Reference no: EM131040600
Risk management and assessment of risk.
1. What is meant by the term 'risk management'?
2. What are the specific elements of a risk management course of action?
3. What is the aim for a risk analysis process?
4 . What are the three risk action options?
5. Why should all elements of a risk management process be documented?
6. When a task has been completed, why is it essential that the effectiveness of the course of action plan is reviewed?
7. State the definition of a 'hazard'.
8. State the definition of 'risk'.
9. How are hazards identified?
10. What are three of the suggested means for performing a specific hazard identification?
11. What is the purpose of a hazard identification process?
12. What are three possible non-electrical hazards?
13. What are two examples of a confined space?
14. What are three hazards to be aware of when carrying out maintenance or breakdown electrical work.
15. What is the 'hierarchy of control'?
16. What is an example of a PPE control?
Review Hazards, risk & Control Measures on Construction Sites.
17 List 4 important safety points for manual handling.
18. When using ladders at heights list 4 points that should be used
19. List suitable protection equipment against silica dust
20. List suitable protection equipment against gases or petrol engine fumes
21. What safety precautions need to be observed when using petrol or diesel motors in confined spaces or enclosed buildings?
Hazards associated with LV, ELV & High Currents.
22 Identify three reasons why it is necessary to break the electrical load of an installation into separate circuits?
Reference:
23. Using AS/NZ3000 as a reference, Determine the following load requirements:
How many 10A double socket outlets may be connected to a circuit wired in V75 2.5mm2 TPS cable with copper conductors installed partially surrounded by thermal insulation and protected by a 16A type C circuit breaker in a domestic installation.
Parts of electrical system & equipment that operate at LV& (ELV)
24 Using the AS3000, explain why Extra Low equipment is installed in Low Voltage Installations
Reference:
25. When can ELV be hazardous?
a. in a confined location with moisture or heat on the work area
b. when connected with a long extension lead
c. in excessive load conditions
d. when disconnecting the supply
26 W hich is the safest PELV or SELV ? and explain why this is so.
27 Electrical equipment needs a separate circuit if the current rating is higher than:
a) 5 Amps
b) 10 Amps
c) 20 Amps
d) 30 Amp
28. in a LV installation give 2 locations where would you expect to find high currents and indicate what precautions you would take in installation design and measurement.
29 ( a) Give an example of HV equipment in an electrical distribution system
b) give an example of equipment that operates at HV in a shopping center.
30 Electrical "creepage" is:
a. slow movement of electrons
b. imperceptible movement of a conductor
c. shortest path between two conductive parts
d. the movement of cables within an installation
31. Upon what factor will the magnitude of the fault current flowing to ground depend?
32. Define the term 'step potential'.
33. Define the term 'touch potential'.
34. Distinguish two kinds of hazardous contact.
35. Describe the term 'direct contact'.
36. Name two measures used to protect against the hazard of indirect contact.
37. List four exposed metal fittings that may require equipotential bonding.
38. What documentation is needed before work on, near or associated with high voltage is carried out?
39. What is the purpose of a switching schedule sheet?
40. State three procedures that the designated person should do before energising a high-voltage system.
41. What is the clearance of the exclusion zone for an instructed person near exposed parts of a high voltage system?
42 Describe two dangers a person may face from being in close proximity to an intense arc fault that has been caused by a short circuit at a high fault current level?
43. Define the term 'low-voltage'.
44. What is meant by the term 'creepage'?
45. Name the three categories of common electrical hazards
Q46 Prior to starting electrical testing of installations or equipment what precaution must always be carried out.
Q47 What are the control measures required before, while and after working on electrical installations, circuits or equipment (Reference:Qld COP Managing Electrical Risks 2013).
Q48 You are required to disconnect a 3 phase motor so it can be taken away for repairs.
List the isolation procedure!
Q49 Complete a Risk Assessment for the isolation of the 3 phase motor ,use the form on the PREVIOUS PAGE to AND the Risk Assessment at the start of this book-E137A as your guide.
Q50 What is the definition of live work.
Q51 In genera/normal circumstances is live work allowed.
Q52 What requirements must be met before carrying out for working live
Q53 List the Control measures for Live Work
54. Describe coherent light.
55. What is the outcome of collimating or focusing a specific wavelength of light?
56. What is laser classification based on?
57. In what units is the term 'accessible emission limit' measured?
58. Lasers used in a worksite must conform to Australian standards and should only be used if precautions are followed. What are these precautions?
59. Describe a serious hazard when working with fibre optics.
60. List 5 PPE items when welders or using a gas torch.
61. List the 3 main phases/stages of safe use of gas torches
62. List 3 OH&S hazards associated with welding.
64. What are the respective colours of the oxygen & acetylene cylinders?
65. list the closing down procedure for oxygen/acetylene.
