Reference no: EM131302504
Codin Theory Assignment
Problem 1 - Let k ≥ 32 be a positive integer, and let n = 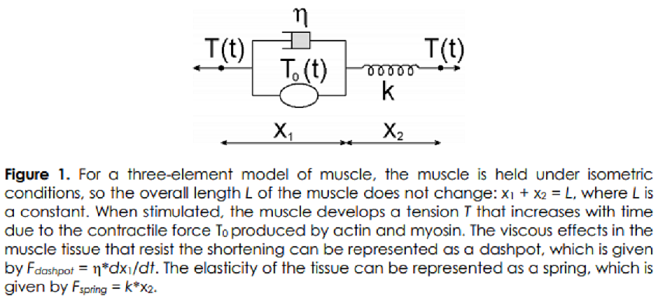 . Consider the k x n binary matrix G whose columns are all the
. Consider the k x n binary matrix G whose columns are all the  binary vectors of length k and hamming weight 3. Let C be the (n, k, d) binary linear code generated by G. What is the minimum distance d of C? Prove your answer.
binary vectors of length k and hamming weight 3. Let C be the (n, k, d) binary linear code generated by G. What is the minimum distance d of C? Prove your answer.
Hint: Let x ∈ C be the sum of some s rows of G. Consider the weight of x as a function of s.
Problem 2 - In this problem, we use the term perfect code to refer specifically to an (n, M, d) binary code (either linear or nonlinear) with n = 2m - 1, M = 2n-m and d = 3, for an integer m ≥ 3. An extended perfect code C is a code of length n + 1 = 2m obtained from a perfect code C of length n by appending an extra coordinate, so that the weight of all the codewords in C* is even.
a. Let C ⊂ Fn2 be a perfect code. Prove that there exists a partition C0, C1, . . . , Cn of Fn2 into perfect codes, where C0 = C and Ci = ai + C is a translate of C for I = 1, 2, . . . , n.
b. Let En+12 be the set of all even weight vectors in Fn+12. Show that, given an extended perfect code C* ⊂ En+12, there exists a partition C*0, C*1, . . . , C*n of En+12 into translates of C*, with C*0 = C*.
c. Let C0, C1, . . . , Cn and C*0, C*1, . . . , C*n be partitions of Fn2 and En+12 as in parts (a) and (b) above. Let π be an arbitrary permutation on the set {0, 1, . . . , n}, and let (a|b) ∈ F2n+12 denote the concatenation of a ∈ Fn+12and b ∈ Fn2. Prove that the code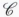 defined below is perfect:
defined below is perfect:
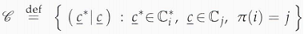
d. Use the construction in part (c) to show that, for all m ≥ 4, there exist nonlinear perfect codes of length n = 2m - 1.
e. Prove that there are at most 2m2^n-m distinct perfect codes of length n = 2m - 1. Here, codes C and C' are considered distinct if the set of codewords of C differs from the set of codewords of C'.
Problem 3 - The decay function D from Fnq to Fn-1q is defined as follows. Each vector x = (x1, x2, . . . , xn) in Fnq is mapped by D into the vector:
D(x) = (x2 - x1, x3 - x2, . . . , xn - xn-1)
The lifespan of a vector x ∈ Fnq is defined as the smallest integer i such that Di(x) = 0; that is, applying the decay function D to x successively i times results in the all-zero vector of length n - i. If no such i exists, then the lifespan of x is defined to be n. The lifespan of the vector 0 is zero, by convention.
a. Prove that if x1 is a vector of length n and lifespan i, and x2 is vector of length n and lifespan j, with j < i, then x1 + x2 is a vector with lifespan i. That is
lifespan (x1 + x2) = max{lifespan(x1), lifespan(x2)}
b. Suppose it is known that the lifespans of the k vectors x1, x2, . . . , xk ∈Fnq are all distinct. Prove that these k vectors are linearly independent over Fq.
c. Let α be a primitive element of Fq, and let x1 and x2 be two vectors of lifespan i in Fnq. Prove that there exists an integer j ∈ {0, 1, . . . , q - 2} such that lifespan (x1 + αjx2) < i.
d. Given a linear code C of length n and dimension k over Fq, let Li denote the number of codewords of lifespan i in C. The integers L1, L2, . . . , Ln are called the lifespan distribution of C. Prove that the lifespan distribution of any such code C contains exactly k nonzero values.
e. Define the cyclic decay function D' from Fnq to Fnq as follows. Each vector x = (x1, x2, . . . , xn) in Fnq is mapped by D' into the vector:
D'(x) = (x2 - x1, x3 - x2, . . . , Xn - Xn-1, x1 - xn)
The lifespan with respect to this function is defined as before. Namely, cyclic-lifespan (x) is the smallest integer i such that applying the cyclic decay function D' to x successively i times results in the all-zero vector of length n. In this part, assume that n is a power of 2 and q = 2. How many binary vectors of length n and cyclic lifespan i are there, for each i = 0, 1, . . . , n?
