Reference no: EM13746207
1. Tax Incentive Arms Race. Tax incentives are frequently used by cities and states in the U.S. in an attempt to make their jurisdictions more desirable places for businesses to invest than other jurisdictions. However, to the extent that other jurisdictions also offer tax incentives, any benefits in terms of attracting new investment are nullified, and all jurisdictions end up suffering as a result of lower tax revenues.
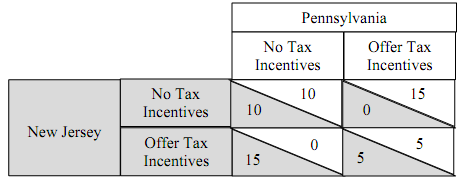
Suppose two states, Pennsylvania and New Jersey, are each deciding whether to offer tax incentives to attract new businesses. The payoffs for each state are as follows:
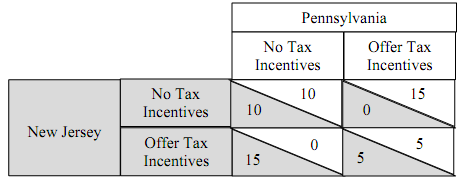
(a) Explain in words what a Nash equilibrium is.
(b) Assume that each state is rational, that rationality is common knowledge, and that the game is common knowledge. If the tax incentive arms race game will be played one time, what is the Nash equilibrium of the game?
(c) Could the Nash equilibrium outcome be different if this game were to be played each year for the next 10 years? Explain why or why not.
(d) The phenomenon you described in this problem is often referred to as a "race to the bottom." Explain why that is an appropriate name for this phenomenon.
2. Princess Bride Game. Our hero Westley (in the guise of Dread Pirate Roberts) challenges the evil Vizzini to a "battle of wits." Two cups of wine are placed on a table, one in front of Westley and one in front of Vizzini. Westley has poisoned one of the two cups of wine with deadly iocane powder (which is colorless, odorless, and tasteless); which cup is poisoned is unknown to Vizzini. The challenge to Vizzini is to select one of the two cups to drink; Westley must drink the other. The payoffs of the game are as follows:
(a) What are the Nash equilibrium of game? Show how you came to your answer.
(b) Suppose that, unbeknownst to Vizzini, Westley is immune to iocane powder, and in fact poisoned both cups. If Westley gets a payoff of 5 from drinking a cup of wine poisoned with iocane powder when Vizzini also drinks a cup of wine poisoned with iocane powder (and Vizzini's payoff is still -10 from drinking a cup poisoned with iocane powder), draw 1 the new game board. What payoffs must each of the two players now get?
3. Governor Race Game. An incumbent governor from a conservative party faces a challenger from a liberal party. They are choosing political platforms. The incumbent chooses first. If both choose the same platform, the incumbent wins; otherwise, the challenger wins.
Let the value of winning be 20 and the value of compromising one's political views be -10; the payoff is the sum of these values. Therefore, there are four possible outcomes:
• The incumbent chooses liberal and the challenger chooses liberal, in which case the incumbent wins (payoff = 20 - 10 = 10) and the challenger loses (payoff = 0).
• The incumbent chooses liberal and the challenger chooses conservative, in which case the incumbent loses (payoff = 0 - 10 = -10) and the challenger wins (payoff = 20-10 = 10).
• The incumbent chooses conservative and the challenger chooses liberal, in which case the incumbent loses (payoff = 0) and the challenger wins (payoff = 20).
• The incumbent chooses conservative and the challenger chooses conservative, in which case the incumbent wins (payoff = 20) and the challenger loses (payoff = 0 - 10 = -10).
(a) Draw the game tree corresponding to this sequential game. Note that the incumbent chooses first whether to pursue a liberal or conservative platform, then the challenger chooses his/her platform after observing what the incumbent chose.
(b) Using backward induction, determine the outcome of the game. Explain how you arrived at your answer.
(c) What if the incumbent becomes convinced that the challenger so strongly stands by his/her principles that the value of compromising his/her views is -30 (but it is still -10 for the incumbent). Would that change the outcome of the game? Draw a new game tree with the new payoffs and explain why the outcome would or would not change.
