Reference no: EM132474728
Problem 1 a) Name five (5) of the effects of equipment failure.
Problem 2
Which condition monitoring method is most appropriate for monitoring of the following conditions (list only one per case):
a) Resonance
b) Misaligned machines
c) Loose/corroded electrical connections
d) Worn bearings
e) Mechanical looseness
f) Unbalance of rotating parts
g) Contamination of lubricant
Problem 3 There are four different maintenance philosophies. Which of them is the least effective and why?
Problem 4 What is the term that is used for vibration at a natural frequency?
Problem 5 (CRITICAL Problem)
Would the following vibrations be caused by a natural frequency or a forced frequency?
a) Pluck a guitar string
b) Misalignment between a motor and pump
c) A worn gear
d) Ringing of a bell
e) Machine tool chatter
Problem 6 What is the frequency of this wave?
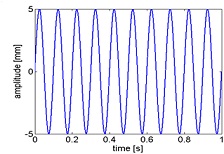
Problem 7 How can you determine if a vibration problem is due to a natural frequency or a forced frequency?
Problem 8 This Problem has two options. If YOU have the EQUIPment specified in option A then yoU can perform the test/s reQUIRED. However, if yoU don't have the necessary eQUIPment then answer the Problem in Option B.
You are not required to complete both options!
Option A
Determine the natural frequency of a given metal object using the bump test.
Option B
What is a bump test and outline how you would estimate the natural frequency of vibration of a metal object using the bump test?
Problem 9 Why are vibrations usually measured on the bearings of a machine?
Problem 10 You note high vibration levels at 1 x rpm on a machine in your plant. What are the probable causes and how can you distinguish between them?
Problem 11 This Problem has two options. If YOU have the EQUIPment specified in option A then yoU can perform the test/s reQUIRED. However, if yoU don't have the necessary eQUIPment then answer the Problem in Option B.
You are not required to complete both options!
Option A
i) Use a phototachometer to measure the rotational speed of a given shaft. Validate the findings using a stroboscope.
ii) Record the measurements at different shaft speeds and repeat the same set of procedures for another shaft
Option B
i) What is a phototachometer and why would you use it to measure the rotational speed of a given shaft?
ii) What is a stroboscope and what are the benefits of using a stroboscope to validate the findings?
iii) Why would you record the measurements at different shaft speeds?
Problem 12 An analyser is set so that the maximum frequency it can read is 80,000cpm. If the bandwidth is 200cpm/line, what would the resolution of the analyser be?
Problem 13 What are the disadvantages of using hand-held probes for vibration monitoring?
Problem 14 What is the advantage of using magnets for vibration sensor mounting? Why does the use of commercially available double adhesive tapes result in distorted measurements?
Problem 15 What type of vibration transducer do you think would be best for an application in the frequency range 2Hz to 20kHz?
Problem 16 A vibration analysis of a positive displacement pump shows a predominant vibration reading at a frequency of 1x the rotational speed of the pump. There is a phase shift of 180º between axial readings taken in the same direction on the drive and non-drive ends of the pump. What would you suspect the cause of the vibration to be?
Problem 17 How would you differentiate between the vibration signatures of parallel and angular misalignment?
Problem 18 A vibration analysis on an electric motor shows significant radial vibrations at 1x, 2x, 3x, 4x the running speed of the motor. A particularly predominant peak shows near 12,000 cpm. If the motor has 4 rotor bars and runs at 2940rpm what would you suspect the problem to be and how would you confirm your suspicions?
Problem 19 What are the manufacturing causes that lead to unbalance?
Problem 20 Distinguish between misalignment and unbalance.
Problem 21 List some of the maintenance actions that may affect balancing.
Problem 22 Which are the locations that are normally preferred for weight addition and removal in balancing?
Problem 23 Define heavy spot. What is the effect of heavy spot on shafts and bearings?
Problem 24 What is centrifugal force with respect to unbalance? What is the formula used to determine centrifugal force?
Problem 25 What factors other than unbalance contribute to high amplitude vibration?
Problem 26 What conditions should be met for taking up Two-plane balancing after Single-plane balancing has proven unsuccessful? What other important assumption is made in this method?
Problem 27 Why are overhung rotor configurations in pumps and fans difficult to balance?
Problem 28 Why is it required for overhung rotors be balanced on or near resonance?
Problem 29 What does the fundamental balancing principle involve? Name the two primary factors in balance tolerances.
Problem 30 What are the four fundamental principles attached to the reverse-dial method? Also bring out the limitations of this method.
Problem 31 Distinguish between parallel and angular misalignment? What are the dominant sources of belt- induced vibrations?
Problem 32 What are the consequences of misalignment in belts? Explain.
Problem 33 Explain how a frequency meter with a laser sensor can be used to determine the natural frequency of a V-belt, and how that relates to the belt tension and speed.
Problem 34 What is the acceptable standard for shaft angularity as per industry practice? On what parameters are the specification for couplings is usually based on?
Problem 35 Briefly describe performance monitoring and how it can be used to monitor the condition of equipment.
Problem 36 With reference to machinery, what is TLC?
Problem 37 What are the three main aspects associated with an oil analysis program?
Problem 38 Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of thermographic imaging.
Problem 39 What is indicated by the thermographic images below?
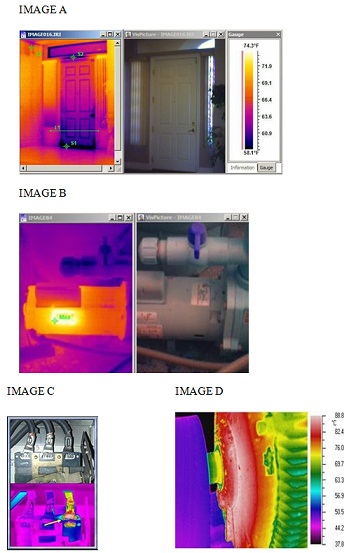
Problem 40 Describe Root Cause Failure Analysis.
Problem 41 Plant/factories typically contain equipment that can be classified as critical, essential or general- purpose. List three (3) relevant factors under each classification that help catagorise the equipment.
Problem 42 You balanced a pump impeller by placing a 5 gram weight at a radius of 100 mm. The original vibration amplitude was 10 mm/s, and after adding the balancing weight, the vibration is 1 mm/s. The speed of the pump is 1500 rpm and the weight of the impeller is 3 kg.
a) Calculate the residual unbalance, the eccentricity and the balancing quality grade according to ISO balancing standard.
b) The stiffness of the pump's shaft is 80 kN/m. Calculate the natural frequency for the pump impeller on the shaft (ignore the weight of the shaft).
c) What is going to happen if the pump speed is increased to 1560 rpm?
Problem 43 Consider the small high-speed pump setup below (measurements in mm). This was one of three new pumps at a water wastewater plant. Alignment must be done on the system using the reverse method of alignment, especially since the pumps operate at a higher speed.
The following measurements were made (motor = dial indicator reading on indicator closest to motor, pump = dial indicator reading on indicator closest to pump):

Using these readings, suggest shims and left-right moves on the machine in order to align it.
motor
0
+1.78
+1.32
+2.92
pump
0
+0.13
+0.97
+1.22