Reference no: EM131026239
Quiz 3-
1. You are given the following information about an economy.
Y = C + I
Y = F(K, L)
The aggregate production function for this economy exhibits constant returns to scale and the marginal products of labor and capital are both subject to diminishing returns.
s = saving rate (assume this is constant) per year
δ= depreciation rate (assume this is a constant) per year
y = Y/L
k = K/L
k* = steady state of capital per worker (K/L)
You are also told that sf(k) < δk.
a. What is sf(k)?
b. What is δk?
c. Interpret the meaning of sf(k) < δk?
d. Draw a graph illustrating both sf(k), δk, and k*. Indicate on your graph where sf(k) < δk. Be sure to label your graph completely.
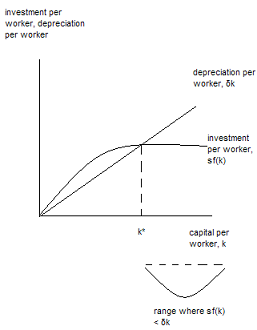
e. Using the Solow Growth Model discussed in class, explain what happens in this economy when sf(k) < δk.
2. You are given the following aggregate production function for an economy:
Y = 10K1/2L1/2
You are also told that K equals 400 units of capital and L equals 625 units of labor. In addition, the money supply equals 10,000 and the velocity of money is constant and equal to 1.
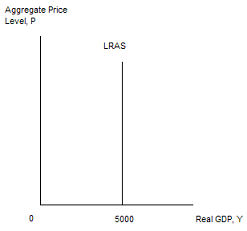
a. What is an equation for the long-run aggregate supply curve (LRAS) for this economy?
b. Draw a graph depicting this long-run aggregate supply curve with real GDP. Y, on the horizontal axis and the aggregate price level, P, on the vertical axis. Label your graph thoroughly.
c. Using the given information, fill in the missing values in the table below which describe points lying on this economy's aggregate demand curve.
d. What is the long-run equilibrium aggregate price level for this economy?
3. The U.S. unemployment rate is currently.
|
Determine the joint probability function of y1 and y2
: Let Y1 denote the number of married executives and Y2 denote the number of never-married executives among the three selected for promotion. Assuming that the three are randomly selected from the nine available, find the joint probability function ..
|
|
Present value of a perpetuity
: What is the present value of a $900 perpetuity if the interest rate is 3%? Round your answer to the nearest cent. If interest rates doubled to 6%, what would its present value be? Round your answer to the nearest cent.
|
|
What would be the total return of the bond in percentage
: A 7.7 percent coupon bond with 15 years left to maturity is priced to offer a 6.35 percent yield to maturity. You believe that in one year, the yield to maturity will be 7.0 percent. What would be the total return of the bond in dollars? What would b..
|
|
Determine the present value of the bonds cash flows
: The Garcia Company’s bonds have a face value of $1,000, will mature in 10 years, and carry a coupon rate of 16 percent. Assume interest payments are made semiannually. a. Determine the present value of the bond’s cash flows if the required rate of re..
|
|
What is the long-run equilibrium aggregate price level
: You are also told that K equals 400 units of capital and L equals 625 units of labor. In addition, the money supply equals 10,000 and the velocity of money is constant and equal to 1. What is the long-run equilibrium aggregate price level for this..
|
|
Capital gains-the tax effect of this transaction
: A corporation is selling an existing asset for $21,000. The asset, when purchased, cost $10,000, was being depreciated under MACRS using a five-year recovery period, and has been depreciated for four full years. If the assumed tax rate is 40 percent ..
|
|
Find the joint probability function for y1 and y2
: Contracts for two construction jobs are randomly assigned to one or more of three firms, A, B, and C. Let Y1 denote the number of contracts assigned to firm A and Y2 the number of contracts assigned to firm B. Recall that each firm can receive 0, ..
|
|
What is the future value of his investment cash flows
: Chuck Brown will receive from his investment cash flows of $3,155, $3,500, and $3,840 at the end of years 1, 2 and 3 respectively. If he can earn 7.5 percent on any investment that he makes, what is the future value of his investment cash flows at th..
|
|
Treasury inflation-protected security with a par value
: Compute the annual interest payments and principal amount for a Treasury Inflation-Protected Security with a par value of $1,000 and a 3-percent interest rate if inflation is 4 percent in year 1, 5 percent in year 2, and 6 percent in year 3.
|