Reference no: EM131921629
International Economics: Trade Assignment -
Answer all questions.
Q1. Answer the questions below based on this diagram, which represents the situation for a monopolistically competitive firm in the short run after a country has "opened up" to trade. You may assume that point A is the long-run equilibrium without trade ("autarky") and NA is the number of firms in the autarky (no trade) equilibrium and when the country "opens up" to trade.
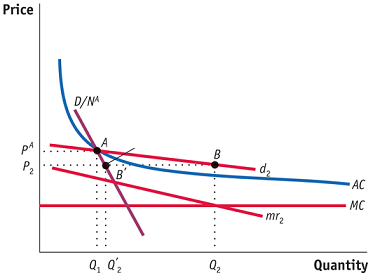
a. Explain the meaning of the two demand curves: what is the difference between d2 and D/NA? Why is d2 flatter?
b. How does the firm try to maximize its profits in this situation? What pulls it away from the autarky equilibrium at point A? Where does the firm try to operate, at B or B′, and why? Where does the firm end up producing, at B or B′, and why? Would the firm be making positive, zero, or negative profits (where negative profits ⇒ losses) at each of these points? How do you know?
c. What adjustments are set in motion by the situation you have just described in part b? Specifically, will firms enter or exit the industry, and why? What will happen to output, average cost, price, and profits for each domestic firm in the long-run equilibrium with trade? A graph is optional, but fully explain what happens in moving to the long-run equilibrium with trade.
Q2. Answer these questions based on the data in the table.
a. Calculate the index of intra-industry trade (IIT) shown on page 192 of the Feenstra-Taylor textbook (also slide 7 of the class presentation for syllabus Topic 4) for each category shown in the table. HINT: The data are available in an Excel file on Black-board (under Assignments/Problem Set 4) so you don't need to retype them, and you can program the calculations in Excel or another spreadsheet program if you wish.
b. Interpret your results. Which branches of the transportation equipment sector (excluding the total at the bottom) have the highest IIT indexes? Which ones have the lowest? What do these numbers mean? What do you notice about the sectors with the lowest IIT ratios (hint: consider the surpluses or deficits in those sectors).
c. Explain why the IIT index is so different for total transportation equipment (the sum of all other categories) than it is for most of the individual types of goods. Why is the index for the total not like an average for the individual industries? What does this tell us about how the level of aggregation (broader or narrower categories of industries) can affect our measurement of IIT (intra- vs. inter-industry trade)?
U.S. Trade in Transportation Equipment, Census Basis, year 2016, in millions of dollars
|
|
Exports
|
Imports
|
IIT Index
|
|
Civilian aircraft
|
60,634
|
13,839
|
|
|
Parts and engines for civilian aircraft
|
60,311
|
36,144
|
|
|
Railway transportation equipment
|
3,645
|
1,254
|
|
|
Vessels (ships) including parts
|
1,730
|
1,222
|
|
|
Spacecraft and parts
|
86
|
223
|
|
|
Automotive - passenger cars (finished)
|
53,154
|
170,041
|
|
|
Trucks, buses & spec purpose vehicles
|
18,008
|
33,854
|
|
|
Automotive parts, engines, bodies & chassis
|
79,151
|
146,222
|
|
|
Total transportation equipment
|
276,718
|
402,798
|
|
Source: U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis and Census Bureau, International Accounts Products for Detailed Goods Trade Data, U.S. Trade in Goods (IDS-0008), Current Installment, February 8, 2018, accessed March 6, 2018, and professor's calculations.
Note: Total transportation equipment is the sum of all other categories shown.
Q3. A globalized production process has the following three stages, shown with the ratio of highly skilled (human capital) to low skilled labor (H/L) in each activity:
A) Research and development; product design - 2
B) Assembly of basic parts and components - 1/4
C) Transformation of parts and components into semi-finished products - 1/2
D) Final assembly, packaging, distribution, and sales of finished goods - 3/4
HINT: It may help to re-order these from lowest to highest H/L ratio!
Suppose that initially stage B is performed in Vietnam, while A, C, and D are performed in (South) Korea. Also assume for simplicity that equal amounts of labor are used in each stage, so that you can take simple averages of the H/L ratios to get average H/L for each country.
a. What are the average H/L ratios in Korea and Vietnam?
b. Now suppose that stage C is "offshored," i.e., stage C is relocated from Korea to Vietnam. What happens to the average H/L ratio in each country? Calculate and explain.
c. What would you expect to be the effect of this offshoring on the relative wages (wage premium) of highly-skilled workers (human capital), WH/WL in each country? Why?
Explain using relative supply and demand graphs (as in chapter 7 of Feenstra-Taylor and the class PowerPoint presentation). [HINT: You may assume that the numbers you calculated reflect relative demand, (H/L)d, so show which way the demand curve shifts and how that affects the relative wage.]
d. What would happen if Vietnam raises the educational level of its labor force, so that the relative supply of highly skilled workers (H/L)s increases? Would you necessarily see the same result as in part c? Why or why not? (Answer qualitatively using a graph).
Attachment:- Assignment Files.rar