Reference no: EM132668306
Question 1: A catalyst is an agent that:
- Speeds up a chemical reaction but is not itself changed in the process.
- Speeds up a chemical reaction and is then used up as part of the process.
- Alters the equilibrium concentrations of reactants and products.
- Forces all reactant molecules to transform to product.
Question 2:
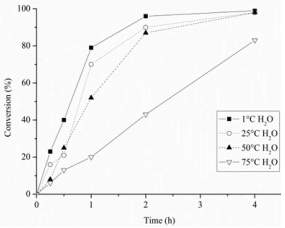
The graph above shows the conversion of glycerol as a function of time using supported Au catalysts prepared in water at the temperatures indicated in the key. The catalyst which gives the fastest rate of reaction is:
- 25°C H2O
- 75°C H2O
- 1°C H2O
- 50°C H2O
Question 3:
During the synthesis of colloidal metal nanoparticles NaBH4 is added as:
A pH modifier to ensure the metal particles adhere to the support.
A capping agent to prevent nanoparticle agglomeration,
A reducing agent to reduce the metal cations in the aqueous salts to the metallic form.
A source of anions to exchange with ligands such as Cl- present in the metal salts..
Question 4:
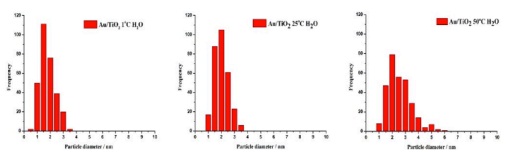
The above graphs are particle size distributions from TEM images of the catalyst materials indicated. Which material has the largest average particle size:
- Au/TiO2 1°C H2O.
- Au/TiO2 25°C H2O.
- All materials have the same average particle size.
- Au/TiO2 50°C H2O.
Question 5:

From the table above the percentage yield of glycerate (Glyc) to two significant figures is:
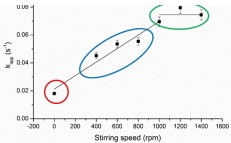
Stirring speed (rpm)
The above graph shows the affect of reactor stirring speed on the apparent rate constant for a reaction. In the blue regime we find:
- The rate constant is linearly dependent on the stirring rate indicating that the stirring speed is too fast to see ° surface reactivity.
- The rate constant is linearly dependent on the stirring rate indicating the reaction should only be carried out ° without stirring.
- The rate constant is linearly dependent on the stirring rate indicating that the reaction rate is controlled by the ° elementary steps on the surface of the catalyst.
- The rate constant is linearly dependent on the stirring rate indicating that the reaction is diffusion limited.
Question 6:
In the paper Chern. Eur.j.17, 6524, (2011), the turn over number iTON) for the catalysts are estimated using the ratio of moles of product and moles of metal present in the catalyst, Which of the following statements is correct?
- The use of the moles of metai in the catalyst will give a lower estimate of 70N because not all metal present will ° be in an active form.
- The use of moles of metal in the catalyst will give a higher estimate of 10N than the true TON because all metal ° is assumed to be in the active state.
- The use of moles of metal in the catalyst to calcula:e 10N is an accurate way :ID judge the true value as at some ° time all metal will be active.
- We can not say if the TON calculated in this way is a lower or upper bound on the true value.
Question 7:
In the paper Chem.. Eur. 17. 6524, (2011), the turn over number (TON) for the disproportionation of benayl alcohol into benzaldehyde and toluene (equation 0)) contains a factor of 2 because.
- The disproprtionation reaction requires two active sites on the catalyst surface.
- Toluene reacts on further in a second reaction catalysed by the active site,
- Each disproportionation reactioll produces two molecules of toluerre.
- The disproportionation reaction involved two molecules of benzyl alcohol reacting at a single catalyst active site.
Question 8:
In the paper Chem.. Eur. J. 17, 6524, (2011), the supported AuPd catalysts are produced using a colloidal method with a capping agent, The capping agent used is
Question 9:
In the paper Chem, Eur.J. 17, 6524, (2011) the TEM electron microscopy shows that on MgO and ZnO there are a sign ir cant number of particles at sizes greater than 10 rim which is evidence that:
- these should be the best support materials for benzyl alcohol oxidation catalysts.
- the microscopy is riot effective for the other support materials.
- particle coalescence has occurred for these supports at the '120°C drying temperature.
- these materiales are able to stabilise the smallest of the rianoparticles produced in the colloid.