Reference no: EM13551554
Question 1 : Conjoint analysis
Consider again the scenario from the previous assignment :
The coast of Brittany is a densly populated and highly touristic area, renowned for its beautiful wild shorelines. Sadly, in December 1999, the tanker Erika sank off the coast of Brittany, in France, creating an oil spill with major environmental impacts on the nearby shoreline.
Suppose that the government wants to evaluate their citizen's WTP for different levels of risk reduction and asks you for your advice as an environmental economist. Propose a conjoint analysis survey that would allow you to calculate the WTP for any level of risk reduction. Write at least 3 specific scenarios you would propose and the associated question you would ask. Describe one potential issue with this method.
Question 2 :
The multinational Khazad-dûm Inc. has purchased The Erebor Mining Company for 100 million gold coins. The Erebor Mining Company owns a single mine which is expected to generate the following net cashflows:
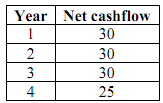
Assume that the mine closes at the end of the fourth year, and that nether mining company has to face any other kind of costs for the exploitation of the mine.
a) At the moment of the purchase, the interest rate on gold coins was 5%. Was this purchase a good deal for Khazad-dûm Inc.?
b) Shortly after the transaction, the interest rate increases to 7% for external reasons unrelated to the transaction. Does that affect your answer in (a)?
c) Based on your answer to questions (a) and (b), why might the managers of The Erebor Mining Company have accepted the offer of 100 million gold coins?
Question 3 :
An activity to improve the well-being of some impoverished people will provide benefits of $1 million right now, but it will obliterate the earth in 200 years. The world's value in 200 years is projected at $1012 (i.e. $1000 billion). There are no costs or benefits between these two dates.
(a) Is it worth avoiding the world's destruction in 200 years at a 10 percent discount rate?
(b) Is it worth avoiding the world's destruction in 200 years at a 6 percent discount rate?
(c) If 10 percent is the interest rate in the private sector, what are some of the arguments for using a 10 percent discount rate?
(d) What are some of the arguments for a lower discount rate?
(e) Do you think discounting and benefit-cost analysis are appropriate ways to handle this problem? Why or why not?
Question 4 :
Suppose that the benefits of cutting down the forest of Greenwood is $1 million now, but the environmental cost of that harvest is $10/year forever.
(a) The private market discount rate is 4 percent. On that basis, which options do you expect the government to choose?
(b) If the government has decided to use a discount rate of 0 percent for its environmental policies (no matter what the market rate is), would that change the government's decision?
(c) Which of these two approaches seems to make more sense in this case?
Question 5:
A policy maker decides that the government should build a dam across a river to protect downstream residents from costly floodings, even though the costs are greater than the benefits. Is the policy maker necessarily behaving irrationally? If not, why might the policy maker plan
the project?
Question 6:
Redwood National Park in northern California contains the tallest known redwood tree, as well as a remnant of the coastal redwood ecotype that once dominated coastal California. It does not receive many visitors: It has been estimated that no more than 5,000 visitors go each year, each spending an average of 3 days, for a total of 15,000 recreation visitor-days (RVDs) per year.
When Redwood National Park was acquired by the federal government from private timber companies (who intended to manage it for redwood lumber), it cost approximately $600 million.
(a) Assuming that the government will keep the national park forever, the initial cost can be converted into an annual cost by supposing that the government finances this purchase through the emission of a perpetuity with a present value of $600 million. What would then be the annual cost of Redwood National Park if the interest rate is 10%?
(b) What is the opportunity cost of the establishment of the park, in terms of use of the land?
(c) Why is it useful to calculate the annual cost of the park in this example? (Hint: we are about to compare benefits to costs.)
(d) What would the benefits per RVD have to be if recreational use were the only justification for Redwood National Park, and if the net present value of the park were to be nonnegative? If recreation were the only justification for the park, do you think that purchasing the park is likely to have been a good decision from a cost-benefit analysis perspective?
(e) What other justifications might exist for establishing Redwood National Park?
(f) There are approximately 100 million households in the United States. How high would average annual household willingness to pay for Redwood National Park have to be to justify the purchase?
Question 7
What type of decision-maker would use benefit-cost analysis as a decision rule? That is, identify a decision-maker whose only interest is the total net benefits to society of an activity, not the distribution of those benefits. If you identify one (or more), explain why distribution is not important to them. If you cannot identify one, discuss whether a benefit-cost analysis might nevertheless be useful.
Question 8 : Discounting for climate change
In class we have seen that two important figures in the economics of climate change, Nicholas Stern and William Nordhaus, have very different views of the appropriate discount rate to use
when calculating the present value of future climate change damage. Suppose that climate change was to be adressed by implementing a global uniform Pigouvian tax (i.e. an optimally chosen tax which is the same in all countries). Which, of Stern and Nordhaus, would recommend the higher level for the tax? Explain with a graph.
Question 9 : International environmental agreements
a) What determines whether an international environmental agreement is needed to address a given pollution problem, or whether action by individual governments is sufficient?
b) In the case of pollutants for which an international environmental agreement is needed, does the agreement necessarily lead to the optimal outcome? Justify you answer by providing an economic model that supports it. Make sure to explain the main assumptions, features and results of the model.
Question 10 : International environmental agreements
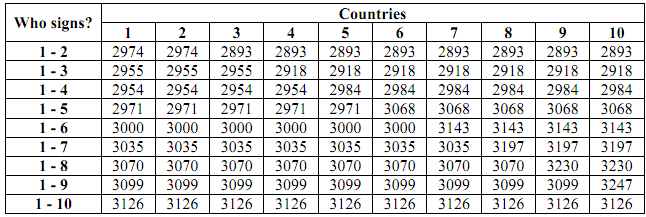
A group of 10 countries facing a common transboundary pollution problem decides to negotiate an agreement to address this issue. The table below gives the net benefit each country would get if the countries which sign the agreement are those indicated in the first column.
According to the model of self-enforcing agreements that we have seen in class, how many countries would choose to sign the agreement in this situation? Explain how you obtained that result : why do they decide to sign, and why do some other countries (if any) decide to stay out?