Reference no: EM13154653
1. Suppose the market for melons can be described by the graph below. Show all work in your answers.
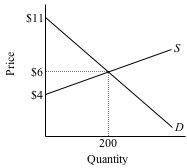
a. If Jon's maximum willingness to pay for a melon is $8, how much surplus per unit is he receiving at the market price of $6?
b. Suppose Figgy Farms requires at least $5 per melon before they will sell in this market. What is Figgy's producer surplus per unit in this market?
c. How much total consumer surplus is received in this market?
d. How much total producer surplus is received in this market?
e. What is the combined surplus in the market?
2. Suppose a competitive firm's cost information is as shown in the table below. Show all work in your answers.
|
Output
|
Marginal Cost
|
Average Variable Cost
|
Average Total Cost
|
|
0
|
|
|
|
|
1
|
$ 8.00
|
$ 8.00
|
$ 17.00
|
|
2
|
7.00
|
7.50
|
12.00
|
|
3
|
6.00
|
7.00
|
10.00
|
|
4
|
5.00
|
6.50
|
8.75
|
|
5
|
6.00
|
6.40
|
8.20
|
|
6
|
7.00
|
6.50
|
8.00
|
|
7
|
8.00
|
6.71
|
8.00
|
|
8
|
9.00
|
7.00
|
8.13
|
|
9
|
10.00
|
7.33
|
8.33
|
|
10
|
11.00
|
7.70
|
8.60
|
a. Suppose the firm sells its output for $9.10. What is the firm's marginal revenue (MR)? Explain.
b. Compare MR to marginal cost (MC) to determine the firm's profit maximizing (loss-minimizing) output level. Be sure to check whether or not the firm should shut down. Show all work & explain your answers well.
c. What is the firm's per-unit profit (loss) and total profit (loss) at this output level? Show all your work.
d. Repeat parts a. through c. assuming the price has fallen to $7.10.
e. Repeat again assuming the price has fallen to $6.10.
f. At what price does the firm earn a normal profit? Explain.
g. At what price must this firm shut down? Explain.
3. A competitive firm's short-run cost information is shown in the table below. Show all work in your answers.
|
Output
|
Marginal Cost
|
Average Variable Cost
|
Average Total Cost
|
|
0
|
|
|
|
|
1
|
$ 8.00
|
$ 8.00
|
$ 17.00
|
|
2
|
7.00
|
7.50
|
12.00
|
|
3
|
6.00
|
7.00
|
10.00
|
|
4
|
5.00
|
6.50
|
8.75
|
|
5
|
6.00
|
6.40
|
8.20
|
|
6
|
7.00
|
6.50
|
8.00
|
|
7
|
8.00
|
6.71
|
8.00
|
|
8
|
9.00
|
7.00
|
8.13
|
|
9
|
10.00
|
7.33
|
8.33
|
|
10
|
11.00
|
7.70
|
8.60
|
a. If the market price is $5.25, how much will this firm produce? Enter in the second column of the table below. Repeat for the remaining prices shown in the table.
b. Fill in the next column to determine the market supply in this industry, assuming there are 2000 identical firms in the industry. Further suppose that the market demand schedule for this industry is given by the last column in the table.
|
Price
|
Quantity Supplied, This Firm
|
Quantity Supplied, 2000 Firms
|
Quantity Demanded
|
|
$ 5.25
|
|
|
20,000
|
|
$ 6.25
|
|
|
18,000
|
|
$ 7.25
|
|
|
16,000
|
|
$ 8.25
|
|
|
14,000
|
|
$ 9.25
|
|
|
12,000
|
|
$ 10.25
|
|
|
10,000
|
c. What is the equilibrium quantity in this market?
d. What is the equilibrium price in this market?
e. What are the resulting output, revenue, cost, and profit of the typical firm?
4. Indicate whether each of the following statements is true or false, and explain why. If a statement is false or true, do not simply give a corrected statement -- you must provide a full explanation as to why that statement is correct or not.
a. Consumer surplus is the difference between the minimum and maximum price a consumer is wiling to pay for a good.
b. Producer surplus is the difference between the actual price a producer receives for a product and the minimum price the producer would have been willing to accept for the product.
c. For Good A, supply elasticity is +2.5 and price elasticity of demand is -1.5. If an excise tax is imposed on Good A, sellers will pay the more of this tax than buyers.
d. A perfectly competitive firm can maximize its economic profit or minimize its losses only by adjusting its output.
e. If a perfectly competitive firm is producing output less than its profit-maximizing output, marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost.
5. Suppose at present firms in a perfectly competitive market are earning negative economic profits (losses). Explain the process by which this industry will reach long-run equilibrium. What will happen to the output produced by the average firm and the prices charged? Why? What will happen to profit? Some graphs to illustrate your answers may be very useful
|
What mass of nahco3 would be required
: A 2.5L bottle of concentrated sulfuric acid H2SO4 (16M) falls and breaks on the floor. What mass of NaHCO3 would be required to neutralize this acid spill through the following reaction HCO3 + H => H2O +CO2
|
|
Credit cards increase the demand for money
: The introduction of a stylish line of Toyotas makes some consumers prefer foreign cars over domestic cars. d. The central bank doubles the money supply. e. New regulations restricting the use of credit cards increase the demand for money.
|
|
Computing expected new net income
: As a result, they estimate that gross profit will increase by $43,208 and operating expenses by $71,922. Compute the expected new net income.
|
|
Explain how the following events would affect the demand
: Explain how the following events would affect the demand for labor. A new education program administered by the company increases labor's marginal product.
|
|
What is the firms per-unit profit
: What is the equilibrium quantity in this market and what is the equilibrium price in this market and what are the resulting output, revenue, cost, and profit of the typical firm?
|
|
Balance-related audit objectives
: Explain the difference between thetwo specific related balance-related audit objectives:
|
|
Find test statistic for test that between two mu is zero
: For the constant sound group: 1, 10, 1, 10, 1, 9, 7, 3. And for the no sound group: 4, 3, 6, 4, 5, 8, 4, 9. A. Assume that the standard deviations are equal and find the test statistic for the test that the between mu1 and mu2 is zero.
|
|
Explain enzymes in the human liver
: Enzymes in the human liver catalyze a large number of reactions that degrade ingested toxic chemicals. By what factor is the rate of a detoxification reaction changed
|
|
Find the herfindahl index for an industry composed
: Find the Herfindahl index for an industry composed of (a) three firms- one with 70 percent of the market, and the other tow with 20 and 10 percent of the market
|