Reference no: EM132304517
Assignment - Short questions
Probability -
In MagicVille (population 1200), exactly a third of the townsfolk have magic wands. Some EdX students need some magic wands for an event, so they decided to visit MagicVille for a day. Unfortunately they can't spend too long there, and they need 50 magic wands. The students also do not know which of the residents have magic wands because they keep their magic wands hidden most of the time and bring them out only on MagicHoliday. Let n be the number of people they visit.
1. What kind of distribution can we use to model the number of magic wands they get?
hypergeometric
binomial
geometric
negative binomial
2. How many people do they need to visit in order to ensure that they get at least 50 magic wands with more than 70% probability. Note: Use of R is highly encouraged.
150
155
157
158
Conditional Probability -
Imagine you are on a gameshow and you're given the choice of three doors: behind one door is a car and behind the other two doors are goats. Of course, you would want to win the car. You have the opportunity to pick a door (say door A), which is not opened. The host, who knows exactly what is behind each door, then opens another door (say door B) that has a goat behind it. Note that the host will not open the door that will reveal the car, which means that if the car is not behind door A, the host will open the door that has a goat behind it. Finally, the host ask you to decide whether to stay with your original choice or switch to the other unopened door.
1. If you chose to stay with the original choice A after the host opened door B, what is the probability of winning the car? Please enter the value with a precision of two decimal points.
2. If you chose to switch doors (from A to C) after the host opened door B, what is the probability of winning? Please enter the value with a precision of two decimal points.
3. Is it in your advantage to switch your selection?
Yes
No
Causal Inference -
Workplace wellness programs are intended to reduce medical spending, increase productivity, and improve well-being among employees. One popular version of this program includes on-site biometric health screening, and a variety of wellness activities, such as stress management, and recreational classes. Suppose you are the CEO of a large company and you are trying to decide whether it would be worthwhile to implement a similar wellness program at your company. To simplify things, suppose you care about only one outcome, total health care spending among your employees. You want to learn the causal effect of a wellness program on health spending.
1. Let Yi stand for the health spending (e.g. cost of doctors appointments, etc) of individual i, and Wi ∈ {0, 1} be the treatment status (enrolling in the wellness program).
What is the treatment effect on the treated using the causal notation from the course?
E [Yi (1) |Wi = 1] - E [Yi (0) |Wi =1]
E [Yi (0) |Wi = 1] - E [Yi (0) |Wi = 0]
E [Yi (1) |Wi = 1] - E [Yi (0) |Wi = 0]
2. As a first attempt at estimating the causal effect of interest, you collect data on the health spending for each individual in a large sample of companies. You then calculate the difference in average spending between the companies that offer wellness programs and those that don't. What is the correct expression for this difference in causal notation?
E [Yi (1) |Wi = 1] - E [Yi (0) |Wi =1]
E [Yi (0) |Wi = 1] - E [Yi (0) |Wi = 0]
E [Yi (1) |Wi = 1] - E [Yi (0) |Wi = 0]
3. You realize that the simple approach in question 2 will likely lead to selection bias. You decide to implement the program by randomly selecting half of your employees to be enrolled. What is randomization trying to achieve?
E [Yi (1) |Wi = 1] - E [Yi (0) |Wi =1]
E [Yi (0) |Wi = 1] - E [Yi (0) |Wi = 0]
E [Yi (1) |Wi = 1] - E [Yi (0) |Wi = 0]
E [Yi (0) |Wi = 1] - E [Yi (1) |Wi = 0]
Maximum Likelihood Estimator -
Let X1, . . . , Xn be i.i.d. uniform random variables in [θ, 2θ], where θ is an unknown parameter, what is the maximum likelihood estimator of θ?
½min(X1, . . . , Xn)
min(X1, . . . , Xn)
maz(X1, . . . , Xn)
½max(X1, . . . , Xn)
Central Limit Theorem -
3 points possible (graded, results hidden)
A poll by Dept. of Statistics is conducted to predict the election result in the country of Statistica. Suppose we know that 50% of the population supports Gosseta, 20% supports Fisheri, and the rest are split between Alpha, Beta and Gamma. The poll asks 400 random people who they support.
1. First let's define
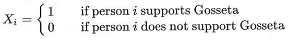
What is the expectation of Xi?
What is the variance of Xi?
2. Use the central limit theorem to estimate the probability that at least 52.5% of those polled prefer Gosseta. Please enter the value with a precision of two decimal points.
Web Scrapping with R -
In this question, we will guide you through the steps of web scrapping using R. We will not provide you the R file, but instead we expect you to follow the steps and try to implement it yourself in R.
