Reference no: EM131586202
Radiology Physics Assignment
Learning Outcomes -
1. Understand the principles and practices involved in X-ray radiography
1.1- Explain key terminology used in radiography and the types of radiographic equipment available
1.2- Explain the process of radiography, how radiation is detected and how radiographic images are produced and processed
1.3- Explain how X-ray techniques are used in diagnosis
1.4- Describe how a CT scan can produce coronal and sagittal images of the body in two or three dimensions
2. Understand the principles and practices involved in Ultrasonography and MRI
2.1- Assess the applicability, benefits and limitations of ultra-sound imaging techniques and discuss their use in diagnosis
2.2- State the general principles involved in MRI and explain the benefits and limitations of the technique
3. Understand the procedures used in radiology and patient care
3.1- State the hazards associated with radiation and explain concepts and methods of radiation protection
3.2- Calculate the effective radiation dose in a given case
3.3- Explain relevant health risks to a patient
3.4- Evaluate, for the patient and clinician, methods of:
- record keeping procedures
- medical exposure control
- radiation safety
- infection control
Part A -
1. What is radiography?
2. Describe what is happening within a particle when radioactive emissions alpha, beta and gamma are produced. Explain at least one medical practical application of each of these forms of radiation.
3. Give a detailed description of the general properties of X-rays that make them useful for medical imaging.
4. Here is a labelled diagram of an X-ray tube:
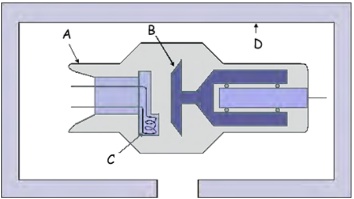
List the parts A-D and describe the function of each part in a table similar to the following:
|
Label
|
Named component
|
Function
|
|
A
|
|
|
|
B
|
|
|
|
C
|
|
|
|
D
|
|
|
5. Describe and explain each step in the process of taking an X-ray photograph; include all the details from when the patient arrives in the radiography department up to when an image is formed.
6. Describe the principle of CT scanning. Explain how coronal, sagittal and transverse images are produced.
Part B -
1. Explain why radiation is dangerous to humans, and explain the different effects on adults and foetuses.
2. Explain and evaluate the measures to protect patients and clinicians from radiation that are incorporated into the procedure for taking ordinary X-ray images.
3. Explain the additional health risks to a patient undergoing a CT scan as compared to an ordinary X-ray photograph.
4. What is the effective dose for an external source in a case where the absorbed dose is 860 J/kg and the radiation is in the form of beta particles, assuming an RBE value of 1.8.
NOTE: Completion notes:
Question 2: For this question you will need to look at:
- record keeping procedures
- medical exposure control
- radiation safety
- infection control
Question 4: show your workings out for the calculation.
Part C -
1. Explain the principle of ultrasound scanning by referring to the way ultrasound waves behave when performing a scan for possible kidney stones.
2. Calculate the fraction of reflected ultrasound energy when ultrasound waves cross from soft tissue into fat if the acoustic impedance for soft tissue is 1.60 x 106 kg m-2 s-1 and for fat has the value 1.40 x 106 kg m-2 s-1.
3. Calculate the diameter of a baby's head if there is a time delay of 96 microseconds between receiving pulses from either side of the skull, and the speed of ultrasound can be assumed to be 1250 m/s.
4. Explain the use of ultra-sonography to develop 3D images of the baby's tissue in a mother's womb.
5. Use the example above to discuss the applicability, benefits and limitations of ultra-sonography techniques. You will need to consider such issues as cost, safety and image quality.
NOTE: Completion notes:
Question 1: Details of how kidney stones can be destroyed by ultrasound are NOT required.
Questions 2 and 3: Show all your workings out for these questions. There are no word count limits for these questions.
Part D -
1. Describe and explain how an MRI scanner produces images. Discuss the effectiveness, benefits and limitations of using MRI compared to other imaging methods.
NOTE: Completion notes:
Make references to the behaviour of the atomic nuclei and the use of radio waves. When discussing the effectiveness, benefits and limitations of using MRI you should consider issues such as cost, safety and image quality and the importance of record-keeping procedures.
For higher grades, discuss the Larmor frequency for resonance induction. Make comparisons between at least two other imaging methods.
Indicative Content
Please note that the indicative content supplied below is intended as a suggested guide only. It is not meant to be a prescriptive, exhaustive or fully delivered content list.
Radiation
- the sub-atomic components of an atom.
- beta (p) and gamma (y) radiation decay equations using a periodic table
- the mechanism of gamma (y) rays indirect ionisation.
- characteristic radioactive decay curves and the "spin-spin" interaction.
- calculations of decay rates, values of half-lives and of half value thickness for absorption.
- the health hazards of using ionising radiation.
Use of X-rays
- labelling the structure of an x-ray tube.
- detecting and measuring radiation intensity via photographic film, via the ionising effect of radiation detected electronically and via scintillation caused by chemical fluorescence.
- suitable techniques of image processing for diagnostic and dosimetric evaluations.
- Comparing and contrasting the use of 2D tomography to computed 3D tomography.
- how the CT scan can produce corona! and sagittal images of the body.
- how CT scanning can be used in diagnosis.
Use of Ultra-sound
- sound waves and how they are reflected from an object.
- speed/time/distance calculations and acoustic impedance equations for ultrasound.
- the applicability, benefits and limitations of ultra-sonography techniques.
- the use of ultra-sonography to develop 3D images of baby tissue in a mother's womb.
Use of Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- how strong magnetic fields can be used to align atomic nuclei.
- how radio waves can be used to disturb the axis of rotation of aligned atomic nuclei.
- the Larmor frequency for resonance induction utilising the gyromagnetic process.
- how the radio frequency emission generated by disturbed nuclei returning to their baseline states can be collected and used to generate an image.
- the effectiveness, benefits and limitations of using MRI.
Safety and Procedures
- assessing the health implications of using ionising radiation.
- methods of radiation safety and infection control for both the patient and the clinician.
- calculating the effective radiation dose for a patient in a given case.
- the health risks to a patient from undergoing treatment such as a CT scan.
- evaluation of methods for record keeping and procedures used for safety precautions.