Q66. List 3 precautions when using handling refrigerant.
67. List 4 hazards associated with refrigerant.
68. Where can asbestos be found in some premises?
69. What does biosoluble mean?
70. Why are the reinforcing glass fibres of some Type X switchboard panels hazardous?
71. State one method used to control emissions of silica dust.
72. Name one type of work activity that results in wood dust.
73. Where could an electrician be exposed to the legionella bacterium?
74. How can infection from bird droppings occur?
75. List the three recognised levels of risk and their likely consequence.
76. Use the COP Managing Electrical Risks 2013 to list the 5 recognised measures to eliminate or control risk.
77. list 4 occasions when the risk management processes should be reviewed through evaluation and improvement activities.
Appendix A:- Exams
Practice Exam --#1
1 Name the legislation and regulations governing workplace health and safety in your- jurisdiction.
2 What are codes of practice?
3 What is the purpose of health and safety regulation in the workplace?
4 Who is responsible for safety at work?
5 List the steps an employer should take to ensure a safe and healthy workplace.
6 Describe in order of importance, measures for controlling the risk from hazards in the workplace.
7 How is safety managed in the workplace?
8 List the ways in which are hazards identified.
9 Give an example of how the level of a risk is assessed.
10 What does risk level 'high' mean?
11 List the sorts of information given in a JSA or SWMS.
12 What precaution should an electrician take before entering an unfamiliar workplace?
13 Outline the purpose of OHS orientation and training
14 Name eight common industry hazards.
15 What are the responsibilities of a work supervisor?
16 List the activities in a task of electrical work, identify the associated hazards and risks and suggest measures for controlling the risks.
17 What is the most common cause of fatal electric shock?
18 List the precautions that should be taken before attempting to work on electrical wiring or equipment.
19 List three risk control measures that the operator of a portable power tool should observe.
20 Why are steel-capped shoes or boots a necessary safety control measure for electrical work?
21 Name two harmful substances encountered in electrical work and where they are used.
22 What is the main purpose of the Wiring Rules?
23 Name three hazards in an electrical installation.
24 What is an exposed conductive part?
25 Why is it important to ensure that the exposed conductive parts are electrically connected to the general mass of earth?
26 What is the hazard of a wrong polarity connection at an appliance?
27 Name one type of appliance that must not be earthed.
28 Mark the correct polarity of the single-phase three-pin and three-phase five-pin plugs viewed from the back.
29 How are earthing conductors identified?
30 In an electrical installation what is the increased hazard for people in areas that are damp or wet in normal use?
31 List the areas of electrical installations known as Damp situations covered by the Wiring Rules.
32 What is the primary hazard with electricity at any voltage?
33 List the possible consequences of an electric shock.
34 Describe the dangers of high current sources.
35 Describe what happens during an arc fault.
36 List some control measures for avoiding exposure to shock hazards.
37 What potentially fatal effects are caused by electric shock?
38 Describe the condition of the heart termed ventricular fibrillation
39 List factors that affect the impedance (resistance) of the human body to the passage of an electric current.
40 What precaution should a rescuer take first?
41 On witnessing an electric shock, what is the first thing you should do?
42 What precaution is needed when rescuing a shock situated above ground level?
43 List three methods for removing a victim from contact
44 Describe how to apply CPR.
45 What is the purpose of CPR?
Practice Exam #2
please complete the following exam.
1. Risk management is about establishing:
a. best practice
b. regulations
c. testing
d. IP ratings
2. The first element in a risk management course of action is:
a. risk recognition
b. determine the task environment
c. risk analysis
d. risk action
3. What element of a risk management process is critical?
a. action plan
b. forms
c. record keeping
d. promotion of principles and responsibilities
4. A hazard is defined as:
a. an occurrence
b. an injury
c. an illness
d. something that has the potential to cause harm
5. Risk means:
a. that harm will occur
b. a consequence might happen
c. potential of harm occurring
d. exposure to a hazard
6. A non-electrical hazard encountered by an electrician is:
a. the disconnection of final sub-circuits
b. lifting of heavy material
c. testing of circuits
d. installation design
7. Which of the following is an energy-isolating device?
a. limit switch
b. pushbutton
c. circuit breaker
d. photoelectric switch
8. Using numbers from 1 to 5 list the preferred order for the hierarchy of hazard control.
[ ] Administrative [ ] Substitution [ ] Engineering [ ] Elimination [ ] PPE
9. Low ac voltage is defined as:
a. voltage less than 12 V
b. voltage below 50 v but above 30 v
c. voltage between 12 V and 30 V
d. voltage exceeding 50 V but not above 1000 V
10. Electrical creepage is:
a. slow movement of electrons
b. imperceptible movement of a conductor
c. shortest path between two conductive parts
d. the movement of cables within an installation
11. state the three categories of electrical hazards.