We are interested in finding out unicorn startup companies and their valuations.
1. Harvest data using R package "rvest"
2. Reading the HTML code from the website. Please use the url we have provided.
3. Next, we need to identify the table we are interested in. We can assume the name tag for the tables is "table" and we are going to extract the first table. (To identify the name tag, we can use the selector gadget Prof. Duflo mentioned in the lecture. The selector gadget has an extension in chrome and is used to pinpoint the names of the tags which we want to capture. Make sure you are using chrome browser.
4. Convert the html data to table format in R. Note: you may want to add additional arguments when the table has inconsistent number of columns.
After you have scrapped the table in R, answer the following questions:
Note: Please enter the number you obtained using R package "rvest". We are aware that the numbers may be different using different software packages. For this reason, we accept a range of reasonable answers that you may obtain.
How many companies are there in the table?
How many companies are from the United States?
Sleeping drug -
We are interested in testing the efficacy of a sleeping drug. We have surveyed 10 patients and recorded their hours of sleep under drug and under placebo respectively in the table below. Does the drug increase hours of sleep enough to matter? We have provided you the R file here sleepdrug.R that contains the data to get you started.
|
patient
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
4
|
5
|
6
|
7
|
8
|
9
|
10
|
|
drug
|
6.1
|
7.0
|
8.2
|
7.6
|
6.5
|
7.8
|
6.9
|
6.7
|
7.4
|
5.8
|
|
placebo
|
5.2
|
7.9
|
3.9
|
4.7
|
5.3
|
4.8
|
4.2
|
6.1
|
3.8
|
6.3
|
We will model the difference of hours of sleep between drug and placebo for each patier as a normal random variable.
1. What would be the power of the hypothesis test?
The probability that the test will conclude that the drug is effective, when in fact it is not.
The probability that the test will conclude that the drug is effective, if it is indeed truly effective.
The probability that the test will conclude that the drug is not effective, when in fact it is.
The probability that the test will conclude that the drug is not effective, if it is indeed not effective.
2. If we don't know the variance of the underlying normal distribution (o-2), which of the following can you use to test the null hypothesis?
Fisher exact test
T-test
Z-test
Kolmogrov Smirnov test
3. Since we don't know the true σ2, we will use the sample variance as an estimate: σ^2 = 1/(n-1) i=1∑n(Xi - X-n)2. Please enter the value with a precision of two decimal points.
4. What would be an appropriate test statistic T under the null hypothesis, so that T ∼ tn-1 (T-distribution with degrees of freedom n - 1)?
5. What is the p-value? Please enter the value with a precision of three decimal points.
6. Can we reject the null hypothesis at a significance level α = 5%?
Yes
No
Fisher Exact Test -
The table below presents observations from a randomized experiment to evaluate the effect of a new teaching technique on learning outcomes. The experiment is done on a class of students. The outcome we are interested in is the exam scores in the class. Half of the classes were taught using the new teaching technique, and the other half were taught using the traditional teaching technique. We have six observations, i = 1, . . . , 6. Three units receive the treatment assignments (Actual Treatment = 1) and three do not(Actual Treatment = 0).
|
Unit
|
Yi(0)
|
Yi(1)
|
Actual Treatment
|
Observed Outcome
|
|
1
|
60.0
|
|
0
|
60.0
|
|
2
|
|
65.0
|
1
|
65.0
|
|
3
|
74.0
|
|
0
|
74.0
|
|
4
|
|
68.0
|
1
|
68.0
|
|
5
|
72.6
|
|
0
|
72.6
|
|
6
|
|
79.2
|
1
|
79.2
|
1. If you plan to run a Fisher exact test, what is the null hypothesis?
The average effect of the new teaching technique on exam scores is zero.
The new teaching technique has no effect on exam scores for all units.
2. Under the assumption that we will have the same number of treated and control units, how many potential treatment assignments across these 6 units are possible?
3. Construct your Fisher exact test using a permutation table or R code. Please enter the p-value you obtained from the test.
4. What does the p-value suggest given a 5% significance level?
Under the null hypothesis, the observed difference is very unlikely to occur, therefore we reject the null hypothesis
Under the null hypothesis, the observed difference could well be due to chance, therefore we don't reject the null hypothesis
Banks -
We are going to examine a study on monetary policy by economists Gary Richardson and William Troost (the full paper is available here). You can also read more in the book "Mastering 'Metrics''. The largest economic downturn in American history - the Great Depression crashed the stock market in October 1929. Subsequently, the banking system broke down in Mississippi in 1930. In their study, they designed a quasi experiment to understand whether monetary policy contributed to the Great Depression and whether more aggressive monetary intervention might have prevented the financial collapse.
