Reference no: EM132925781
Acid-Base Consolidated Problems
WEAK ACID AND BASE PROBLEMS
Weak acids and Bases; Ka and Kb
1. Phenylacetic acid, HC8H7O2, accumulates in the blood of individuals with PKU, an inherited disorder that can cause mental retardation or even death. A 0.085 M solution of this substance is found to have a pH of 2.68. Calculate the Ka for this weak acid.
2. A particular sample of Dierberg's vinegar is found to have a pH of 2.90. Vinegar contains acetic acid (HC2H3O2), which is a weak acid. Calculate the initial concentration of acetic acid in vinegar. The Ka for acetic acid is 1.80 x 10-5.
3. A sample of hypochlorous acid, which is used in bleach and pool chlorinator, has an initial concentration of 0.0750M. Calculate the concentrations of H+1, ClO-1, and HClO at equilibrium. The Ka for hypochlorous acid is 3.50 x 10-8.
4. Formic acid, or HCO2H, It is an important intermediate in chemical synthesis and occurs naturally, most famously in the venom of bee and ant stings. A 0.100M sample was analyzed by a student, and found to have a pH of 2.38 at 250C. Calculate the Ka for formic acid, and calculate its percent ionization at this temperature.
5. Niacin, or nicotinic acid, HC6H4NO2, is a precursor to NADH, NAD, NAD+, and NADP, which play essential metabolic roles in living cells. It is also known as vitamin B-3. If niacin has a Ka of 1.50 x 10-5, then what is the pH of a 0.0100 M solution of nicotinic acid?
6. What is the pH of a 0.00370M solution of H3PO4, commonly used to make soda? It has a Ka of 7.10 x 10-3. H3PO4 dissociates primarily into H+1 and H2PO4 -1.
7. Up to 200 pounds of ammonia can be applied to each acre of agricultural crop a year in this country to provide plants with nitrogen, an essential element. What is the concentration of hydroxide ion in a 0.150M solution of ammonia? The Kb for ammonia is 1.80 x 10-5. NH3 reacts with water to form NH4+1 and OH-1.
8. Ethylamine (C2H5NH2) is an important base used in the production of many organic compounds. What is the molar concentration of hydroxide ions in a 0.0750M solution of ethylamine? What is the pH of the solution? The Kb for ethylamine is 4.00 x 10-6. Ethylamine reacts with water to form C2H5NH3+1 and OH-1.
9. Ephedrine (C10H15ON), a central nervous system stimulant, is used in nasal sprays as a decongestant. It acts as a weak base in the body. What are the equilibrium concentrations of C10H15ON, C10H15ONH+, and OH- , in a 0.0350M solution that has a pH of 11.33? What is the K for ephedrine?
Hydrolysis
10. Label each of the following as being a strong acid, a weak acid, or a species that has negligible acidity. Then, in each case, write the formula for its conjugate base as it dissociates or reacts with water:
a. HNO2 b. H2SO4 c. HIO2 d. HCl
11. Predict whether aqueous solutions of the following will be acidic, basic, or neutral:
a. NH4Br b. FeCl3 c. NaF d. KClO4
12. Calculate either [H+1] or [OH-1] for each of the following solutions. Then, calculate the pH of the solution.
a. 0.100 M NaCN Kb = 1.60 x 10-5
b. 0.0800 M NH4Cl Ka = 5.80 x 10-10
13. Potassium sorbate, KC6H7O2, is added to cheese to inhibit mold growth. What is the pH of a solution of potassium sorbate containing 4.93 grams of potassium sorbate in 0.500L of solution? Potassium sorbate has a Kb of 5.90 x 10-10.
pH of Acid-Base Reactions
14. What is the pH of a solution of 60.0 mL of 2 M KOH with 20.0 mL of 2 M HNO3?
15. What is the pH after mixing 20 mL of 2M HF with 60 mL of 2M KOH? (Ka = 7.2 x 10-4 Kb=1.4 x 10-11)
16. What is the pH after mixing 60 mL of 2M HF with 20 mL of 2M KOH? (Ka = 7.2 x 10-4 Kb=1.4 x 10-11)
17. Calculate the pH formed by adding 10.0 mL of 0.05 M NaOH to 40.0 mL of 0.0250 M benzoic acid, HC7H5O2, Ka = 6.3x10-5).
