Reference no: EM131311221
Part 1 Key Engineering Terms: fill in the blanks -
1. Phase: a _____________________________________ homogeneous and distinct portion of material system.
2. Degrees of freedom: number of variables that can be changed ___________________________________________ without changing phases of the system.
3. Eutectoid: a steel with ____________________________ percent C.
4. Austenite has ____________________________________ crystal structure and maximum carbon solubility of 2%.
5. Martensite: a ______________________________________ interstitial solid solution of carbon in __________________________________________ iron.
6. Tempering: the process of _____________________________________________ a quenched steel to increase its toughness and ductility.
7. Spherodite: a mixture of particles of _________________________ in α iron matrix.
8. Hardenability: the ease of forming _________________________________________ in a steel upon quenching from austenitic condition.
9. White cast irons: contains large amounts of _____________________________________ which make them hard and brittle.
10. Gray cast iron: contain large amount of _______________________________ flakes.
11. Ductile cast iron: contain large amount of carbon in form of ___________________________________________.
12. Malleable cast iron: __________________________________ is added to composition other than iron and carbon.
13. Intermetallics: ___________________________________ compounds of metallic
elements with high hardness and high temperature strength but brittle.
14. Shape memory alloys: metal alloys that recover previously defined shape when subjected to an appropriate _______________________________________.
15. Amorphous metal: metals with a ___________________________________ structure also called glassy metal.
16. Octahedral interstitial site: has coordination umber of ____________________________.
17. Tetrahedral site: has coordination number of _______________________________.
18. Ceramic materials: __________________________________ nonmetallic materials that consist of metallic and nonmetallic elements bonded together by ionic or covalent bonds.
19. Buckyball: is a soccer shaped molecule of _____________________________________ carbon atoms.
20. Firing: heating a ceramic material to high temperature to cause ______________________________________________ to form between particles.
21. Dry pressing: ______________________________________ uniaxial compaction and shaping of ceramic granular particles in a die.
22. Isostatic pressing: the simultaneous compaction and shaping of a ceramic powder by pressure applied ____________________________________ in all directions.
23. Sintering: the process in which fine particles of ceramic material become chemically bonded together at high temperature for _______________________________________ to occur between particles.
24. Vitrification: melting or formation of _______________________________________.
25. Refractory material: that can withstand the action of ___________________________________ environment.
26. Glass: a ceramic material made of _______________________________________ materials.
27. Glass transition temperature: a center of temperature range in which a ________________________________________________ solid changes from being glass brittle to being _________________________________________.
28. Porcelain enamel: a glass coating applied to _____________________________________ substrate.
Part 2 (Learning concepts/reflections/problems)
1. List the 2 material properties and 2 relevant application for following alloying elements in aluminum:
a. Copper
b. Silicon
c. Magnesium
d. Silicon + Copper
2. (a) Describe the 5 steps in the slip-casting process for ceramic products.
(b) What is tempered glass? How is it produced? Why is tempered glass considerably stronger in tension than annealed glass? What are some applications for tempered glass?
3. Identify the following phase diagram. Identify the 3 stages of age/precipitation hardening as shown in the figure below and explain the various phases and their features/properties/microstructure at these stages.
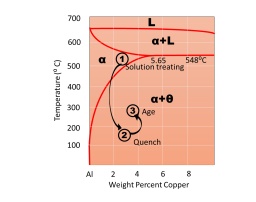
4. For the following types of ceramic materials explain material properties and one relevant application for each.
a. alumina
b. diamond
c. silica
d. silicon carbide
e. boron nitride
5. (a) Sketch the microstructure of pearlite, bainite and spherodite and explain key features.
Part 3 Materials Design Problems
1. (a) Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of using advanced ceramics in the structure of internal combustion engines.
(b) Propose some methods of overcoming the shortcomings of ceramics for this application.
2. Identify 2 properties and 2 relevant applications of following materials:
(1) Brass (2) Bronze
1. What are glass intermediate oxides? How do they affect the silica-glass network? Why are they added to silica glass?
2. Explain, from an atomic structure point of view, why metals can be plastically deformed to form large and complex shapes while complex ceramic parts cannot be manufactured by this technique.
Note: Please use extra sheets wherever necessary to answer the questions. All HW must be uploaded via D2L Dropbox system. Students are highly encouraged to refer textbook, notes and slides.