The U.S. Federal Reserve System is organized into 12 districts, and the border between the Sixth and Eighth districts defines a natural experiment for us. In the depression-era, regional Feds had considerable policy independence. The Atlanta Fed, running the Sixth District, preferred lending to troubled banks. By contrast, the St. Louis Fed that ran the Eighth Ditrict thought that the central bank should restrict credit in a recession. In the experiment, the Eighth District is treated as a control group, where policy was to do little or even restrict lending, while the Sixth District is a treatment group, where policy was to increase lending.
1. First, we can take a look at the number of banks still operating in each District on October 1, 1931, about 11 months after the beginning of the crisis. On that day, 132 banks were open in the Eighth District and 119 were open in the Sixth District.
However, we need to take into account the fact that the two districts weren't the same ininitally. This can be seen from the apparent difference in the number of banks operating on May 1, 1930, well before the crisis, with 139 banks open in the Sixth District and 165 banks open in the Eighth.
What is the Difference in Differences (DiD) estimate of the effect of lending to troubled banks in terms of the banks open?
2. In practice, however, the DID is best analyzed with regression models fit to samples of more than four data points. Therefore, we construct a sample of size 12 (on August 1st of each year from year 1929 to 1934) and use the following regression by estimating:
Ydt = α + βTREATd + γPOSTt + δTREATd * POSTt + ∈dt
TREATd is equal to 1 for data points from the Sixth District and zero otherwise.
POSTt = 1 indicates the observations from 1931 onwards (including year 1931) and zero otherwise. We have provided you banks.csv file that contains the relevant information. You are responsible for transforming the data into a format that can be used by R. Estimate the model in R. What value do you obtain for the DiD estimate? Please enter the value with a precision of one decimal point.
Demand for Cigarettes -
A classic application of instrumental variables regression is estimating the elasticity of demand for a product. In our case, the product of interest is cigaretts. In economics, the elasticity of demand is the ratio of the percentage change in quantity demanded to the percentage change in price of a commodity. To express percentage change, we transform the variables using natural logs, so the relationship can be written as follows:
Ln Q = α + β ln P + ∈
where β is the estimate of the elasticity (percentage change in quantity for a 1% change in price). We have observations on price and quantity of cigaretts, and it seems like we could run an OLS regression of In Q on in P and obtain an estimate of the elasticity.
However, there is a problem. Quantity demanded, apparently depends on price, but price is also determined by market demand. When customers have a high demand, the price tends to go higher. Therefore, because of the causaility going both ways, the elasticity of demand cannot be estimated by an OLS regression of log quantity on log price.
1. Which of the following best describes the problem as mentioned above?
Obmitted Variable Bias
Selection Bias
Endogeneity
To get around this problem, one way is to use an instrumental variable that is correlated with price but does not directly affect quantity demanded. Sales tax could be a good choice of instrument because it determines the sales price, but is not a direct determinant of demand. The data set cigs.csv consists of annual cigarette consumption in 48 U.S. states in 1985.
- Packs: the number of packs of cigarettes sold per capita in the state
- Price: the real (that is, inflation-adjusted) average retail cigarette price per pack, including taxes
- Income: real per capita income
- SalesTax: the average tax, in cents per pack
2. First, we need to think about whether the sales tax on cigarettes satisfies the conditions of a good instrument. What conditions does it need to satisfy? Select all that apply.
A high sales tax increases the sales price
The sales tax must affect the demand for cigarettes only indirectly through the price
The sales tax is correlated with the error term
We are going to use the natural log of packs as our dependent variable, the log of the real retail cigarette price per pack as our regressor and sales tax as our instrument.
3. Let's first take a look at the first-stage regression, where we regress ln (Pi) on SalesTaxi. Run the regression model in R and estimate φ. Please enter the value with a precision of three decimal points.
In (Pi) = α + φSalesTaxi
4. Now run the IV regression using the sales tax instrument. In (Qi) is regressed on In (Pi), what is the estimated percentage point change in demand quantity with an increase in the price of 1%? Please enter the value with a precision of three decimal points.
5. Even though the elasticity was estimated using an instrument variable, there might still be omitted variable bias. One such omitted variable could be state income. Thus, we would like to reestiamte our demand elasticity including income as an additional regressor by including the log of income in the estimation.
ln (Qi) = α+ βln(Pi) + γln(Inci) + ∈
What is the new 2SLS estimate? Please enter the value with a precision of three decimal points.
Attachment:- Assignment File.rar