Reference no: EM132047916
Assignment -
Question 1 - Suppose you are studying protein denaturation by the fluorescence emission of a Trp residue of the protein. You obtained a fluorescence spectrum of the protein at 20oC and another at 65oC, and you know that the protein is folded at 20oC and unfolded (denatured) at 65oC. Note that the spectrum of the unfolded protein is red-shifted. Then you recorded a fluorescence spectrum of this protein at 45oC. The three spectra, all normalized to the fluorescence of the highest value recorded, are shown below. The spectrum in gray (45oC) appears intermediate between those at 20oC and 65oC.
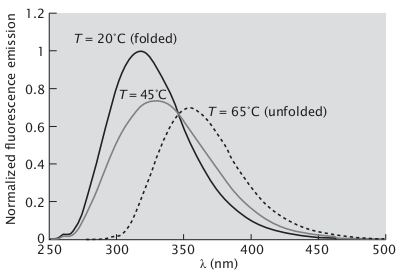
What is the fraction of folded protein at 45oC?
Question 2 - Suppose you are following the denaturation of protein A, but now you measure its circular dichroism (CD) spectrum as you increase the temperature. This protein, when folded, is entirely α - helical; when unfolded, it loses all structure (random). The graph below shows the CD spectrum of protein A at a certain temperature T (dashed line) together with the characteristic spectra for an α-helix (solid) and a random coil (dotted). What percent of the proteins are denatured at this temperature?
Question 3 - If ammonium sulfate ((NH4)2SO4) increases the Gibbs energy of the native state (which it does), why doesn't it denature proteins? As the Gibbs energy of the native state increases, it should become higher than that of the denatured state. Why doesn't this happen? What is wrong with this argument?
Question 4 - Why is it easier to convert a β-sheet into an α-helix than the other way around?
Question 5 - A protein has two conformations, A and B, that exist in equilibrium. It binds a ligand X, but only in conformation B.
(a) Draw the diagram for this case.
(b) Write the partition function.
(c) Write the isotherm for binding of X.
Question 6 - Table shows ligand binding data for three different proteins. Determine which binding isotherm is best to analyze each set of data, and calculate the dissociation constants. You have to figure out how many sites are needed in each case and which model to use.
|
Table - Binding isotherms for three proteins (L1, L2, and L3)
|
|
Concentration
|
Fractional occupancy (θ)
|
|
(μM)
|
L1
|
L2
|
L3
|
|
0.041
|
0.023
|
0.133
|
0.001
|
|
0.050
|
0.028
|
0.153
|
0.001
|
|
0.061
|
0.034
|
0.172
|
0.002
|
|
0.074
|
0.040
|
0.207
|
0.002
|
|
0.091
|
0.050
|
0.225
|
0.003
|
|
0.111
|
0.061
|
0.265
|
0.005
|
|
0.135
|
0.070
|
0.291
|
0.007
|
|
0.165
|
0.087
|
0.329
|
0.010
|
|
0.202
|
0.106
|
0.341
|
0.016
|
|
0.247
|
0.125
|
0.397
|
0.023
|
|
0.301
|
0.151
|
0.423
|
0.032
|
|
0.368
|
0.178
|
0.460
|
0.046
|
|
0.449
|
0.219
|
0.468
|
0.067
|
|
0.549
|
0.234
|
0.507
|
0.095
|
|
0.670
|
0.271
|
0.536
|
0.130
|
|
0.819
|
0.331
|
0.612
|
0.191
|
|
1.000
|
0.365
|
0.626
|
0.261
|
|
1.221
|
0.415
|
0.650
|
0.338
|
|
1.492
|
0.483
|
0.707
|
0.417
|
|
1.822
|
0.513
|
0.712
|
0.547
|
|
2.226
|
0.589
|
0.753
|
0.652
|
|
2.718
|
0.638
|
0.822
|
0.685
|
|
3.320
|
0.678
|
0.794
|
0.775
|
|
4.055
|
0.709
|
0.843
|
0.846
|
|
4.953
|
0.749
|
0.840
|
0.861
|
|
6.050
|
0.789
|
0.867
|
0.905
|
|
7.389
|
0.798
|
0.885
|
0.983
|
|
9.025
|
0.849
|
0.914
|
1.000
|
Question 7 - You collected the data in Table for the binding of a ligand to a protein. There is only one binding site on each protein. The data represent the fluorescence intensity (in arbitrary units) of the protein at 340 nm as a function of total ligand concentration [X]T (in μM). The total protein concentration is [P]T = 4 μM. Use these data and the subtraction method to determine Kd as outlined in the text. Note that before you do any calculations, you need to plot the data and convert the fluorescence intensity data to fractional binding (θ). Hint: The total amplitude of the change in the y-axis must correspond to the range of θ, from ≈ 0 to ≈ 1.
