Reference no: EM13762253
Suppose that the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) administers the price floor for cheese, set at $0.17 per pound of cheese. (In real life the actual price floor was officially set at $16.10 per hundredweight of cheese. One hundredweight is 100 pounds.) At that price, according to data from the USDA, the quantity of cheese produced in 2009 by U.S. producers was 212.5 billion pounds, and the quantity demanded was 211 billion pounds. To support the price of cheese at the price floor, the USDA had to buy up 1.5 billion pounds of cheese. The accompanying diagram shows supply and demand curves illustrating the market for cheese.
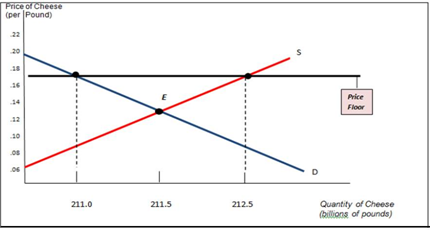
a. In the absence of a price floor, the maximum price that a few of the consumers are willing to pay is $0.20 for a pound of cheese whereas the market equilibrium price is $0.13 per pound. The graph also shows that the minimum price at which a few of the producers are willing to sell is $0.06 per pound. In the absence of a price floor, how much consumer surplus is created?
b. How much producer surplus?
c. What is the total surplus?
d. The maximum price that a few of the consumers are willing to pay is $0.20 per pound of cheese, and the price floor is set at $0.17 per pound. With the price floor at $0.17 per pound of cheese, consumers buy 211 billion pounds of cheese. How much consumer surplus is created now?
e. The minimum price at which a few of the producers are willing to sell a pound of cheese is $0.06, and the price floor is set at $0.17 per pound. With the price floor at $0.17 per pound of cheese, producers sell 212.5 billion pounds of cheese (some to consumers and some to the USDA). How much producer surplus is created now?
f. The surplus cheese USDA buys is the difference between the quantity of cheese producers sell (212.5 billions of pounds of cheese) and the quantity of cheese consumers are willing to buy at the price floor (211 billions of pounds of cheese). How much money does the USDA spend on buying up surplus cheese?
g. Taxes must be collected to pay for the purchases of surplus cheese by the USDA. As a result, total surplus (producer plus consumer) is reduced by the amount the USDA spent on buying surplus cheese. Using your answers for parts d, e, and f, what is the total surplus when there is a price floor?
h. How does this compare to the total surplus without a price floor from part c?
|
What was jekylls outcome
: Do you ever feel as if you are part Jekyll, part Hyde? What was Jekyll's outcome? What do you expect yours to be? Is Hyde evil? Why or why not?
|
|
Challenges of business for addressing health disparities
: The challenges faced by health plans to address health disparities by using a business case, particularly when trying to achieve a positive return of investment (ROI).
|
|
Cash method of accounting
: Related Party Transactions. Sally is an attorney who computes her taxable income using the cash method of accounting. Sage Corporation, owned 40% by Sally's brother, 40% by her cousin, her cousin, and 20% by her grandmother, uses the accrual metho..
|
|
Describe a case you have experienced as a manager
: Describe a case you have experienced or a story within the last three years that you have found through a reputable news source, where the manager(s) of a company did not act ethically or align.
|
|
What is the total surplus and producer surplus
: How much producer surplus - what is the total surplus - With the price floor at $0.17 per pound of cheese, consumers buy 211 billion pounds of cheese. How much consumer surplus is created now?
|
|
Explain why networking standards are important
: Explain why networking standards are important and why equipment that uses these standards should be purchased
|
|
Ethics case-magnetic toys can hurt
: Mega Brands has been selling Magnetix toys for many years. It also sells Mega Bloks, construction toys based on Spider-Man, Pirates of the Caribbean, as well as other products in over 100 countries.
|
|
Corporations and professional accountants
: What are philosophy approaches to ethical decision making relevant to modern corporations and professional accountants?
|
|
Narrows the spectrum to the mean-median
: Trend forecasters, sometimes called "futurists," use three "P's": Possible, Probable, and Plausible. "Possible" includes the "outliers" on the classic bell curve. "Probable" narrows the spectrum to the mean, median, and mode at the top of the be..
|