Reference no: EM131138399
1. The following figure shows a set of representative indifference curves for Alice over apples and oranges. Alice' preferences meet all the assumption of "typical" preferences.
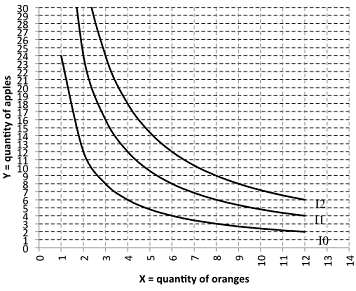
a. Suppose the price of an orange (PX) is $6 and the price of an apple (PY) is $2. If Alice' income is $48, graph her budget constraint and label it BC0.
b. An equation for Alice' budget constraint is:
c. Label Alice' optimal consumption point A. Under these conditions Alice will consume ______ oranges and ______ apples.
At point A, her marginal rate of substitution (MRS) will be ________ because (briefly explain how you know and what her MRS means):
2. Suppose that BEFORE THE TAX, the inverse demand for laptops is P=1200-Q while the inverse supply is P = Q.
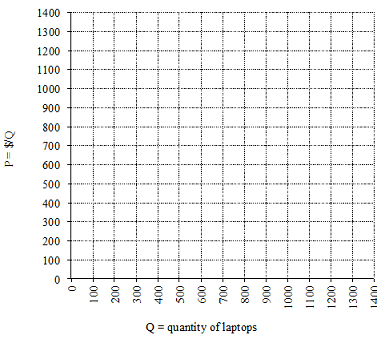
a. WITHOUT the tax:
i. Graph the supply (S0) and demand (D0).
ii. Algebraically or graphically, find the equilibrium price and quantity of laptops.
P*= ______ Q*= ________
iii. When the market is in equilibrium, what is the consumer surplus and producer surplus? Calculate it numerically.
iv. When the market is in equilibrium, what is the price elasticity of demand at (Q*, P*)? Calculate it numerically and interpret your calculation.
b. Now, suppose the government imposes a $400 per unit tax on suppliers of laptops. WITH the tax:
i. Write an equation for the new inverse supply (Stax).
ii. Algebraically or graphically, find the equilibrium price and quantity of laptops with the tax.
P'=______ Q'= _______
iii. When the market is in equilibrium with the tax, what is the government revenue? Calculate it numerically.
iv. Is there any deadweight loss from this per unit tax? If so, calculate it numerically and label it on the graph.
c. A local politician thinks the tax might be more popular if the $400 per unit tax were evenly divided between consumers and producers. That is, consumers would be statutorily responsible for a $200 tax and producers would be statutorily responsible for a $200 tax. Theoretically, how would this affect economic incidence?
3. Andrew spends all his income on DVDs and other things, Y. The following graph represents a set of his convex indifference curves (I) representing his preferences for DVDs and other things.
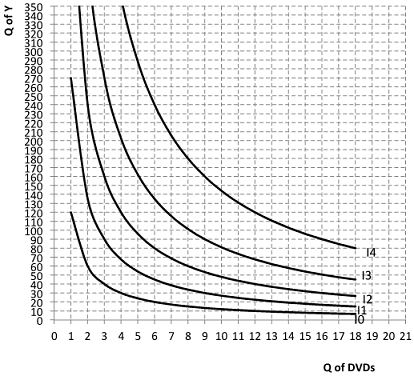
a. Andrew has an income of $360 to spend on DVDs and Y. If the price of DVDs, PD, is $20 and the price of Y, PY, is $2, draw Andrew's budget constraint (BC0) and label his optimal consumption point A.
b. If the price of DVDs, PD, increases to $60 and everything else stays the same, draw Andrew's new budget constraint (BC1) and label his new optimal consumption point C. If necessary, draw new indifference curves.
At point C, Andrew consumes ____ DVDs and ____Y.
c. On the graph, draw (as carefully as possible) Andrew's budget line (BC2) that reflects the substitution effect. Label this intermediate consumption point B. With the substitution effect ONLY: At point B, Andrew consumes ______DVDs and _____Y.
d. Does the substitution effect of the increase in the price of DVD make him buy more or less DVDs? How many more or less?
e. Can you tell whether DVDs are a normal or inferior good? Why or why not?
|
Bounded rationality and sub-optimization
: Explain the following decision making terms in your own words. Use examples, if necessary and make sure you read and respond to the postings of others. Bounded rationality. Sub-optimization. Expected value of perfect information.
|
|
What benefits of a comprehensive juvenile justice strategy
: What are the benefits of a comprehensive juvenile justice strategy? What aspects of a comprehensive strategy contribute to those benefits? What are the drawbacks to implementing a comprehensive juvenile justice?
|
|
Explain the basic principles of cash flow estimation
: Compute the relevant initial outlay in this capital budgeting decision - Should the company invest in this new equipment?
|
|
Compare intentional tort and negligence
: Compare Intentional Tort and Negligence. What is the relationship between Breach of Duty and Standard of Care? In Strict Liability cases, why does the Defendant try to convince the Court that it is a Negligence case and not a case of Strict Liabili..
|
|
What is the consumer surplus and producer surplus
: When the market is in equilibrium, what is the consumer surplus and producer surplus? Calculate it numerically. When the market is in equilibrium, what is the price elasticity of demand at (Q*, P*)? Calculate it numerically and interpret your calcu..
|
|
What provisions exist for the principle of due process
: Define the roles, responsibilities, and ethics of teachers, students and parents in the process of education, as found in the publication resources (teacher handbooks, student-parent handbooks and school board policy).
|
|
Simple moving average and weighted moving average
: Simple Moving Average (SMA), Weighted Moving Average (WMA) and Exponential Smoothing (ES) are three quantitative methods of forecasting. Compare and contrast the three techniques by identifying their relative advantages and disadvantages.
|
|
How much did income per person change
: Say that in 1964 a country had a labor force participation rate of 60% and by 2014 it fell to 50%. Also, assume that over this time labor productivity grew by 2% a year. How much did income per person change?
|
|
When a nation experiences economic growth
: When a nation experiences economic growth: - Economists generally believe that a country should specialize in the production of a good or service if:
|