|
Table - Fluorescence intensity data for the binding of a ligand X to a protein P, with [P]T = 4 μM
|
|
[X]T(μM)
|
Fluorescence
|
|
0.0
|
100
|
|
0.11
|
117
|
|
0.30
|
140
|
|
0.55
|
169
|
|
0.82
|
192
|
|
1.00
|
209
|
|
1.22
|
233
|
|
1.49
|
267
|
|
1.82
|
296
|
|
2.23
|
318
|
|
2.72
|
373
|
|
2.32
|
416
|
|
4.06
|
457
|
|
4.95
|
510
|
|
6.05
|
549
|
|
7.39
|
558
|
|
9.03
|
583
|
|
11.0
|
599
|
|
13.5
|
617
|
|
16.5
|
635
|
|
20.9
|
633
|
|
24.5
|
652
|
|
30.0
|
653
|
Question 8 - We considered thermal unfolding of lysozyme at pH 7. We calculated ΔGuo for unfolding at 25oC, as well as the corresponding equilibrium constant. That is an apparent equilibrium constant for unfolding (Kuapp). The apparent constant is what you actually measure if you do an experiment at 25oC and pH 7. It is called apparent because it depends on pH. Here we revisit this problem to consider the effect of pH.
(a) One of the active site residues of lysozyme is Glu-35. In the denatured (unfolded) state, pKa = 4.3, which is normal for the Glu side chain. But in the native state, its value is anomalously high, pKa ≈ 6.5. What does this suggest about the local environment of Glu-35 in the native state?
(b) If the pKa of Glu-35 were the only anomalous one in the protein, it would indicate that lysozyme releases protons upon unfolding at pH 7,
Lysozyme-Glu-35-H (folded) ⇔ Lysozyme-Glu-35- (unfolded) + H+.
Assuming that there are no other anomalous pKa's in lysozyme, what does Le Chatelier's principle tell you about the effect of lowering the pH on the unfolding equilibrium of this enzyme?
(c) Under these assumptions, make a quantitative prediction of the effect of pH on lysozyme stability, by calculating the apparent equilibrium constant and ΔGou at pH 5 and 25oC. You will need to write the partition function for the protein, including the ionization effects of Glu-35. Begin by drawing a diagram that includes unfolding and protonation of the folded and unfolded states explicitly. You know Kuapp (25oC) at pH 7. Calculate it at pH 5. Think about your result. (Note that at pH 5 there is not much of an effect on stability arising from the ionization of groups with normal pKa values, so the effect should arise only from Glu-35.)
Question 9 - In the absence of oxygen, hemoglobin behaves as a two-state system. Write its partition function. If the protein were 99.0% in the T state at room temperature, what would be the Gibbs energy difference between the T and R states?
Question 10 - Derive the binding isotherm for the alternative cooperative model whose partition function is given by Equation 6.91. Plot the binding isotherm. Use K= 5 x 104M-1 and α = 100. Choose a ligand concentration range that allows you to see the full binding isotherm (until θ ≈ 1), but in such a way that the inflection point corresponds to a ligand concentration at ≈ 1/5 of the range.
Question 11 - The red blood cell contains millimolar concentrations of 2, 3-bisphosphoglycerate (BPG). Regulation of the concentration of BPG in the erythrocyte is the most important component of the high-altitude adaptation mechanism. The normal BPG concentration is 5 mM at sea level. But when a person moves to high altitude, this concentration increases to ≈ 8 mM. In the complete absence of BPG, the affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen is actually too high, and the protein would not release sufficient oxygen in the tissues.
Question 12 - In DHFR, the rate of hydride transfer depends on pH. At very low pH khyd ≈ 950 s-1. The pH dependence arises because protonation of the active site, with pKa = 6.5, must take place for hydride transfer to occur. Derive the pH dependence of khyd. Use it to calculate khyd at pH = 5, 7, 8.5, and 10.
Question 13 - You have isolated an unknown enzyme D and determined that one of its substrates is pyrophosphate (PPi). Then you performed a series of experiments to better understand the interaction of PPi with enzyme D.
You performed the same experiment at several other concentrations of PPi. The apparent (observed) rate constants (kapp) obtained are listed in Table. Complete the table with the kapp determined in (b) for 0.20 mM PPi. Then plot kapp as a function of [PPi]. Determine the on-rate (k1) and the off-rate (k_1) constants. Calculate the equilibrium dissociation constant Kd from these data.
|
Table - Apparent rate constant for binding of pyrophosphate (PPi) to enzyme D as a function of [PPi]a
|
|
[PPi] (mM)
|
Kapp (s-1)
|
|
0.20
|
-
|
|
0.40
|
116
|
|
0.60
|
132
|
|
0.80
|
161
|
|
1.00
|
172
|
|
1.20
|
187
|
Textbook - Proteins: Concepts in Biochemistry By Paulo Almeida.