Reference no: EM132951266
Resonance and Benzene Compounds
Question 1. Resonance Terminology
a. What is the difference between localized electrons vs. delocalized electrons? What does that mean in terms of stability?
b. Re-write the rules for resonance structures that we went over in class (from our class lecture notes):
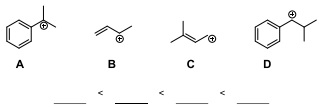
Question 2. Rank the following carbocations in order from least stable to most stable THEN justify your answer thoroughly in words:
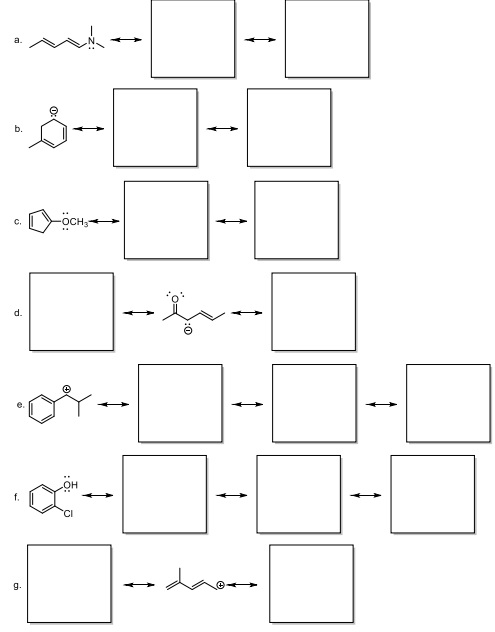
Question 3. PRACTICE WITH A TON OF RESONANCE CONTRIBUTOR EXAMPLES! Draw the resonance contributors for the species/molecules shown in the boxes below. Then, indicate which species (if any) is the MAJOR contributor towards the resonance hybrid (most stable).
Question 4. Reaction Fill-ins! Predict the product(s) OR starting material of the following reactions. Remember, Hydride shifts are possible if/when a more stable carbocation can exist (depending on reaction mechanism)! Put your answers in the indicated boxes.
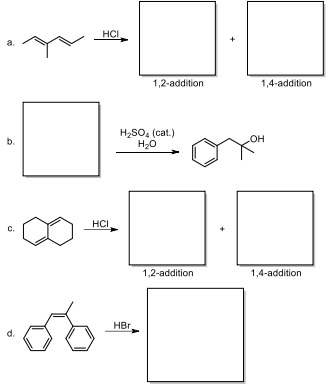
e. Draw the FULL electron-pushing mechanism for the reaction in part c above, INCLUDING ALL resonance contributors. Explicitly label all formal charges and/or electron pairs. Label the nucleophile and electrophile in each reaction step.
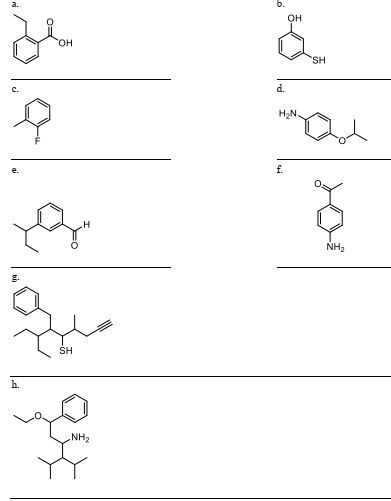
Question 5. Nomenclature. Give the IUPAC name of the compound below; put your answer on the line below the compound. Remember that benzene compound may have common names as parent names - make sure you know the 6 from the lecture slides!
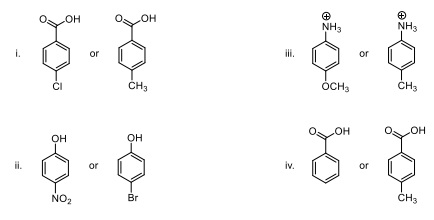
Question 6. For each of the following pairs of compounds, circle the one that is the stronger acid. WHY did you choose that acid? Explain in one sentence.