4. Two airlines, Drexel Air and Dragon Jet, operate flights from Philadelphia to Miami. Weekly demand for seats on flights from Philadelphia to Miami is given by Q = 1300 - 2P, where Q is the number of seats and P is the price in dollars. Suppose that both airlines have a marginal cost of $50 per seat. Suppose that Drexel Air and Dragon Jet simultaneously choose the quantity of seats to offer on the route (i.e., suppose they are Cournot competitors).
(a) Given that Drexel Air and Dragon Jet choose their quantities simultaneously, solve for the optimal quantities for each to offer. What is the price of a seat in this market? What are the economic profits for Drexel Air and Dragon Jet?
(b) Suppose that executives at both companies realize that their competition on the Philadelphia-Miami route may be costing them profits. In a closed-door meeting, they decide to collude. What's the greatest economic profit they could each make by colluding (assuming they split production and profits equally under collusion)?
(c) Show mathematically and explain in words why the collusive arrangement you solved for in part (c) is not sustainable if this "game" is played once. In what sense is this situation similar to a prisoner's dilemma game?
(d) Suppose the two firms are not colluding, but Drexel Air figures out a way to cram more seats onto a plane such that its marginal cost is $44 per seat instead of $50. Assuming Dragon Jet's marginal cost is still $50 per seat, solve for the new optimal quantities, price, and economic profits.
5. Suppose that, unlike in the previous question, Drexel Air and Dragon Jet move sequentially instead of simultaneously (i.e., suppose that they are Stackelberg competitors). Weekly demand for seats on flights from Philadelphia to Miami is still given by Q = 1300 - 2P, where Q is the number of seats and P is the price in dollars. Assume again that both airlines have a marginal cost of $50 per seat.
(a) Assuming that Drexel Air chooses its quantity of seats first and Dragon Jet chooses its quantity second, solve for the optimal quantity of seats for each airline to offer. What is the price of a seat in this market? What are the economic profits for Drexel Air and Dragon Jet in this case?
(b) Compare your answer in (a) of this question to your answer from part (a) of question 4. Does Drexel Air gain an advantage by moving first? Explain in words why or why not.
(c) Suppose now that the two firms proposed to merge to become a monopolist on this route. Concerned about the decrease in quantity of seats supplied and increase in prices that might result from the merger, the Department of Justice moves to block the merger.
In response, the two airlines claim that because of cost efficiencies that will arise as a result of the merger, their marginal cost will fall from $50 per seat to $25 per seat. If this is true, will the monopoly price for tickets in fact be lower than the Stackelberg price that you
solved for in part (a)?
(d) Suppose that the Department of Justice allows the merger to occur. Calculate the deadweight loss under Stackelberg competition and under monopoly (assuming that, as the airlines claimed, the marginal cost falls to $25 after they merge). Did the deadweight loss surplus increase, decrease, or stay the same?
6. Suppose that Drexel is auctioning off a VIP food truck pass that gives the owner free food at any food truck on campus for a year. Your valuation of the pass is $250.
(a) Suppose that Drexel is using a first-price, sealed-bid auction. If there is only one other bidder in the auction and you believe his valuation has equal odds of being anywhere from $100 to $300, what is your optimal bid? What is your expected surplus?
(b) If there were more bidders in the first-price, sealed-bid auction (and you believe that all have valuations with equal odds of being anywhere from $100 to $300), would that increase, decrease, or not change your optimal bid relative to what you solved for in part
(a)? Explain in words.
(c) Explain in words why a Dutch auction is equivalent to a first-price, sealed bid auction in terms of bidding strategies.
(d) Now suppose that Drexel is using a second-price, sealed-bid auction. If there is only one other bidder in the auction and you believe his valuation has equal odds of being anywhere from $100 to $300, what is your optimal bid? What is your expected surplus?
(e) If there were more bidders in the second-price, sealed-bid auction (and you believe that all have valuations with equal odds of being anywhere from $100 to $300), would that increase, decrease, or not change your optimal bid relative to what you solved for in part
(d)? Explain in words.
(f) Explain in words why an English auction is equivalent to a second-price, sealed-bid auction in terms of bidding strategies.