Reference no: EM13983360
Assignment
Complete the following questions.
The angiogram is the standard test used to diagnose the occurrence of stroke. However, the test is invasive and researchers are looking into an alternative screening test that is non-invasive. Sixty-four patients with transient monocular blindness, or TMB (where a person temporarily loses vision in one eye) were given both tests. The results for stroke diagnosis were as follows:
|
|
Angiogram Positive
|
Angiogram Negative
|
Total
|
|
Non-Invasive Test Positive
|
32
|
8
|
40
|
|
Non-Invasive Test Negative
|
3
|
21
|
24
|
|
Total
|
35
|
29
|
64
|
Define the screening test as the non-invasive test and the diagnostic test as the Angiogram.
1. What is the predictive value positive of the non-invasive test?
2. What is the predictive value negative of the non-invasive test?
3. What is the sensitivity of the non-invasive test?
4. What is the specificity of the non-invasive test?
5. What is the prevalence of stroke in the given sample according to the angiogram result?
6. What is the prevalence of stroke in the given sample according to the non-invasive test?
7. Suppose the prevalence of strokes among TMB patients is 20%. What is the predictive value positive based on this information?
8. Suppose the prevalence of strokes among TMB patients is 20%. What is the predictive value negative based on this information?
The in-hospital mortality rate for 16 clinical conditions at 981 hospitals was recently reported. It was reported that in-hospital mortality was 10.5% for coronary-bypass. Suppose an institution changes from an academic institution to a private for-profit institution. They find that after the change, of the first 30 patients receiving coronary-bypass surgery, 3 die.
9. What is the probability that of 30 patients receiving coronary-bypass surgery, exactly 3 will die in-hospital, if this hospital is representative of the total pool of 981 hospitals?
10. What is the probability of at least 3 deaths among the coronary-bypass patients? Hint: Avoid a lot of hand calculations by calculating the complement and using 1 = Pr(A) + Pr(Ac)
11. What is the probability of no more than 3 deaths among the coronary-bypass patients?
12. What is the expected number (i.e. mean number) of people to die after receiving coronary- bypass surgery?
13. What is the standard deviation?
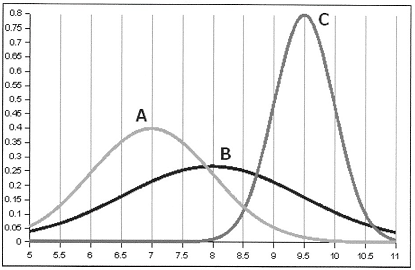
14. Which curve has the largest standard deviation visually?
a. Curve A
b. Curve B
C. Curve C
d. All curves have equal standard deviation.
15. Which curve has the smallest standard deviation visually?
a. Curve A
b. Curve 13
c. Curve C
d. All curves have equal standard deviation.
16. What is the mean of curve A?
17. For Curve A, what is the standardized Z-score for X = 6.58 assuming σ = 0.5?
18. For Curve A, what is the Pr(X < 5.58) assuming a = 0.5? (3 pts)
19. For Curve B, what is standardized Z-score for X = 8.75 assuming the mean = 8 σ = 1.25?
20. For Curve B, what is the Pr(X > 8.75) assuming the mean = 8 and σ = 1.25?
Suppose curves A, B, and C represent the duration of time (in hours) in which patients experience relief from migraines of three different medications. Suppose you choose a random sample of 15 patients from the medication C population which has μ = 9.5 and σ = 0.3.
21. What is the standard error of the mean for Group C?
22. What is the probability that the sample's mean duration of relief is less than 9.35 hours? Round your Z-score to 2 decimal places so you're able to use the Z-table.
21 What is the probability that the sample's mean duration of relief is greater than 9.75 hours? Round your Z-score to 2 decimal places so you're able to use the Z-table.