a. electric shock, arcing and capacitive coupling
b. electric shock, arcing and toxic gases
c. arcing, toxic gases and live exposed conductors
d. toxic gases, electric shock and voltages on unused conductors
12. When can ELV be hazardous?
a. in a confined location with moisture or heat on the work area
b. when connected with a long extension lead
c. in excessive load conditions
d. when disconnecting the supply
13. Which laser class has a low risk to eyes and no risk to skin?
a. Class 1M
b. Class 2M
c. Class 3R
d. Class 4
14. A serious hazard with optical fibre is:
a. their slow deactivation times
b. metal hardware
c. the tiny shards of glass
d. their visible light output
15. What type of product that an electrician may encounter in a roof space is biosoluble?
a. rock wool
b. asbestos
c. silica dust
d. wood dust
16. Who is able to apply lockout and tagout devices?
a. any worker
b. a licensed electrician
c. only workers authorised through training and qualifications
d. the apprentice
17. What is meant by the term 'touch voltage zone'?
a. the work area
b. a zone near live terminals
c. a working area where it is safe to touch energised conductors
d. an area 2400 mm in height by 1000 mm in width where a prospective fault voltage may appear
1. The purpose of risk assessment is to identify: (tick the most correct answer)
a) persons who work in an unsafe manner
b) electrical hazards in the workplace only
c) non-electrical hazards in the workplace only
d) both electrical and non-electrical hazards in the workplace
2. When should a risk assessment be carried out? (tick the most correct answer)
a) After you have commenced work in an unfamiliar workplace
b) After an accident has occurred
c) Before starting work on a new and unfamiliar workplace
d) Before the ‘work-team' members arrive at the workplace
3. The third step in the five step risk management process is:
4. Describe one source of an electric shock that can be identified as a hazard when conducting a risk assessment
5. A risk is the possibility of something happening. It is measured in terms of:
(tick the most correct answer)
a) current and voltage
b) high and low voltage
c) consequences and likelihoods
d) hazards and risk assessment
e) none of the above
6. It is discovered that an accident was caused by the lack of training of an individual. This is an example of: (tick the most correct answer)
a) risk control
b) hazard identification
c) a high likelihood
d) an electrical fault.
e) none of the above
7. Describe two factors that can increase the risk of a hazard:
8. At what stage, in the risk assessment/risk management process can a ‘risk rating' be determined for a particular hazard? (tick the most correct answer)
a) Directly after the hazard has been identified
b) Before the control measures are discussed and decided upon
c) After the control measures have been implemented
d) After monitoring and reviewing the effectiveness of the control measures
9. When considering working on any electrical equipment, electrical article, and/or electrical conductors, the golden rule is to first: (tick the most correct answer)
a) test all exposed metal or conductors before you touch
b) carry out an insulation resistance test
c) carry out an earth continuity resistance test
d) to start carrying out repairs without testing the above items
10. An apprentice in his first six months of employment (unless he is certified to be a ‘competent assistant'), must not be allowed to be in close proximity to exposed live terminals of switchboards and live conductors. (tick the most correct answer)
a) True
b) False
11. If a short-circuit occurred in a low-voltage domestic circuit approximately 250 metres away from a supply transformer, would the prospective fault current flowing through the circuit be: (tick the most correct answer)
a) higher in value than if the fault occurred 10 metres from the source of supply i.e. the transformer
b) lower in value if the fault had occurred 10 metres from the source of supply, i.e. the transformer
c) the same value as if the fault occurred 10 metres from the source of supply, i.e. the transformer
d) no effect at all over any distance
12. A cable supplying a circuit for power circuits operates at: (tick the most correct answer)
a) ELV
b) LV
c) HV
d) EHV
13. An example value of alternating current ELV is: (tick the most correct answer)
a) 6000 Volts
b) 60 Volts
c) 600 Volts
d) 6 Volts
14. An example value of alternating current LV is: (tick the most correct answer)
a) 6000 Volts
b) 60 Volts
c) 60000 Volts
d) 6 Volts
15. An example value of alternating current HV is: (tick the most correct answer)
a) 6000 Volts
b) 60 Volts
c) 600 Volts
d) 6 Volts
Consider the diagram below in Figure 1 showing a typical transmission system.
