle.
Calculate the magnitude of the displacement.
3. Find the magnitude of the force.
Calculate the work done by F.
Calculate the angle between F→ and s→.
4. A 3.59 × 10-5 kg raindrop falls vertically at constant speed under the influence of gravity and air resistance.
After the drop has fallen 62.5 m, what is the work done by gravity? The acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s2.
5. What is the work done by air resistance?
A block starts at rest and slides down a frictionless track. It leaves the track horizontally, flies through the air, and subsequently strikes
the ground.
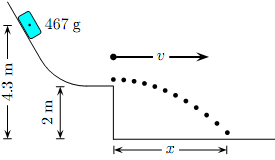
What is the speed of the ball when it leaves the track? The acceleration of gravity is 9.81 m/s2.
6. What horizontal distance does the block travel in the air?
7. What is the speed of the block when it hits the ground?
8. A block of mass 531 g is pushed against the spring (located on the left-hand side of the track) and compresses the spring a distance
4.9 cm from its equilibrium position (as shown in the ?gure below). The block starts from rest, is accelerated by the compressed spring, and slides across a frictionless horizontal track (as shown in the ?gure below). It leaves the track horizontally, flies through the air, and
subsequently strikes the ground.
The acceleration of gravity is 9.81 m/s2.
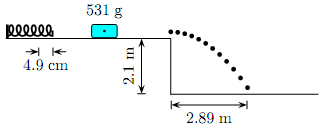
What is the spring constant?