Reference no: EM132293624
Microeconomics Assignment - Consumer Demand Theory
Q1. When total utility (TU) increases, marginal utility (MU) is
(a) negative and increasing
(b) negative and declining
(c) zero
(d) positive and declining
Q2. At the saturation point for Good X, the MU is
(a) positive
(b) negative
(c) zero
(d) any of the above
Q3. Which of the following are not clearly ordered preferences?
(a) pizza > Thai food > Cornish game hens > vegetarian
(b) vegetarian > Thai food > pizza > Cornish game hens
(c) Thai food > vegetarian > Cornish game hens > pizza
(d) vegetarian > pizza > Cornish game hens > vegetarian
Q4. The marginal-utility-to-price ratio is a representation of the
(a) law of demand
(b) total satisfaction a consumer gets from a good
(c) additional satisfaction a consumer gets from a good
(d) satisfaction per dollar spent that a consumer gets from a good
Q5. Given the marginal-utility-to-price ratio equalization principle, if MU1/P1 > MU2/P2,
(a) the consumer should consume more of Good 1 and less of Good 2
(b) the consumer should consume more of Good 2 and less of Good 1
(c) the total utility of Good 1 is greater than the total utility of Good 2
(d) the total utility of Good 2 is greater than the total utility of Good 1
Q6. The marginal-utility-to-price ratio tells us that if the price of a good falls, then
(a) its marginal-utility-to-price ration falls
(b) its marginal-utility-to-price ratio rises
(c) its marginal utility falls
(d) its marginal utility rises
Q7. Kate plans to brighten up her apartment in New York City with house plants and framed prints. The total utility she derives from the plants and prints is as follows:
|
Number of Plants
|
TU of Plants
|
Number of Prints
|
TU of Prints
|
|
1
|
120
|
1
|
20
|
|
2
|
200
|
2
|
36
|
|
3
|
264
|
3
|
50
|
|
4
|
304
|
4
|
60
|
|
5
|
334
|
5
|
68
|
|
6
|
360
|
6
|
74
|
Suppose the price of plants is $40 and the price of prints is $20. The MU/$ spent on the fourth plant is
(a) 6
(b) 10
(c) 1
(d) .8
(e) .5
Q8. Suppose there is a sale on prints, reducing the price from $20 to $10. If Kate had $140 to spend on plants and prints, how many of each would she buy to maximize her total utility?
(a) 3 plants and 2 prints
(b) 4 plants and 3 prints
(c) 6 plants and 2 prints
(d) 2 plants and 2 prints
(e) 6 plants and 0 prints
Q9. Suppose Kate, who is a freelance publicist for several alternative music labels, earns $50,000 annually. To maximize her total utility, she will spend her income in such a way that
(a) the marginal utility she derives from every good she buys is zero
(b) the marginal utility-to-price ratio for each of the goods she buys is zero
(c) the marginal utility-to-price ratio for each of the goods she buys is at a maximum
(d) the marginal utility-to-price ratio for each of the goods she buys is at a minimum
(e) the marginal utility-to-price ratio for each of the goods she buys is equal
Questions 10-12 refer to the following graph:
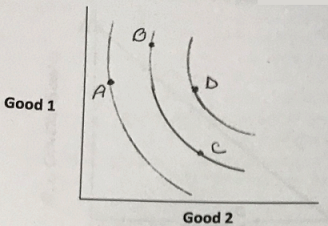
Q10. Which point offers the highest level of utility? (a) A (b) B (c) C (d) D
Q11. Which point offers the lowest level of utility? (a) A (b) B (c) C (d) D
Q12. Which points offer the same level of utility? (a) A & B (b) A & C (c) B & C (d) C & D
Questions 13-14 refer to the graph below:
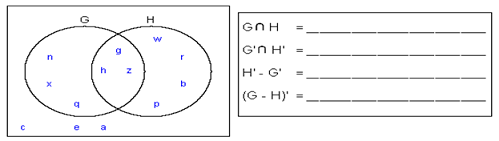
Q13. A shift in the budget constraint from AB to AC is best explained by
(a) a tax cut
(b) a salary increase
(c) a reduction in the price of cabbage
(d) a reduction in the price of beets
Q14. A shift in the budget constraint from AB to DC is best explained by
(a) a salary increase
(b) a reduction in the price of cabbage
(c) an increase in the price of beets
(d) the shift is not possible
Questions 15-17 refer to the following graph:
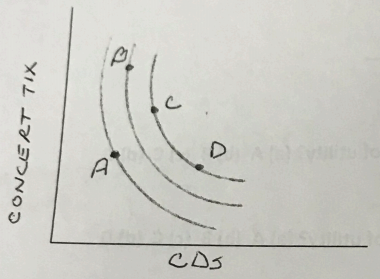
Q15. Which of the following movements would not be an improvement in welfare?
