Reference no: EM133265437
Question 1. A 1.0-g sample of carbon dioxide (CO2) is fully decomposed into its elements, yielding 0.273 g of carbon and 0.727 g of oxygen.
(a) What is the ratio of the mass of O to C?
(b) If a sample of a different compound decomposes into 0.429 g of carbon and 0.571 g of oxygen, what is its ratio of the mass of O to C?
(c) According to Dalton's atomic theory, what is the empirical formula of the second compound?
Question 2. Sodium reacts with oxygen in air to form two compounds: sodium oxide and sodium peroxide. In forming sodium oxide, 23.0 g of sodium combines with 8.0 g of hydrogen. In forming sodium peroxide, 23.0 g of sodium combines with 16.0 g of oxygen.
(a) What are the mass ratios of oxygen in the two compounds?
(b) What fundamental law does this experiment demonstrate?
Question 3. A chemist finds that 30.82 g of nitrogen will react with 17.60, 35.20, 70.40, or 88.00 g of oxygen to form four different compounds.
(a) Calculate the mass of oxygen per gram of nitrogen in each compound.
(b) How do the numbers in part (a) support Dalton's atomic theory?
Question 4. In the Millikan oil-drop experiment (see Figure 2.5), the tiny oil drops are observed through the viewing lens as rising, stationary, or falling, as shown here.
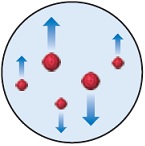
(a) What causes their rate of fall to vary from their rate in the absence of an electric field?
(b) Why do some drops move upward?
Question 5. Suppose a scientist repeats the Millikan oil-drop experiment but reports the charges on the drops using an unusual (and imaginary) unit called the warmomb (wa). The scientist obtains the following data for four of the drops:
|
Droplet
|
Calculated charge (wa)
|
|
A
|
3.84 X 10-8
|
|
B
|
4.80 X 10-8
|
|
C
|
2.88 X 10-8
|
|
D
|
8.64 X 10-8
|
(a) If all the droplets were the same size, which would fall most slowly through the apparatus?
(b) From these data, what is the best choice for the charge of the electron in warmombs?
(c) Based on your answer to part (b), how many electrons are there on each of the droplets?
(d) What is the conversion factor between warmombs and coulombs?
Question 6. Millikan determined the charge on the electron by studying the static charges on oil drops falling in an electric field. A student carried out this experiment using several oil drops for her measurements and calculated the charges on the drops. She obtained the following data:
|
Droplet
|
Calculated Charge (C)
|
|
A
|
1.60 X 10-19
|
|
B
|
3.15 X 10-19
|
|
C
|
4.18 X 10-19
|
|
D
|
6.31 X 10-19
|
(a) What is the significance of the fact that the droplets carried different charges?
(b) What conclusion can the student draw from these data regarding the charge of the electron?
(c) What value (and to how many significant figures) should she report for the electronic charge?
Question 7. Consider an atom of 32P.
(a) How many protons, neutrons, and electrons does this atom contain?
(b) What is the symbol of the atom obtained by adding one proton to 32P?
(c) What is the symbol of the atom obtained by adding one neutron to 32P?
(d) Are either of the atoms obtained in parts (b) and (c) isotopes of 32P? If so which one?
Question 8. (a) Define atomic number and mass number. (b) Which of these can vary without changing the identity of the element?
Question 9. Write the correct symbol, with both superscript and subscript, for each of the following.
(a) the isotope of hafnium that contains 106 neutrons,
(b) the isotope of mercury with mass number 201,
(c) the isotope of rhenium with mass number 187,
(d) the isotope of calcium that has an equal number of protons and neutrons.
Question 10. Iron has three major isotopes: 54Fe (atomic mass = 53.9396 u; abundance 5.85%), 56Fe (atomic mass = 55.9349 u; abundance 91.75%), and 57Fe (atomic mass = 56.9354 u; abundance 2.12 %). Calculate the atomic weight (average atomic mass) of iron.
Question 11. Naturally occurring lead has the following isotopic abundances: What is the average atomic mass of Pb?
|
Isotope
|
Abundance (%)
|
Atomic mass (u)
|
|
204Pb
|
1.4
|
203.9730
|
|
206Pb
|
24.1
|
205.9744
|
|
207Pb
|
22.1
|
206.9759
|
|
208Pb
|
52.4
|
207.9766
|
Question 12. Bromine has two naturally occurring isotopes, bromine-79 (atomic mass = 78.9183 u; abundance = 50.69%2 and bromine-81 1atomic mass = 80.9163 u; abundance = 49.31%). Calculate the atomic weight of bromine.