Reference no: EM131021111
Second Midterm - I
Binary Choice:
1) True or False? The nominal GDP growth rate from 2013 to 2014 in the US was 3.88%. From this statement we can conclude that the real output (quantity of goods) produced in 2014 was larger than in 2013.
a. True
b. False
2) Why does the U.S. Bureau of Labor (BLS) use a high standard for considering an individual as unemployed?
a. The BLS uses this standard since it is the most efficient and correct way to measure unemployment in the U.S.
b. A more lenient standard would result in higher levels of reported unemployment that might not be an accurate reflection of actual labor market conditions.
3) True or False? The natural rate of unemployment is defined as the sum of the frictional and structural unemployment rates. Alternatively, the natural rate of unemployment is equal to the value of the actual unemployment rate minus the cyclical unemployment rate.
a. True
b. False
4) Suppose that lenders want a real return of 3 percent per year and the lenders expect the inflation rate to be 2 percent over this year. If the actual inflation rate turns out to be 3 percent, then lenders will find that their real return on this loan will be approximately equal to:
a. 2 percent
b. 3 percent
5) Suppose Bill borrows $2000 from Jane for one year. At the end of the year, Bill pays Jane $2500. Given this information, which of the following statements is true?
a. If the actual rate of inflation turns out to be more than the expected rate of inflation, then Bill will be worse off.
b. If Jane thinks inflation will be 10% for this time period, then she expects to receive a real return of approximately 15% on this loan.
6) Consider the aggregate production function for a small economy depicted in the following graph:
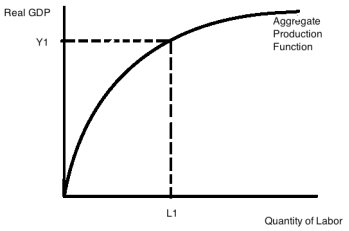
Suppose that from the initial situation shown in the graph, this economy hires a smaller number of workers. Given this information and holding everything else constant, the level of labor productivity will:
a. decrease.
b. increase.
7) Recall the examples given in lecture about price levels in Germany right after World War I. The story about the guy who went to the bar and bought two beers at a time instead of one beer is a clear example of:
a. deflation
b. hyperinflation
8) Suppose that in an economy human capital increases. Holding everything else constant including population, real GDP must increase and real GDP per capita must increase. This statement:
a. Is true.
b. Might be true, depending upon what happens to labor productivity.
9) Consider the market for loanable funds that is initially in equilibrium. Holding everything else constant, an increase in the government's deficit will:
a. Increase the equilibrium rate of interest and reduce the level of private investment.
b. Increase the equilibrium rate of interest and have no effect on the level of private investment.
10) Consider the market for loanable funds. You note that relative to the initial equilibrium, this market now has a lower equilibrium interest rate and a higher equilibrium level of private investment. A possible explanation for this outcome is:
a. There has been an increase in net capital inflows from the rest of the world.
b. That investors expect an improvement in economic conditions.
Multiple Choice:
11) Which of the following statements is NOT true?
a. The prices used to calculate nominal GDP are current year prices.
b. The prices used to calculate real GDP for year n are the prices from the base year.
c. The values of real GDP and nominal GDP for a particular year are always different.
d. The GDP deflator for year n can be computed if real GDP for year n and nominal GDP for year n are known.
Use the following information to answer the next two (2) questions.
Suppose that the real GDP per capita this year is $55,000 in the U.S. and $15,000 in China, and that the growth rate of real GDP is 2% in the U.S. and 7% in China. For each country assume that the annual growth rate of real GDP is constant and does not change over time.
12) Using the rule of 70 as an approximation, how long would it take for China to double its real GDP per capita?
a. 5 years
b. 10 years
c. 15 years
d. 20 years
13) Using the rule of 70 as an approximation, what would be the approximate difference in real GDP per capita between China and the U.S. in 40 years?
a. China's real GDP per capita would approximately equal U.S. real GDP per capita.
b. China's real GDP per capita would exceed the U.S. real GDP per capita by less than $130,000.
c. China's real GDP per capita would exceed the U.S. real GDP per capita by more than $130,000.
d. The U.S. real GDP per capita would exceed China's real GDP per capita by less than $130,000.
