Reference no: EM13496241
1. Continuous improvement
a. Is used to reduce inventory levels.
b. Is applicable only in service businesses.
c. Rejects the notion of "good enough."
d. Is used to reduce ordering costs.
e. Is applicable only in manufacturing businesses.
2. A direct cost is one that is
a. Variable with respect to the cost object.
b. Traceable to the cost object.
c. Fixed with respect to the cost object.
d. Allocated to the cost object.
e. A period cost.
3. Costs that are incurred as part of the manufacturing process, but are not clearly traceable to the specific unit of product or batches of product, are called
a. Period costs.
b. Factory overhead.
c. Sunk costs.
d. Opportunity costs.
e. Fixed costs.
4. The three major cost components of manufacturing a product are
a. Direct materials, direct labor, and factory overhead.
b. Period costs, product costs, and sunk costs.
c. Indirect labor, indirect materials, and fixed expenses.
d. Variable costs, fixed costs, and period costs.
e. Opportunity costs, sunk costs, and direct costs.
5. A company reports the following for the current year.

Its cost of goods manufactured for the current year is
a. $1,500.
b. $1,700.
c. $7,500.
d. $2,800.
e. $4,700.
6. A company's predetermined overhead allocation rate is 150% of its direct labor costs. How much overhead is applied to a job that requires total direct labor costs of $30,000?
a. $15,000
b. $30,000
c. $45,000
d. $60,000
e. $75,000
7. A company's cost accounting system uses direct labor costs to apply overhead to goods in process and finished goods inventories. Its production costs for the period are: direct materials, $45,000; direct labor, $35,000; and overhead applied, $38,500. What is its predetermined overhead allocation rate?
a. 10%
b. 110%
c. 86%
d. 91%
e. 117%
8. A company's ending inventory of finished goods has a total cost of $10,000 and consists of 500 units. If the overhead applied to these goods is $4,000, and the predetermined overhead rate is 80% of direct labor costs, how much direct materials cost was incurred in producing these 500 units?
a. $10,000
b. $ 6,000
c. $ 4,000
d. $ 5,000
e. $ 1,000
f.
9. A company's Goods in Process Inventory T-account follows.
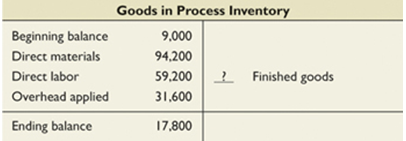
10. The cost of units transferred to Finished Goods inventory is
a. $193,000
b. $211,800
c. $185,000
d. $144,600
e. $176,200
11. At the end of its current year, a company learned that its overhead was underapplied by $1,500 and that this amount is not considered material. Based on this information, the company should
a. Close the $1,500 to Finished Goods Inventory.
b. Close the $1,500 to Cost of Goods Sold.
c. Carry the $1,500 to the next period.
d. Do nothing about the $1,500 because it is not material and it is likely that overhead will be overapplied by the same amount next year.
Carry the $1,500 to the Income Statement as "Other Expense."
12. Equivalent units of production are equal to
a. Physical units that were completed this period from all effort being applied to them.
b. The number of units introduced into the process this period.
c. The number of finished units actually completed this period.
d. The number of units that could have been started and completed given the cost incurred.
e. The number of units in the process at the end of the period.
13. Recording the cost of raw materials purchased for use in a process costing system includes a
a. Credit to Raw Materials Inventory.
b. Debit to Goods in Process Inventory.
c. Debit to Factory Overhead.
d. Credit to Factory Overhead.
e. Debit to Raw Materials Inventory.
14. The production department started the month with a beginning goods in process inventory of $20,000. During the month, it was assigned the following costs: direct materials, $152,000; direct labor, $45,000; overhead applied at the rate of 40% of direct labor cost. Inventory with a cost of $218,000 was transferred to finished goods. The ending balance of goods in process inventory is
a. $330,000.
b. $17,000.
c. $220,000.
d. $112,000.
e. $118,000.
15. A company's beginning work in process inventory consists of 10,000 units that are 20% complete with respect to direct labor costs. A total of 40,000 units are completed this period. There are 15,000 units in goods in process, one-third complete for direct labor, at period-end. The equivalent units of production (EUP) with respect to direct labor at period-end, assuming the weighted-average method, are
a. 45,000 EUP.
b. 40,000 EUP.
c. 5,000 EUP.
d. 37,000 EUP.
e. 43,000 EUP.
16. Assume the same information as in question 4. Also assume that beginning work in process had $6,000 in direct labor cost and that $84,000 in direct labor is added during this period. What is the cost per EUP for labor?
a. $0.50 per EUP
b. $1.87 per EUP
c. $2.00 per EUP
d. $2.10 per EUP
$2.25 per EUP