16. What voltage range (ELV, LV, HV) would be found on Line C?
17. What voltage range (ELV, LV, HV) would be found on Line D?
18. Consider the diagram shown.
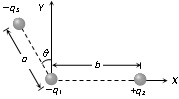
a) Mark on the diagram the where the greatest fault current would occur under fault conditions.
b) Give one example of an incident that could cause a high fault current to flow at the point you have identified.
19. Provide one example of an item of electrical equipment, in a domestic installation, which operates a ELV.
20. Explain what is meant by the term ‘touch voltage' in relationship to high-voltage circuits:
21. Explain what is meant by the term ‘induced voltage' in relationship to high-voltage circuits:
22. Explain what is meant by ‘creepage' in relationship to high-voltage circuits:
23. Describe two control measures for dealing with potential hazards associated with high-voltage circuits:
24. Describe two control measures for dealing with potential hazards associated with working with optical fibres:
25. What are the steps to safe isolation and disconnection? (tick the most correct answer)
a) Inform client, locate and isolate at CB, attach danger tag, test tester, check that supply is off, disconnect equipment, terminate wiring in an enclosure.
b) Find the fuse/CB, test check, disconnect equipment, attach danger tag, test tester, terminate wiring in an enclosure.
c) Inform client, test tester, disconnect equipment, terminate the wires.
d) Pull the fuse/CB, hang danger tag, test tester, disconnect, terminate the wires.
26. What are the steps to safely reconnecting equipment? (tick the most correct answer)
a) Test cables are isolated, connect cables, turn on supply, test polarity, test equipment operation.
b) Test cables are isolated, test tester, check insulation resistance connect cables, check earth continuity, remove danger tag, turn on supply, test polarity, test equipment operation.
c) Test cables are isolated, connect cables, check insulation resistance and earth continuity, turn on supply, test polarity, test equipment operation.
d) Connect cables, turn on supply, test equipment.
27. Describe two control measures when working live of LV electrical equipment:
28. "Personal Danger tags" are used by: (tick the most correct answer)
a) electrical workers only.
b) tradespeople working on electrical equipment only.
c) Occupational Health & Safety representatives only.
d) Any type of worker working on any equipment.
e) none of the above
29. Out of service tags can be correctly used to: (tick the most correct answer)
a) prevent equipment from being used excessively.
b) identify non-electrical equipment to be worked on.
c) replace "personal danger tags".
d) identify faulty machinery, placed out of service.
e) none of the above.
30. When testing an electrical circuit to establish if the supply has been disconnected, it is essential to: (tick the most correct answer)
a) notify the area supervisor.
b) use low voltage test lamps.
c) test the tester.
d) monitor the circuit current.
e) none of the above.
31. A personal danger tag may be removed by: (tick the most correct answer)
a) the job foreman only
b) the person who placed it there only
c) an authorised person after investigation only
d) either person listed in (b) or (c)
e) none of the above.
32. Identify the device shown and explain how it are used:
33. Asbestos is contained in: (tick the most correct answer)
a) Most plastics
b) Insulation Batts
c) Fibro sheeting
d) Chipboard products
34. When working in areas that contain glass wool insulation, name another item of PPE besides gloves, long sleeved shirt, long pants, good shoes, goggles that would reduce some health discomfort.
35. Name two work activities that will produce harmful airborne dust.
36. Workers can be exposed to the legionella bacterium when: (tick the most correct answer)
a) Drilling into concrete slabs.
b) Working on large air conditioning systems.
c) Cutting chipboard products.
d) Contacting bird droppings
37. Test instruments used for LV systems should have a category rating of: (tick the most correct answer)
a) AAA
b) 2
c) III
d) XXX
38. When testing for dead on disconnected cables a digital voltmeter may give an incorrect reading because of:
(tick the most correct answer)
a) Incorrect polarity
b) A high resistance connection
c) Poor meter sensitivity
d) Induced voltages
39. List two inspections that can be conducted on an insulation resistance/continuity tester before the tester is used.
40. All test instruments that are used to test low-voltage sources must have:
(tick the most correct answer)
a) fused probes
b) colour coded leads
c) long leads to get to difficult places
d) analogue displays
41. Describe (3) methods of protecting and storing test instruments.
42. Indicate the time interval between the calibrations of test instruments used in the electrical workplace.
For figures 1&2, identify the occupational hazards for each of the work site
You are require to
1. Complete a hazard Identification table for each of the hazards (your table should have the following: site; date; conducted by; hazard; process; consequence; how to eliminate)
2. Design a risk assessment form for each of these sites and complete it
3. Determine the degree of risk for each hazard
4. Identify control measures to eliminate the risk
You need to demonstrate an understanding of occupational hazard identification, risk assessment and control measures to eliminate or mitigate the risk