Reference no: EM131022706
First Midterm Exam - II
I. Binary Choice Questions:
Refer to the following information for the following two questions.
Blefuscu and Lilliput are two countries that produce shoes and watches. Both countries have linear PPFs and each country has 80 hours of labor available to use in the production of these two goods. The following table tells you how many hours of labor are needed in each country to produce one pair of shoes or one watch.
|
|
Hours of Labor Needed to Produce One Pair of Shoes
|
Hours of Labor Needed to Produce One Watch
|
|
Blefuscu
|
5 hours of labor
|
2 hours of labor
|
|
Lilliput
|
4 hours of labor
|
8 hours of labor
|
1) Which country has an absolute advantage in the production of shoes?
a) Blefuscu
b) Lilliput
2) Which country has a comparative advantage in the production of shoes?
a) Blefuscu
b) Lilliput
3) Suppose that the country of Duloc produces only mushrooms and pumpkins. Furthermore suppose that the opportunity cost of producing 1 mushroom in Duloc is constant and equal to 2 pumpkins. Suppose the citizens of Duloc wanted to specialize in producing pumpkins and trading these pumpkins for mushrooms produced by another country. Which of the following statements must be true?
a) The price of 1 mushroom must be below 2 pumpkins.
b) The price of 1 mushroom must be above 2 pumpkins.
4) Assume the price of books is initially $10. First the price rises by 10%. Then the price decreases by 20% from its new price. What is the percent change from the original price to the final price? The final price
a) Decreases by 12% relative to the initial price.
b) Decreases by 9% relative to the initial price.
5) Emoryton is a city that produces only Bicycles and Macbooks. The graph below depicts Emoryton's production possibility frontier for these two goods. Comparing point A and point B, we know that the opportunity cost of producing bicycles at point B is ________ at point A.
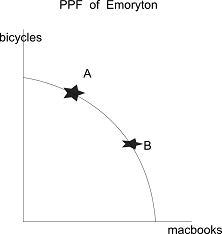
a) less than
b) greater than
6) For this country's PPF, going from curve R to curve W is most likely caused by
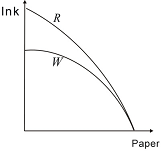
a) An increase in technology
b) A decrease in technology
7) In order for a price control to create a shortage in the market, what must be true?
a) The government sets a price ceiling at a price below the equilibrium price in the market.
b) The government sets a price floor at a price above the equilibrium price in the market.
8) Evaluate whether the following statement is positive or normative: "Relative to California, Wisconsin has an absolute advantage in producing cheese."
a) Positive
b) Normative
9) Suppose that there is an increase in population in Zeppo while at the same time the cost of sugar, a major ingredient, in hot chocolate decreases. Holding everything else constant, what do you know about the new equilibrium quantity and price of hot chocolate in Zeppo?
a) The equilibrium quantity of hot chocolate increases while the equilibrium price of hot chocolate may increase, decrease, or remain at its initial level.
b) The equilibrium quantity of hot chocolate may increase, decrease, or remain at its initial level while the equilibrium price of hot chocolate increases.
10) Consider the market for footballs which is initially in equilibrium. Which of the following scenarios will result in the equilibrium price and quantity of footballs increasing?
a) The price of basketballs (a substitute) increases.
b) The government implements an excise tax on the producers of footballs.
II. Multiple Choice Questions:
Refer to the following information for the following two questions.
11) Line A goes through points (x,y) = (3,8) and (x,y) = (2,10). Line B has an X-intercept of 1 and a slope of 1. Where do the two lines intersect?
a) (x, y) = (4,5)
b) (x, y) = (6,3)
c) (x, y) = (3,6)
d) (x, y) = (5,4)
12) Suppose that for every Y value, line A shifts to the right by 3 units. At the same time Line B shifts upward by 6 units. Where will these two lines intersect now?
a) (x, y) = (5,10)
b) (x, y) = (5,-2)
c) (x, y) = (1,6)
d) (x, y) = (9,2)
Refer to the following information for the following three questions.
There are two countries, Kreplakistan and Petoria, which produce bags and wallets using only labor. Both countries have linear PPF's. You are given the following information about the amount of labor that is needed in each country to produce bags and wallets.
|
|
Hours of Labor Needed to Produce One Bag
|
Hours of Labor Needed to Produce One Wallet
|
|
Kreplakistan
|
3 hours of labor
|
2 hour of labor
|
|
Petoria
|
5 hours of labor
|
2 hours of labor
|
You are also given the following information about the current level of production of wallets and radios. Both countries are currently producing at an efficient level.
|
|
Current Level of Bag Production
|
Current Level of Wallet Production
|
|
Kreplakistan
|
20
|
15
|
|
Petoria
|
10
|
25
|
13) Which of the following production combinations is an efficient output for Kreplakistan?
a) 21 bags and 16 wallets
b) 22 bags and 12 wallets
c) 22 bags and 16 wallets
d) 21 bags and 12 wallets
14) Kreplakistan's opportunity cost of 1 wallet is _______ bags and Petoria's opportunity cost of 1 wallet is ______ bags.
a) 1/2, 1
b) 3/2, 2/5
c) 2/3, 2/5
d) 3/2, 5/2
15) Which of the following would be an acceptable trading range of prices for one bag?
a) Between 2/5 and 2/3 wallets
b) Between 3/2 and 5/2 wallets
c) Between 2/3 and 5/2 wallets
d) Between 2/3 and 3/2 wallets
Refer to the following information for the following four questions.