Problem 4 - In this problem, we deal with three different finite fields: the ground field GF(q), its extension GF(qm) of degree m, and the extension of GF(qm) of degree n, namely the finite field GF(qmn). Throughout this problem, assume that n divides q - 1.
a. Prove that the polynomial xn - 1 has n distinct roots in GF(q).
b. Prove that for any finite extension GF(qm) of GF(q), there exists a primitive element β ∈ GF(qm) such that {β, βq, βq^2, . . . , βq^m-1} is a basis for GF(qm) over GF(q).
c. Now let γ be a primitive element of GF(qmn) such that {γ, γq, γq^2, . . . , γq^nm-1} is a basis for GF(qmn) over GF(q). You have proved in part (b) that such an element exists. You have also proved in part (a) that all the n distinct roots of the polynomial xn - 1 lie in in GF(q). Let us denote these roots by e1, e2, e3, . . . , en. Define n elements α1, α2, . . . , αn ∈ GF(qmn) as follows:
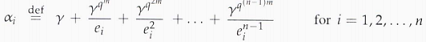
Prove that the elements (α1)n, (α2)n, . . . , (αn)n lie in the subfield GF(qm). That is, show that (αi)nq^m = (αi)n for all i = 1, 2, . . . , n.
Hint: First show that this holds for n = 2, with q odd and e1 = 1, e2 = -1.
d. Prove that the elements in the set
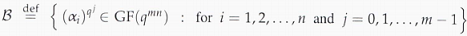
are linearly independent over GF(q). Therefore, conclude that the set B is a basis for GF(qmn) as an mn-dimensional vector space over GF(q).
Problem 5 - Let C be a binary linear cyclic code of length n with zeros at {αz1, αz2, . . . , αzr}, where α ∈ GF(2m) is a primitive n-th root of unity. That is C = (g(x)), where deg g(x) = r and the r roots of g(x) are precisely αz1, αz2, . . . , αzr. For any subset I = {i1, i2, . . . , iμ} of {0, 1, . . . , n-1} define the code
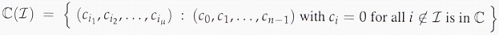
In other words, C(I) is the code obtained from C by shortening C at all the positions that are not in I. Throughout this problem, assume that n = n1n2 is an odd composite integer.
a. Write down a parity-check matrix for C(I).
b. Let β ∈ GF(2m_1) be a primitive n1-th root of unity, where m1 is the least integer such that n1 divides 2m_1 - 1. Prove that β ∈ GF(2m), where m is the least integer such that n divides 2m - 1.
c. For I = {0, n2, 2n2, . . . , (n1 - 1)n2}, show that C(I) is a cyclic code and find the set of zeros of C(I) in terms of {z1, z2, . . . , zr} and β. In particular, if C is a narrow-sense BCH code of length n1n2 = 31.3 = 93 with designed distance 11, express the zeros of C and C(I) as unions of cyclotomic cosets modulo 93 and 31, respectively. What is the dimension of C(I)?
d. Now let C be a BCH code with zeros at α0, α1, . . . , αδ-1 and their conjugates. Let I1, I2 be such that {αi: i ∈ I2} = {αa + αi: i ∈ I1} for some fixed a. Show that C(I2) = C(I1).
Problem 6 - Throughout this problem, let BCH(n, q; δ) denote a narrow-sense BCH code of length n with designed distance δ over the finite field GF(q). Further, assume throughout that n and q are relatively prime, and let m denote the least integer such that n divides qm - 1.
a. Let C be a linear cyclic code of length n over GF(q), and let Z denote the set of zeros of C. That is C = (g(x)), and Z is the set of exponents of all the zeros of g(x). Prove that C contains its dual code C⊥ if and only if Z ∩ Z-1 = Φ, where Z-1 =def {-z mod n: z ∈ Z}.
b. In this part, assume that n = q - 1. Show that BCH(n, q; δ)⊥ ⊆ BCH(n, q; δ) if and only if δ ≤ (n+1)/2, where BCH(n, q; δ) ⊥ denotes the dual code of BCH(n, q; δ).
c. Prove that if δ ≥ q√n, then BCH(n, q; δ)⊥ ? BCH(n, q; δ).
Hint: Express the length n in base q, namely write n = n0 + n1q + · · · + nsqs for some s.
d. Now let us consider binary BCH codes only. Suppose that n > 2⌈m/2⌉ and δ ≤ n2⌈m/2⌉/(2m - 1). Show that under these conditions, we have
dim BCH(n, 2; δ) = n - m ⌈(δ-1)/2⌉.