Reference no: EM13278008
1. In the figure below, q1 = -2e, q2 = +2e, q3 = +4e, and q4 = +2e, where e is the elementary charge. Charge q4 is located at the origin, while q2 and q3 are each a distance d2 = d3 = (2d)/3 from the origin. Charge 1 is a distance d1 = d from the origin. The dashed line connecting charge 1 and charge 4 makes an angle θ1 with respect to the negative x direction. Our goal is to find the net electric force on charge q4.
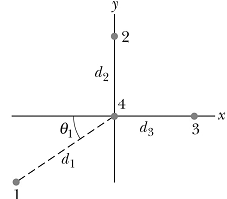
a. Let F41 be the force that q1 exerts on q4, �F42�� be the force that q2 exerts on q4, and F43 ��be the force that q3 exerts on q4. Draw vectors on the figure above that indicate the direction of each of these three forces (i.e. draw a free body diagram).
Remember to label each vector.
b. Determine � �F41 ��, �and �F42, F43��,�� in unit vector notation. Put your answers in terms of d, θ1, and physical constants.
c. Determine the net force ��exerted on q4 in unit vector notation. Put your answer in terms of d, θ1, and physical constants.
d. Determine the magnitude of F4. Put your answer in terms of d, θ1, and physical constants.
2. In the figure below, a non-conducting rod has a length L and a charge -q uniformly distributed along its length. Point P is a distance a from the right edge of the rod. Our goal in this problem is to find the electric field (both magnitude and direction) at point P. Assume that positive x is to the right.
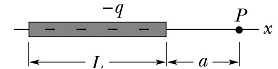
a. What is the direction of the electric field at point P?
b. Determine the linear charge density. Put your answer in terms of q, L, a, and physical constants.
c. Determine the electric field �� due to a differential element of width dx, that is located a distance x from the left side of the rod. In other words, x = 0 at the left side of the rod. Put your answer in terms of q, L, a, x, dx, and physical constants.
d. Integrate to determine the net electric field at point P due to the entire rod. Put your answer in terms of q, L, a, and physical constants.
e. What is the electric field at point P if a is much larger than L? Let a → ∞ and determine the electric field using your answer from part d. Put your answer in terms of q, a, and physical constants. What type of charge distribution does the rod behave like when a is much larger than L?
|
Formulate a linear optimization model and solve this problem
: MSA Computer Corporation manufactures two models of minicomputers, the Alpha 4 and Beta 5. The firm employs 5 technicians, working 160 hours each per month, on its assembly line.
|
|
Explain neutral acidic or basic
: Identify the following salts as neutral acidic or basic: 1. LiNO3 2. SrBr2 3. LiF 4. KCN 5. NH4ClO4 6. NH4Br 7. NH4CN Please include why are they neutral basic or acidic.
|
|
Find what is the value of vo across the capacitor
: A circuit consists of a voltage source (Vin = 10 V at 75o phase shift, ω = 10 rad/s) in series with a parallel RL combination (R = 10 Ω, L = 0.5 H), which is in series with a capacitor (C=0.05 F). What is the value of Vo(t) across the capacitor
|
|
What is the length of the race
: A tortoise can run with a speed of 14.0 cm/s, and a hare can run 20 times as fast. In a race, What is the length of the race
|
|
What is the direction of the electric field
: What is the direction of the electric field at point P and determine the linear charge density. Put your answer in terms of q, L, a, and physical constants.
|
|
Determine refractive index of the active ingaas layer
: Graded-index separate confinement double heterostructure (GRIN-SCH) InGaAs/GaAs lasers with various cavity lengths were tested in the lab. The 100m wide oxide strip lasers consists of two pairs of 10nm In0.2Ga0.8As quantum-well (QW).
|
|
Determine the average speed of the athlete
: An athlete completed a marathon in 2 h, 39 min, 41 s. Determine the average speed (in miles per hour) of the athlete.
|
|
Determine the average speed for the trip
: A person travels by car from one city to another with different constant speeds between pairs of cities. Determine the average speed for the trip
|
|
Calculate the rotor power loss and the input current
: IN a 2-pole, 208 V (line-to-line, rms), 60-Hz, motor, Rs= 0.5Ω and R'r = 0.45Ω, Xls= 0.6Ω, and X'tr = 0.83Ω. The magnetizing reactance Xm = 28.5Ω. This motor is supplied by its rated voltages. The rated torque is developed at teh slip s = 0.04.
|