Reference no: EM133199359
Assignment:
1. Economics is BEST defined as the study of how:
A) resources are apportioned by a benevolent government.
B) people make constrained decisions.
C) to classify resources used to produce final goods and services.
D) technology can be used to change scarce resources into free resources.
2. Microeconomics is concerned with issues such as:
A) interest rates.
B) which job to take.
C) unemployment.
D) inflation.
3. If you were not studying economics, you could be doing one of the following: sleeping in (which you value at $5), playing cards with your friends (which you value at $10), or working (you would have earned an extra $8). The opportunity cost of studying economics is therefore:
A) $23.
B) $10.
C) $8.
D) $5.
4. Which of the following is NOT an economic factor of production?
A) labor
B) land
C) money
D) entrepreneurial ability
5. In economics, the term "land" includes:
A) mostly agricultural land.
B) all natural resources.
C) resources found on Earth's surface.
D) natural resources excluding water resources.
6. In economics, capital refers to:
A) funds used by businesses to acquire goods and services.
B) the process of raising money in the stock market.
C) actual manufactured products used in the production process.
D) anything that adds to human capital.
Use the following to answer question 4:
Bananas Apples
A 12 2
B 9 4
C 5 6
D 0 8
7. (Table) Given the production possibilities schedule shown in the table, what is the opportunity cost of moving from C to B?
A) 2 bananas
B) 3 bananas
C) 2 apples
D) 4 apples
Use the following to answer question 8:
Figure: Bread and Honey
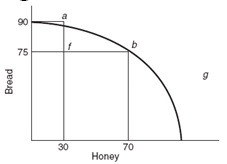
8. (Figure: Bread and Honey) In the graph, a movement from point f to point g could occur if:
A) technological improvements occur.
B) unemployed workers find jobs.
C) people decide they prefer bread to honey.
D) people decide they prefer honey to bread.
Use the following to answer question 9:
9. (Table) In the table, if society wants to increase production of HDTVs from 2,000 to 3,000 the opportunity cost of doing so will be:
A) 500 iPads.
B) 1,500 iPads.
C) 1,000 iPads.
D) 2,000 iPads.
10. Which of the following is a positive microeconomic statement?
A) Imports last year were nearly 2 trillion dollars.
B) Pharmaceutical companies should offer drugs at a lower price to seniors and low income households.
C) The government should only use monetary policy to prevent recessions.
D) Because of the higher minimum wage, Wendy's and other fast food chains have started using self-serve kiosks.
7. We would expect the cross price elasticity of Pepsi and Coke to be:
a. Positive, indicating normal goods
b. Negative, indicating inferior goods
c. Positive, indicating substitute goods
d. Negative, indicating substitute goods
8. If the income elasticity of women's purses is 1.5, then a 5% reduction in income will cause
a. A 1.5% reduction in quantity demanded of purses
b. A 1.5% increase in quantity demanded of purses
c. A 15% decrease in quantity demanded of purses
d. A 10% increase in quantity demanded of purses
e. A 7.5% decrease in quantity demanded of purses
9. All of the following would increase the elasticity of a good (make it more elastic), except
a. An increase in the availability of substitutes
b. An increase in the amount of time to make the decision
c. A broader definition of the market
d. If the good became more of a luxury than a necessity
10. Suppose you work for an advertising firm. Your boss suggests that by lowering the price of print ads by 3%, you could increase total revenues. However, after the reduction in price, total revenues actually fell. What might you infer about the price elasticity of demand for print ads?
a. Demand is inelastic
b. Demand is elastic
c. Demand is unitary elastic
d. None of the above
11. Suppose that Bob's weekly income went from $500 to $450 due to the recession and his purchases of frozen pizzas went from 3 a week to 4 a week. We can conclude
a. Frozen pizzas are a normal good
b. Frozen pizzas are an inferior good
c. Frozen pizzas are a luxury
d. None of the above
12. Suppose the price of local cable TV service has increased from $16.20 to $19.80 and as a result, the number of cable subscribers decreased from 224,000 to 176,000. Price elasticity of demand is:
a. -0.8
b. -1.2
c. -1.6
d. - 8
13. As summer approaches, the local supermarket notices that as the price of fresh corn falls from $0.67 an ear to $0.25 an ear of corn, the quantities sold of canned corn fall from 150 to 75 cans per week. What is the cross price elasticity?
a. 0.46
b. 0.73
c. 1.37
d. 2.28
14. The first Pepsi provides Craig 18 utils and second yields him an additional 12 utils. If his total utility from 3 Pepsis is 38 utils, what is the marginal utility of the third Pepsi?
a. 26 utils
b. 6 utils
c. 8 utils
d. 38 utils
15. Mrs. Green is spending all of her income by buying bottles of soda and bags of pretzels such that the last bottle provides 60 utils and the marginal utility of the last bag is 30 utils. The prices of soda and pretzels are $0.60 per bottle and $0.40 per bag of pretzels. It can be concluded that
a. The two commodities are substitutes.
b. Mrs. Green should spend more on pretzels and less on soda.
c. Mrs. Green should spend more on soda and less on pretzels.
d. Mrs. Green is buying soda and pretzels in the utility-maximizing amounts.