(a) A to B
(b) B to C
(c) C to D
(d) B to D
Q16. Which point has the highest marginal rate of substitution of CDs for concert tickets?
(a) A (13) B (c) C (d) D
Q17. Which point has the lowest marginal rate of substitution of CDs for concert tickets?
(a) A (b) B (c) C (d) D
Question 18 refers to the following graph:
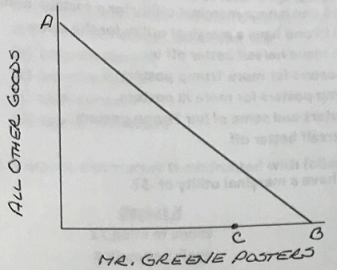
18. The pivot in the budget constraint from AB to AC represents
(a) a reduction in income
(b) an increase in the price of Mr. Greene posters
(c) a decrease in the price of Mr. Greene posters
(d) an increase in the price of all other goods
Q19. Which of the following is not an example of utility maximizing behavior?
(a) Giving $10 to a homeless person
(b) Buying a new cell phone
(c) Quitting a job you hate
(d) Losing your Microeconomics notes two days before the final
Q20. If the MRSxy of Frisbees for soccer balls is seven
(a) an individual is willing to give up seven Frisbees in order to get one soccer ball
(b) an individual is willing to give up seven soccer balls for one Frisbee
(c) an individual is indifferent between seven soccer balls and seven Frisbees
(d) none of the above
Q21. If the marginal utility of soccer balls is 4 and the marginal utility of Frisbees is 1, what is the price of Frisbees if soccer balls sell for $8?
(a) $1
(b) $2
(c) $4
(d) $8
Q22. Suppose there are two goods in the world, Xi Jinping posters and Donald Trump posters. Xi Jinping posters cost $10 and have a marginal utility for a certain individual of 2. Donald Trump posters cost $15 and have a marginal utility for the same individual of 3. This Individual can make herself better off by:
(a) trading away some of her Xi posters for more Trump posters
(b) trading away some of her Trump posters for more Xi posters
(c) giving away some of her Xi posters and some of her Trump posters
(d) this individual cannot make herself better off
Q23. Which of the following is likely to have a marginal utility of -5?
(a) electricity
(b) carrots
(c) a dictionary
(d) mosquitoes
Q24. As we move along an indifference curve in an upward direction, the MRSyx
(a) falls
(b) rises
(c) remains constant
(d) fluctuates erratically
Q25. If a consumer is below his budget line, the consumer
(a) is in equilibrium
(b) is not spending all of his income
(c) is spending all of his income
(d) is giving away most of his income
Q26. At equilibrium, the slope of the indifference curve is
(a) less than the slope of the budget line
(b) greater than the slope of the budget line
(c) equal to the slope of the budget line
(d) determined by the relative prices of the goods under consideration
Q27. Think once again of our freelance publicist, Kate-you remember, the young woman from Questions 7-9. Think of Kate, chocolate pudding, and apple pie. An indifference curve, with regard to these two goods, represents for Kate
(a) the maximum utility she derives from consuming those goods
(b) combinations of the two goods that yield the same total utility for her
(c) the quantities of the two goods she will buy if their prices are identical
(d) the quantities of the two goods she will buy at different levels of income
(e) her indifference to both goods if they cannot be purchased individually
Q28. Assume that the quantity of food is measured on the horizontal axis, and the quantity of clothing on the vertical axis. If the price of food rises 20% and the price of clothing rises 30%, the budget constraint will
(a) become steeper
(b) become flatter
(c) shift outward
(d) remain stationary
Q29. Suppose a consumer is confronted with following two baskets of goods, X and Y:
|
Basket X
|
Basket Y
|
|
11 pairs of shoes
|
12 pairs of shoes
|
|
8 diamond rings
