Reference no: EM13799163
Experiment: Rotational Dynamics
Part 1: TORQUE
Close a door by pushing on the doorknob. Close the door again using approximately the same force but applying it 5 centimeters away from the hinges. Try again by applying the force on the edge of the door in a direction pointing toward the hinges. Summarize and explain your observations. Comment on the difference between force and torque.
Part 2: CONSERVATION OF ANGULAR MOMENTUM
Newton's second law could be stated either as F→ = ma→ or as force equals time rate of change of linear momentum. For simple rotational motion the corresponding law is stated as τ→ = Iα→ or torque equals time rate of change of angular momentum. Momentum is conserved when there is no external force. Angular momentum is conserved when there is no external torque.
To test this, sit on a rotating stool with your hands in by your sides. While rotating, extend your arms away from your body. Repeat while holding masses in your hands. Describe the effects. Give an explanation.
Part 3: SHAPE AND MOMENT OF INERTIA
A heavy mass in free fall does not fall faster than a light mass. The extra weight is compensated for by extra resistance. A heavy mass on a frictionless plane does not slide down faster than a light mass. A heavy ring and a light ring both roll down an inclined plane with the same speed. What about a ring and a disk? Try this with combinations of rings and disks of different masses. Describe the results and give an explanation. It may be helpful to write down an energy equation for the case of 2 rings of different radii and different masses. Also try the energy equation for a ring and a disk of the same radius and mass.
Part 4: CONSERVATION OF ANGULAR MOMENTUM (AGAIN)
This demonstration is more complicated because it involves a vector. For a rotating wheel, thedirection of the angular momentum, L→, is found by curving the fingers of your right hand in the direction of the rotation, your thumb then points along L→. The angular momentum vector is perpendicular to the plane of the wheel.
Sit on the rotating stool used in part II. Hold a bicycle wheel with its axis vertical. While the stool is at rest, have your partner spin the bicycle wheel. Carefully note the direction of spin of the wheel and of the stool. Give an explanation in terms of conservation of angular momentum. While the stool is still rotating, carefully turn the bicycle wheel upside down. Explain what happens.
Part 5: PRECESSION OF A SPINNING TOP (GROUP DEMONSTRATION)
This is an interesting phenomenon, and a very difficult one to explain. Both torque and angular momentum must be treated as vectors. Torque causes angular momentum to change according to the following equation:
ΔL→ = τ→Δt
To use this equation the direction of a torque vector must be defined. Follow the moment arm with the fingers of your right hand. Then turn your fingers to follow the force. As you do this, your thumb will point in the direction of the torque vector.
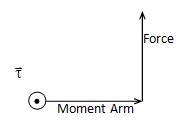
A bicycle wheel will be set up so that it can be suspended from a rope as it spins. What is the direction of the torque vector for the accompanying diagram?
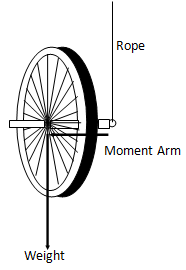
Set the bicycle wheel spinning so that when viewed from the left in the diagram, it is spinning counterclockwise. Release the wheel. What happens? Show the direction of the angular momentum vector.
At the head of the angular momentum vector, draw a short vector in the correct direction to represent the change in angular momentum, ΔL→, in a short period of time, Dt. Apply the rule for vector addition and draw a vector to represent the new angular momentum, Lnew→, which is the sum of the original angular momentum, L→, and the change in angular momentum, ΔL→ . How does this change in angular momentum explain the continuous precession of the wheel? Repeat the experiment with the wheel spinning clockwise. Draw diagrams similar to those above and explain what you observe.
This experiment is qualitative. You won't be taking any quantitative measurements. However, you can use equations to help explain each of the physical phenomena going on. Type a full discussion for each part explaining in detail what you have observed and how this relates to the physical concepts.