Use the following information to answer the next two (2) questions.
Suppose that the Republic of Economists (ROE) is a country with a population of 30,000 people. Of those 30,000 people, 20,000 of them are age 16 or older. You also know that in this economy there are 9,000 employed people and 1,000 unemployed people. Among the 1,000 unemployed workers, 250 of these workers are involved in job searches focused on locating jobs that are a good fit for their specific skills and talents. An additional 200 of these unemployed workers are searching for jobs in the market where there are few vacancies, at the prevailing wage rate, due to the type of job that is being sought. Assume that there are no seasonally unemployed workers in this economy.
14) What is the labor force participation rate in the ROE? For this calculation assume that all adults are part of the population to be considered (i.e., there is no military, no institutionalized people, and no other scenario where the adult population is not considered when calculating this labor force participation rate).
a. 50%
b. 55%
c. 60%
d. 70%
15) Given the above information, which of the following statements is true?
a. 250 people are structurally unemployed in this country.
b. The frictional unemployment rate is 2.5%.
c. The natural unemployment rate is less than 4%.
d. The cyclical unemployment rate is 5.8%.
Use the following information to answer the next two (2) questions.
Suppose that the Republic of Economists (ROE) produces two goods: books and potatoes. The following table provides information about the prices and outputs for these goods for the years 2013, 2014 and 2015. Assume that the base year is 2013 and that the GDP deflator is measured on a 100-point scale.
|
|
Price per book
|
Quantity of books
|
Price per potato
|
Quantity of potatoes
|
|
2013
|
$5
|
10
|
$5
|
5
|
|
2014
|
$10
|
10
|
$5
|
10
|
|
2015
|
$10
|
20
|
$5
|
10
|
16) Which of the following statements is true?
a. Nominal GDP in 2013 is higher than real GDP in 2013.
b. Real GDP in 2014 is $100, so we know that there was not any inflation between 2013 and 2014.
c. There was a recession in 2014.
d. Both nominal GDP and real GDP in 2015 are higher than they were in 2014.
17) Given the above information, which table depicts the GDP deflators for each year accurately?
Table A:
|
Year
|
GDP deflator with BY 2013
|
|
2013
|
80
|
|
2014
|
100
|
|
2015
|
120
|
Table B:
|
Year
|
GDP deflator with BY 2013
|
|
2013
|
100
|
|
2014
|
127
|
|
2015
|
150
|
Table C:
|
Year
|
GDP deflator with BY 2013
|
|
2013
|
100
|
|
2014
|
150
|
|
2015
|
167
|
Table D:
|
Year
|
GDP deflator with BY 2013
|
|
2013
|
120
|
|
2014
|
167
|
|
2015
|
192
|
a. Table A
b. Table B
c. Table C
d. Table D
Use the following information to answer the next three (3) questions.
In the small island country of Montecristo, people consume only services. Thus, their representative consumer basket for one year consists of 5 haircuts, 20 bus rides, 4 visits to the dentist, 10 visits to the movies, and 1 consultation with a lawyer. The prices of these services for the years 2013, 2014, and 2015 per usage (visit) in US dollars are as follows:
|
Service/Year
|
2013
|
2014
|
2015
|
|
Haircut
|
$8 per haircut
|
$20 per haircut
|
$20 per haircut
|
|
Bus Ride
|
$2 per bus ride
|
$3 per bus ride
|
$5 per bus ride
|
|
Dentist
|
$20 per dentist visit
|
$20 per dentist visit
|
$25 per dentist visit
|
|
Movies
|
$4 per movie
|
$8 per movie
|
$10 per movie
|
|
Lawyer
|
$50 per consultation with a lawyer
|
$80 per consultation with a lawyer
|
$100 per consultation with a lawyer
|
18) Given the above information, what is the value of the CPI in 2015 when the base year is 2013 and what is the value of the CPI in 2015 when the base year is 2014? Assume that the CPI is measured on a 100-point scale and is rounded to the nearest whole number.