|
12 diamond rings
|
|
1 Audi
|
1 Audi
|
|
8 apples
|
8 apples
|
Assumptions about an individual's preferences requires that the consumer
(a) rank Basket X over Basket Y
(b) rank Basket Y over basket X
(c) be indifferent between Basket X and Basket Y
(d) no prediction about the individual's behavior can be made in this case
Q30. If a consumer makes consistent choices among product combinations, then it would follow that
(a) if A is preferred to B, and B to C, then C must be preferred to D
(b) if B is preferred to C, and A is also preferred to C, then the consumer must be indifferent between A and B
(c) if C is preferred to A, and A is preferred to B, then C must be preferred to B
(d) all of the above are true
Q31. Suppose a budget line shifts to the right, with its slope unchanged. Such a shift might be caused by
(a) a decrease in income with no change in prices
(b) an increase in the price of one of the commodities, with no change in income or the price of the other commodity
(c) an increase in income with no change in prices
(d) a decrease in the price of one of the commodities, with no change in income or the price of the other commodity
Problems -
Q1. Suppose that you are already at the point of maximizing utility in your consumption of four goods: T-shirts, movies, music downloads, and streaming video services like Netflix- and the following table represents this maximization. Fill in the missing numbers for prices and marginal utilities to make the maximization work.
|
|
T-shirts
|
Movies
|
Music Downloads
|
Streaming Services
|
|
Marginal Utility
|
45
|
|
15
|
|
|
Price
|
10
|
5
|
|
20
|
Q2. Assume that the data in the accompanying table give the indifference curve for Andrew Osborne. Graph this curve, putting Good Y on the vertical axis and Good X on the horizontal axis. Assume that the prices of Good Y and Good X are $1.50 and $1.00 respectively, and that Andrew has $48 to spend. Add his budget constraint to the graph of his indifference curve. What combination of Good Y and Good X will Andrew purchase? Does your answer meet the MRS = Px/Py rule for equilibrium?
|
Units of Good Y
|
Units of Good X
|
|
32
|
12
|
|
24
|
16
|
|
16
|
24
|
|
8
|
48
|
Q3. Columns 1 through 4 of the accompanying table show the amount of marginal utility, measured in utils, that Adam Smith would get from purchasing various amounts of products A, B, C, and D. Column 5 shows the marginal utility Adam would get from saving. Assume that the prices of A, B, C, and D are $18, $6, $4, and $2, respectively, and that Adam has an income of $106.
|
Column 1
|
Column 2
|
Column 3
|
Column 4
|
Column 5
|
|
Units A
|
MU
|
Units B
|
MU
|
Units C
|
MU
|
Units D
|
MU
|
$ Saved
|
MU
|
|
1
|
72
|
1
|
24
|
1
|
15
|
1
|
36
|
1
|
5
|
|
2
|
54
|
2
|
15
|
2
|
12
|
2
|
30
|
2
|
4
|
|
3
|
45
|
3
|
12
|
3
|
8
|
3
|
24
|
3
|
3
|
|
4
|
36
|
4
|
9
|
4
|
7
|
4
|
18
|
4
|
2
|
|
5
|
27
|
5
|
7
|
5
|
5
|
5
|
13
|
5
|
1
|
|
6
|
18
|
6
|
5
|
6
|
4
|
6
|
7
|
6
|
.5
|
|
7
|
15
|
7
|
2
|
7
|
3.5
|
7
|
4
|
7
|
.25
|
|
8
|
12
|
8
|
1
|
8
|
3
|
8
|
2
|
8
|
.125
|
a. What quantities of A, B, C, and D will Adam purchase in maximizing his utility?
b. How many dollars will Adam choose to save?
c. Check your answers by substituting them into the algebraic statement of the utility maximizing rule.
Essay -
What information is contained in an indifference curve? Why are indifference curves (a) downward sloping and (b) convex to the origin? Why does total utility increase as the consumer moves to indifference curves farther from the origin? Why can't indifference curves intersect?
Note - Just do multiple choices and the problems and don't do the last question which is the essay.