Reference no: EM133064011
SECTION A
Question 1. Write illustrated notes on TWO of the following:
(a) Draw the graph of a typical cell voltage vs. current density dependence (polarization curve) for a fuel cell and explain the three main characteristic regions. Use equations that define the cell voltage and labeled diagrams to illustrate your answer. What are the major losses of energy?
(b) Explain the concept of cyclic voltammetry and the criteria for a reversible system. Show an example that includes a detailed labelled current vs. potential curve. Explain how the concentration of the electroactive species on the surface of the electrode change as the potential moves away from the equilibrium value.
(c) Explain the principle of redox flow cells. Are they suitable to store large amounts of electrical power? Why? What is the driving force? Illustrate your answer with some examples.
(d) What is the purpose of an ion exchange membrane? Give examples where these membranes are used. Explain which is the main transport mode of ions inside the ionic membranes and why. Mathematical expressions and diagrams should be used.
(e) Explain the difference between galvanic (self-driven) and electrolytic (driven) cells. Give examples of each system and explain the direction of the reaction in terms of Gibbs free energy.
Question 2. Answer ALL parts of this question.
(a) Write the overall cell reaction and the value of the standard cell potential of a galvanic cell that consist of the following half-cell reactions. Clearly indicate what the oxidizing and reducing agents are:
Al3+ + 3e- 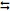 Al(s) Ε0Al3+/Al = -1.66 V vs. SHE (1)
Al(s) Ε0Al3+/Al = -1.66 V vs. SHE (1)
Cu2+ + 2e- 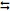 Cu(s) E0Cu2+/Cu = +0.34 V vs. SHE (2)
Cu(s) E0Cu2+/Cu = +0.34 V vs. SHE (2)
(b) Write the notation of the cell indicating the phase boundary and the salt bridge.
(c) Calculate the Gibbs Free Energy change ΔG and the ln K for this reaction where K is the equilibrium constant.
(d) In the following reaction:
Zn(s) + 2H+(aq) 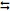 Zn2+(aq) + H2(g) The half-cell reactions are:
Zn2+(aq) + H2(g) The half-cell reactions are:
Zn2+ + 2e- Δ Zn(s) Ε0 = -0.76 V vs. SHE (1) 2H+ + 2e- Δ H2(g) E0 = +0.0 V vs. SHE (2)
i) Write the Nernst equation for the whole reaction and suggest how decreasing the concentration of Zn2+ would affect the cell potential, Ecell.
ii) Using the Nernst equation, what is the effect on the cell potential when metallic Zn increases?
iii) What is the standard cell potential of the cell, E0cell?
iv) What is the real cell voltage of the cell at 25°C when the concentration of [Zn2+] is 0.5 M? The partial pressure of hydrogen, pH2 is 10 atm and the pH is 6.
Faraday constant, F = 96 485 C mol-1, Gas rate constant, R = 8.314 J mol-1 K-1 273.15°C = 0 K; 25°C 298.15 K
F/RT = 38.92 V-1
RT/F = 0.02569 V
2.303 RT/F = 0.05916 V
Question 3. Answer ALL parts of this question.
A pilot-scale borohydride - air fuel cell consumes 100 g of fuel per hour.
(a) State the most likely anode-, cathode- and cell reactions and potentials.
(b) If the open-circuit potential of a single cell during operation is 1 V, calculate the theoretical maximum energy in kJ mol-1 and kW h kg-1 available from the cell.
(c) Calculate the maximum energy available in kJ from the stack in 15 hours.
(d) Calculate the cell current, stating all assumptions.
(e) What is the importance of the cell design for a successful operation of a borohydride fuel cell? State the strategies to achieve high energy from a stack.
SECTION B
Question 4. Answer ALL parts of this question.
(a) A beam of light at a wavelength of 500 nm, with a spectral width of 8 nm and spectral irradiance of 1000 W m-2 μm-1, illuminates an area of 10 cm2. Determine the photon flux density in the beam and the power, voltage and current that this beam could generate if converted to electricity.
(b) The standard solar spectrum can be approximated by the following spectral irradiance function (in units of W m-2 μm-1) as a function of the wavelength λ (in µm):
eλ(λ) = 0 (λ < 0.4 µm)
eλ(λ) = 325/λ3 (0.4 ≤ λ < 3.1 µm)
eλ(λ) = 0 (3.1 µm ≤ λ)
(i) What is the total photon flux density (in photons per square metre per second) in the spectrum?
(ii) What maximum short-circuit current can be generated by 10 cm x 10 cm crystalline silicon solar cell?
(iii) What is the maximum efficiency of this crystalline silicon solar cell?
(iv) What is the maximum efficiency of a tandem solar cell made from semiconductors with bandgaps of 1 and 2 eV?
Hint: You may wish to convert first the spectral irradiance as a function of λ into a function of photon energy.
Electron charge q = 1.602 x 10-19 C Bandgap of crystalline silicon = 1.12 eV Where appropriate, use a fill factor ff = 0.75
Question 5: Answer ALL parts of this question.
(a) Concisely discuss technologies that are available for the manufacture of solar cells which are available commercially as well as those under development in research laboratories. Your discussion should include brief notes about the expected efficiencies, costs, status of development and / or market penetration and possible applications.
(b) A 15% efficient crystalline silicon solar cell is manufactured from a 350 μm thick silicon wafer. Assuming 200 μm kerf loss in wafering, what is the silicon usage (in grams per Wp) in the cell manufacture?
(c) A solar cell has an open-circuit voltage of 0.7 V, short circuit current 3.5 A and efficiency 20% under standard test conditions. It operates at a temperature of 25 C under concentrated sunlight with a concentration ratio of 10. What short-circuit current, open circuit voltage and efficiency would you expect in this case?
Boltzmann constant kB = 8.61 x10-5 eV K-1 Temperature conversion 0 C = 273.15 K Silicon density = 2.33 g cm-3
Question 6. Answer ALL parts of this question.
(a) With the help of simple circuit diagrams where appropriate, describe concisely the roles of the following components in a photovoltaic system:
• charge regulator
• maximum power point tracker
• islanding protection
• by-pass diode
• blocking diode
• load (low voltage) disconnect
(b) A photovoltaic module, consisting of 36 crystalline silicon solar cells, has an open - circuit voltage of 21 V and a short - circuit current of 3 A. The series resistance of one cell has been determined to be 40 mΩ. If the fill factor ffo of a similar ideal solar cell (without series resistance) is 0.892, what is the power of this module at the maximum power point?
(c) What is the dark saturation current of one cell in the module in Part (b) under standard test conditions?
(d) How many of the modules in Part (b) and how large battery (in Wh) would you need to power a daily load of 300 Wh in a location with daily solar radiation of 4.5 kWh m-2, for a system that operates without a maximum power-point tracker, having 6 days of autonomy?