For the fish market in Japan, demand is defined by the equation: Qd = 150 - 3P and supply is defined by the equation: Qs = 2P - 50 where Q is quantity of fish and P is the price per unit of fish.
16) Suppose the fish market is in equilibrium. What is the value of consumer surplus in this market?
a) $400
b) $600
c) $700
d) $150
17) Suppose a price floor of $45 per unit of fish is implemented in this market. Given this price floor which of the following statements is true?
a) There will be a shortage of 40 units of fish.
b) There will be a shortage of 25 units of fish.
c) There will be a surplus of 40 units of fish.
d) There will be a surplus of 25 units of fish.
18) For this question, the price floor above is no longer in place. Now suppose that the government decides to charge fish producers a tax of $5 per unit of fish produced. (This is an excise tax.) Given this tax, calculate the value of the deadweight loss that occurs in this market because of the imposition of the tax.
a) $6
b) $12
c) $16
d) $15
19) Given the excise tax described in the last question, the net price received by sellers (that is, the price they receive after paying the tax to the government) in the fish market is _____ and the total tax revenue collected by the government is ______.
a) $40, $160
b) $37, $120
c) $42, $160
d) $42, $120
20) Suppose a country is capable of producing 102 radios and 68 beds. Which of the following outputs MUST be attainable?
a) 103 radios and 4 beds
b) 101 radios and 68 beds
c) 12 radios and 69 beds
d) 100 radios and 70 beds
21) Which of the followings will not cause inefficiency?
a) A price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price.
b) A minimum wage is set above the equilibrium price.
c) A price floor is set above the equilibrium price.
d) The government places a limit on the production of the good where the upper limit is greater than the equilibrium quantity in this market.
22) Which of the following statements is true?
I. An effective price floor results in a surplus of the good.
II. An effective tariff will increase domestic producer surplus relative to the level of domestic producer surplus in this market with free trade.
III. An effective quota limiting the amount of the good imported into an economy will increase domestic consumer surplus relative to the level of domestic consumer surplus in this market with free trade.
IV. An effective tariff has no efficiency cost to the country imposing the tariff.
a) Statement I is true.
b) Statements I and II are true.
c) Statements I , II, III and IV are true.
d) Statements II and III are true.
Refer to the following information for the following three questions.
Cloth is measured in yards of cloth and butter is measured in pounds of butter.
23) Consider the joint PPF for these two countries. Which of the following points represents the kink for this joint PPF?
a) (180 yards of cloth, 500 pounds of butter)
b) (2500 yards of cloth, 500 pounds of butter)
c) (180 yards of cloth, 3600 pounds of butter)
d) (2500 yards of cloth, 3600 pounds of butter)
24) Which of the following points is feasible for Country A to produce?
a) (75 yards of cloth, 2500 pounds of butter)
b) (100 yards of cloth, 1700 pounds of butter)
c) (150 yards of cloth, 600 pounds of butter)
d) (55 yards of cloth, 2600 pounds of butter)
25) If Country A and Country B decided to trade with each other, then Country A would be a ______ for ______, and Country B would be a _______ for _________.
a) buyer, cloth; producer, butter
b) producer, cloth; producer, butter
c) producer, cloth; buyer, butter
d) buyer, cloth; buyer, butter
Refer to the following information for the following question.
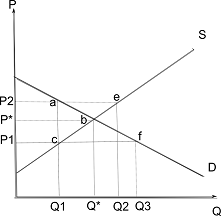
26) Originally the government implemented a price ceiling at P1 in the above market(i.e. the above graph). Subsequently, the government decided to eliminate the price ceiling and impose a price floor at P2. What is the change in producer surplus due to this policy reversal?
a) (P2-P1)(Q*)
b) (Q2-Q1)(P2)
c) (P*-P1)(Q1)
d) (P2 - P1)(Q1)
27) Suppose a small open economy imposes an effective tariff on the sale of an imported good. In this small economy the tariff will result in the price of the good __________ while the level of imports into the economy _____________. Simultaneously the overall domestic demand for the good will __________ while the overall domestic supply of the good will _____________.
a) increasing, decrease, increase, increase
b) increasing, increase, decrease, increase
c) increasing, decrease, decrease, increase
d) decreasing, decrease, increase, reduce
Refer to the following information for the following three questions:
The following are the domestic demand and domestic supply equations for a single good in a small open economy:
Domestic Demand: P = 20-Q
Domestic Supply: P = 4Q
Suppose the world price of the good is $10.
28) What is the value of total surplus in this market in the small open economy?
a) $12.50
b) $40.00
c) $50.00
d) $62.50
29) Suppose that this small open economy imposes a tariff of $2 on the good. What is the deadweight loss associated with this tariff?
a) $ 1.50
b) $ 3.00
c) $ 2.50
d) $ 5.00
30) In this small open economy, the imposition of this tariff results in domestic consumer surplus _____________ and domestic producer surplus ___________.
a) decreasing, increasing
b) decreasing, decreasing
c) increasing, increasing
d) increasing, decreasing