Buffers
18. Propionic acid (HC3H5O2) is used as a preservative in baked goods. Often, potassium propionate is used in conjunction to buffer the acid and its effect. What is the pH of a 0.0850M solution of propionic acid, in 0.0600M potassium propionate (KC3H5O2)? The Ka for propionic acid is 1.34 x 10-5.
19. What is the pH of a solution made by adding 0.300 mol of ascorbic acid (vitamin C), and 0.0300 mol of sodium ascorbate, to enough water to make 1.00 L of solution? The Ka for ascorbic acid (HC6H7O6) is 7.9 x 10-5. Buffers containing ascorbic acid and sodium ascorbate are used in vitamin C tablets.
20. Lactic acid is used in the production of yogurt and cheese. What is the pH of a buffered solution that is 0.120 M in lactic acid, HC3H5O3, and 0.10M in sodium lactate, NaC3H5O3? The Ka for lactic acid is 1.38 x 10-4.
21. Soft drink companies have been under fire recently for the use of benzoic acid (HC7H5O2) and sodium benzoate (NaC7H5O2) in their beverages, for the potential carcinogenic properties of these chemicals. What concentration of sodium benzoate is necessary to produce a pH of 4.00 in a 0.200 M solution of benzoic acid? The Ka for benzoic acid is 6.40 x 10-5.
22. What must be the molarity of NH4Cl in a 0.10M solution of NH3 to form a buffer with a pH of 9.00? Assume that the addition of NH4Cl does not change the volume of the solution. The Kb for NH3 is 1.8 x 10-5.
23. A buffered solution of 0.10 mol acetic acid and 0.13 mol of sodium acetate is prepared to grow cells for cancer research. They are in 1.00 L of solution. What is the pH of this solution? The Ka for acetic acid is 1.75 x 10-5.
Titrations
24. Calculate the pH when the following quantities of 0.100 M HNO3 have been added to 25.00 mL of 0.100 M KOH solution:
a. 24.90 mL b. 25.00 mL c. 25.10 mL
25. A 20.0 mL sample of 0.200M HBr solution is titrated with 0.200M NaOH solution. Calculate the pH after the following volumes of base have been added:
|
a. 10.0 mL
|
b. 15.0 mL
|
b. 19.9 mL
|
d. 20.0 mL
|
|
e. 20.1 mL
|
f. 35.0 mL
|
|
|
26. Calculate the pH of the solution at the equivalence point when 0.00250 mol of nicotinic acid in 1 L of solution is titrated by 0.00250 mol sodium hydroxide. Nicotinic acid (HC6H4NO2) has a Ka of 1.50 x 10-5. What would be an appropriate indicator for the equivalence point of this reaction? Assume volume changes are negligible!
27. What is the pH at the equivalence point when 35 mL of 0.20 M ammonia is titrated by 0.12 M hydrochloric acid? What would be an appropriate indicator for the equivalence point of this reaction? The Kb for ammonia is 1.8 x 10-5.
28. A chemist has synthesized a weak monoprotic acid and wants to determine its Ka value. To do so, the chemist dissolves 2.00 x 10-3 moles of the solid acid in 100.0 mL of water and titrates the solution. After adding 20.0 mL of .0500 M NaOH, the pH is 6.00. What is the Ka of the acid?
29. An unknown monoprotic acid is discovered to have restored mitochondrial function in rats, thereby killing cancer cells. This acid is isolated, and a 1.550 g sample of it is dissolved in 50.00 mL water for titration. After it is titrated to 75.00% completion with 90.23 mL of 0.1M sodium hydroxide solution, the pH of the solution is 1.960. The full titration curve is shown below:
a. What is the Ka of the acid?
b. If 1.550 grams of the unknown acid were titrated, then what is the molar mass of the acid?
c. What would be the pH at the equivalence point?
d. What would be an appropriate indicator for the equivalence point of this reaction?
30. This figure demonstrates the titration curves for two monoprotic acids:
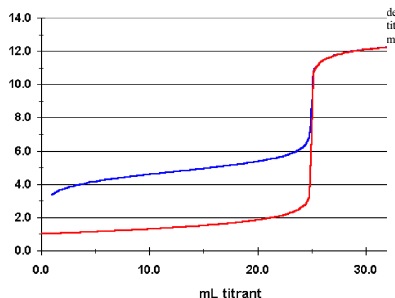
a. Which curve is that of a strong acid? What is the pH at the equivalence point?
b. Which curve is that of a weak acid? What is the pH at the equivalence point?
c. How do the concentrations of the two acids compare if 25.0 mL of each is titrated with the same concentration of a strong base?