a. The CPI in 2015 with base year 2013 is 100; the CPI in 2015 with base year 2014 is 95.
b. The CPI in 2015 with base year 2013 is150; the CPI in 2015 with base year 2014 is 110.
c. The CPI in 2015 with base year 2013 is 200; the CPI in 2015 with base year 2014 is 125.
d. The CPI in 2015 with base year 2013 is 250; the CPI in 2015 with base year 2014 is 140.
19) Given the above information, what is the inflation rate from 2014 to 2015?
a. 0%
b. 25%
c. 50%
d. 75%
20) Suppose Edmond lives in Montecristo and Mercedes is Edmond's wife. Their combined annual nominal income in 2014 is $8,000. What should Mercedes' annual nominal income in 2015 be so that the two together don't experience a drop in their real income, if Edmond's nominal income in 2015 is $6,250?
a. $3,000
b. $3,250
c. $3,500
d. $3,750
Use the following information to answer the next two (2) questions.
Suppose that there are only 10 people living on a small island. The following people live there.
- Adam, age 34, teaches preschool. He has a wife, Beth, and two sons, David and Eric.
- Beth is Adam's wife, and she does not have a job because she is very busy taking care of two wild boys.
- David is 4 years old, and he thinks he is so cute.
- Eric is 2 years old, and he does not like his brother.
- Frank, age 28, is Adam's brother. He was looking for a job in 2013, but he failed to find one, so he gave up looking for work years ago. Now (11/16/2015) he lives with his kind brother.
- George, age 41, left his current job 2 weeks ago to move to a new job. He began working at the new job yesterday.
- Harry, age 18, is a swimming instructor. It is the only skill he has. Now it is winter and he is unemployed, because there is no indoor swimming pool on this island. He is sure to get a job as a swimming instructor next summer.
- Jenny is 23 years old. When she was 21 years old, she won the lottery, so she has enough money for her entire life. She does not have a job and will never look for one.
- Kyle, age 50, was fired from his job last month because his company bought new equipment that could do Kyle's job in less time. He is looking for a job, available for work, and submitting job applications every week.
- Lois, age 46, is a steelworker. She was laid-off from her job 3 months ago, because the economy on the island is sluggish and orders for new cars are below their usual level. She is looking for a job, applied for a job at the local hardware store last week, and is available to work.
21) Given the above information, which of the following statements is TRUE?
a. David and Eric will be included in the government's calculations when the government measures the unemployment rate.
b. Frank is cyclically unemployed, and George is frictionally unemployed.
c. Harry is seasonally unemployed, and Jenny is a discouraged worker.
d. Adam is in the labor force, and Beth is not in the labor force.
22) Given the above information, what is the unemployment rate today (11/16/2015) on this small island?
a. 100%
b. 80%
c. 75%
d. 60%
23) Assume that as a result of increased political instability, loanable funds are moved out of the country of Macroland. Which of the following statements describe the outcome in Macroland given this information?
a. There is a rightward shift in the demand for loanable funds curve in Macroland and this shift results in a lower equilibrium interest rate in this market.
b. There is a a leftward shift in the demand for loanable funds curve in Macroland and this shift results in a higher equilibrium interest rate in this market.
c. There is a leftward shift in the supply of loanable funds curve in Macroland and this shift results in a higher equilibrium interest rate in this market.
d. There is a rightward shift in the supply of loanable funds curve in Macroland and this shift results in a lower equilibrium interest rate in this market.
24) Assume that The University of Wisconsin-Madison releases an annual index of business confidence for the United States, which indicates that business confidence in the United States has dropped over the past year. At the same time, consumers in China decide to increase their domestic consumption of goods and services. When you consider the loanable funds market from the perspective of the United States, which of the following statements is true given the above information and holding everything else constant?
a. The real interest rate in the United States must increase.
b. The interest rate in the United States must decrease.
c. The interest rate in the United States might increase.
d. The level of investment spending in the United States must increase.