Answer the following question on the basis of the two schedules below.
|
Units of J
|
MU (J)
|
Units of K
|
MU (K)
|
|
1
|
56
|
1
|
32
|
|
2
|
48
|
2
|
28
|
|
3
|
32
|
3
|
24
|
|
4
|
24
|
4
|
20
|
|
5
|
20
|
5
|
12
|
|
6
|
16
|
6
|
10
|
|
7
|
12
|
7
|
8
|
16. Refer to the data above. If the consumer has income of $52 and the prices of J and K are $8 and $4 respectively, the consumer will maximize their utility by purchasing:
a. 2 units of J and 7 units of K
b. 5 units of J and 5 units of K
c. 4 units of J and 5 units of K
d. 6 units of J and 3 units of K
17. The marginal utility of the last unit of A consumed is 12 and the marginal utility of the last unit of B consumed is 8. What set of prices for A and B respectively would be consistent with consumer equilibrium?
a. $4 and $6
b. $6 and $4
c. $8 and $12
d. $16 and $9
19. Which of the following is likely to be a fixed cost?
a. Shipping costs
b. Rent on property
c. Wages
d. Expenditures on raw materials
|
# of workers
|
Output
|
|
0
|
0
|
|
1
|
40
|
|
2
|
90
|
|
3
|
126
|
|
4
|
150
|
|
5
|
165
|
|
6
|
180
|
20. Refer to data above. Diminishing marginal returns become evident with the addition of the:
a. Sixth worker
b. Fourth worker
c. Third worker
d. Second worker
|
Output (Q)
|
Total Cost
|
|
0
|
24
|
|
1
|
33
|
|
2
|
41
|
|
3
|
48
|
|
4
|
54
|
|
5
|
61
|
|
6
|
69
|
21. Refer to data above. The average fixed cost of producing 3 units of output is:
a. $8.00
b. $7.40
c. $5.50
d. $6.00
22. Refer to data above. The marginal cost of the sixth unit is:
a. $24
b. $12
c. $16
d. $8
23. In the short run the Sure-Screen T-Shirt Company is producing 500 units of output. Its average variable costs are $2.00 and its average fixed costs are $0.50. The firm's total costs are:
a. $2.50
b. $1250
c. $750
d. $1100
24. Suppose that when producing 10 units of output, a firm's AVC = $22, its AFC = $5, and its MC = $30. We can conclude that the:
a. ATC = $35
b. ATC = $57
c. TC = $30
d. TC = $270
25. If the marginal cost curve is above the average cost curve, what can we conclude?
a. Total costs must be falling.
b. Average variable costs must be falling.
c. Average fixed costs must be rising.
d. Average variable costs must be rising.
e. Both a and b are correct.
SHORT ANSWER: Make sure to show all of your work in the space provided. If you need more room, please see your instructor for additional paper.
1. Draw a typical MP curve and a typical MC curve (on 2 separate graphs) and explain how they are related. On the MP curve, identify regions of increasing, diminishing and negative returns.
2. Your boss at Johnson's Sports Shop has just come to you and asked if he should raise the price of canoes in an attempt to generate more revenue. To correctly answer her, you collect the following data on recent sales. In April when the price of a canoe was $350, you sold 12 canoes. In May when the price of a canoe was $375, you sold 10 canoes. Calculate the price elasticity of demand and report what advice (about changing the price) you would give to your boss. If the boss decides to raise the price by 5%, calculate the percentage change in total revenues.
3. Assume that Joe is a college student who has $25 a week to allocate for soda pop or potato chips. If soda pop costs $2.50 a pack and chips cost $2.00 a bag, draw the specific budget constraint for Joe. Show what would happen to Joe's budget constraint if the price of chips increased to $2.50 a bag. On a new graph, start with the original budget constraint and show what would happen instead if Joe's income fell to $20.
4. Clearly describe four characteristics that affect elasticity of demand. Which would be expected to be more elastic, demand for red delicious apples or demand for all apples?
5. Suppose that the government imposes a tax on the production of wine. Using a completely labeled market model, show what would happen in the wine market. Make sure to report the impact on equilibrium price and quantity. Then, in a separate market model, show and explain what would happen to the beer market if some people think wine and beer are substitutes. Report what happens to the equilibrium price and quantity of beer as well.
6. Given the following information about a firm's costs, complete the following chart.
|
Q
|
TC
|
TFC
|
TVC
|
ATC
|
AFC
|
AVC
|
MC
|
|
0
|
|
|
|
|
|
--
|
|
|
25
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.00
|
|
|
50
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.00
|
|
75
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.00
|
|
|
100
|
|
|
|
|
12.00
|
7.00
|
|
|
125
|
1950
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
150
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.00
|
|
|
175
|
|
|
1400
|
|
|
|
|
|
200
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.00
|
|