Use the following information to answer the next two (2) questions.
In a closed economy, the production function is given by:
Y = 10(K.5)(L.5)
Where Y is output or real GDP, K is units of capital and L is units of labor.
This economy is currently at full employment equilibrium with 100 units of workers. This means L=100. The capital stock is constant and equal to 100 units (K=100). You are also told that the consumption and investment functions are given by the following equations where C is consumption spending, I is investment spending, and i is the nominal interest rate expressed as a whole number in the equation (e.g., if i = 5%, then the value of I in these two equations would be given as 5):
C = 400 - 200i
I = 1100 - 100i
Finally, assume that government spending is represented by G = 100. For this problem assume that taxes and transfers are equal to 0: this will greater simplify our analysis even if it is not particularly realistic. Hint: you will need to use some of your knowledge of GDP measurement to proceed with this question.
25) Given the information above, what is the equilibrium nominal interest rate and the equilibrium quantity of investment in this economy?
a. The equilibrium interest rate is 3%, and the equilibrium quantity of investment is $900.
b. The equilibrium interest rate is 3%, and the equilibrium quantity of investment is $800.
c. The equilibrium interest rate is 2%, and the equilibrium quantity of investment is $900.
d. The equilibrium interest rate is 2%, and the equilibrium quantity of investment is $800.
26) Now, suppose that investors expect a worsening in the economic conditions and therefore at each interest rate the desired level of investment is lower. The new investment function is given by the following equation:
I = 1080 - 100i
But, the government does not want the equilibrium level of investment spending to decrease in this economy from its initial level (the level you found in the last problem): so, the government decides to implement a policy with regard to the level of government spending that results in the level of investment spending by businesses staying at its original level. Given this information and holding everything else constant, the government should:
a. Increase the level of government spending which will increase the size of the government deficit.
b. Decrease the level of government spending which will decrease the size of the government deficit.
c. Increase the level of government spending which will decrease the size of the government deficit.
d. Decrease the level of government spending which will increase the size of the government deficit.
Use the following information to answer the next three (3) questions.
Suppose Y is output, K is capital, L is labor, and A is the level of technology in an economy and we can express the relationship between output and K, L, and A with the following aggregate production function:
Y = A(K.5)(L.5)
Initially K is equal to 100 units, the state of the technology is represented by A = 10 and L is equal to 100 units. Now assume that in one decade the technology improves in such a way that the economy can now produce exactly twice as much output as it could initially with the same amount of capital and labor (that is, now A = 20). During the same decade, the country suffers an earthquake that destroys a big part of its capital stock (fortunately the population and the labor force remain constant). Now the stock of capital is 1/4 of its initial level.
27) Holding everything else constant, the GDP rate of growth over the decade was:
a. 0 %
b. -10%
c. 10%
d. 50%
28) Assume the same initial situation as in the previous problem (that is K=100, L=100, A=10). Assume that in this economy there is an outflow of workers because they expect better living conditions in some other country. Now the number of workers in this country has fallen to L=81. Given this information and holding everything else constant, what would need to happen to the stock of capital in this economy in order to maintain the original level of labor productivity?
a. The stock of capital would need to increase by 21 units from its original level.
b. The stock of capital would need to increase by 10% from its original level.
c. The stock of capital would need to decrease by 19 units from its original level.
d. The stock of capital would need to decrease by 10% from its original level.
29) Start again from the initial situation (A=10, K=100, L=100). Assume that the rate of growth in GDP was 10% over a year. Suppose that the state of technology and the number of workers remained constant over that one-year time period and that the reason this economy grew during this period was because the capital stock increased. Given this information and holding everything else constant, capital productivity at the end of this year will be:
a. Lower than 10 units of output per unit of capital.
b. Higher than 10 units of output per unit of capital.
c. Equal to 10 units of output per unit of capital.
d. Impossible to compute from the given information.