Reference no: EM13826980
Question 1:
Suppose a firm operating in pure competitive industry. The firm maximizes its profit when:
Units of output produced: 20 units
Marginal Revenue (MR) = Marginal Cost (MC) = Price (P) = $50
Average Fixed Cost (AFC) = $15
Average Variable Cost (AVC) = $35
1. What is the average total cost (ATC)?
2. Does the firm realize a profit or a loss and why?
3. Will the firm produce or shut-down its business and why?
4. What is the profit or loss per unit?
5. What is firm''s total profit or total loss?
Question 2:
1. Suppose a firm''s total revenue is $750 when producing 30 units.
a) Determine the price per unit if the given firm is operating in pure competitive market.
b) What are the marginal and average revenues if the firm chooses to produce one more unit?
Question 3:
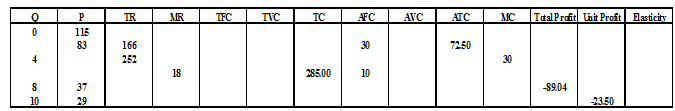
1. Suppose a firm''s total revenue is $500 when producing the price per unit is $25.
a) Determine the quantity produced by the firm.
b) What are the average and the marginal revenues if the firm chooses to produce one more unit?Question 4:(15%)
Question 4:
You are given the following curves that represent a firm operating in pure competitive industry:
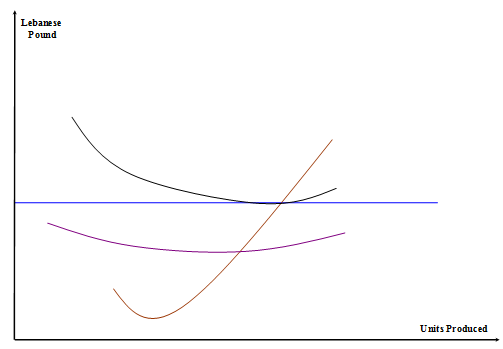
1. Label the above four curves?
2. Determine graphically the units produced when the firm maximizes its profits.
3. Will the firm realize profit or loss and why?
4. Will the firm continue to produce or shut down and why?
5. Determine graphically the firm's profit or loss graphically.
6. Determine graphically the firm's average fixed cost (AFC) when it maximizes its profit?
Question 5:
1. What are the degrees of influence firms can have over price in a pure monopoly and monopolistic competitive markets.
2. Suppose a firm's total revenue is $500 when producing the price per unit is $25.
a) Determine the quantity produced by the firm.
b) What are the average and the marginal revenues if the firm chooses to produce one more unit?
Multiple Choice Questions:
1. A firm stands to gain by operating instead of shutting down as long as ________ sufficiently covers ________.
A) Price; average variable cost
B) Price; average fixed cost
C) Total revenue; total fixed costs
D) Operating profit; economic profit
2. If TR > TC, a firm would ________ in the short run and ________ in the long run.
A) Operate; expand
B) Operate; contract
C) Shut down; expand
D) Shut down; contract
3. We can call a profit-maximizing strategy a loss-minimizing strategy when a perfectly competitive firm produces where
A) AVC < P < ATC.
B) P > ATC.
C) P = ATC.
D) MR = MC < P.
4. If a firm's operating profit is $0, then
A) TR equals TC.
B) TR equals TVC.
C) TR equals TFC.
D) TFC is zero.
5. Economists usually assume that labor is ________ input in the ________ run.
A) A fixed; short
B) A fixed; long
C) A variable; short
D) Part fixed and part variable; long
6. Amy spends $6,000 on remodeling a storefront that she then opens as a take-out deli. After opening her deli her business is terrible and she needs an additional $2,000 to keep the deli open. Which of the following is TRUE?
A) The $6,000 Amy spent on remodeling represents a part of the total variable cost of her business.
B) The $6,000 Amy spent on remodeling represents a sunk cost of her business.
C) The $2,000 Amy needs to keep the deli open represents her marginal costs of production.
D) The $2,000 Amy needs to keep the deli open represents her total fixed costs.
7. A firm ________ if it earns zero economic profit.
A) Earns a negative rate of return
B) Will leave the industry
C) Earns a positive but below normal rate of return
D) Earns exactly a normal rate of return
8. In the short run, a firm
A) Has at least one fixed factor of production.
B) Cannot enter an industry where positive profits are being earned.
C) Can exit and industry and all of its factors of production are variable.
D) Both (A) and (B) are correct.
9. Firms must make all of the following decisions EXCEPT
A) How much output to supply.
B) Which production technology to use.
C) How much of each input to demand.
D) What price to charge for its output.
10. To determine the optimal method of production for a good or service, a firm needs to know
A) The market price of output.
B) The technologies of production that are available to the firm.
C) The prices of inputs.
D) All of the above are correct.
11. The fact that good substitutes are available is the feature that differentiates monopolistic competition from:
A) Monopoly.
B) Perfect competition.
C) All of the other market structures.
D) None of the other market structures. Any industry has good substitutes for the good it produces.
12. Refer to the figure below and select the best answer choice. Assume that the firm is producing 600 units. What should the firm do in order to maximize profit?
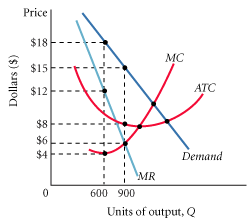
A) The firm should maintain output at 600 units, because at this output level, marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost, marginal cost is minimized, and price is the highest.
B) The firm should increase the level of output because at 600 units, marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost.
C) The firm should increase output because at 600 units price is above marginal cost.
D) The firm should increase the level of output until it reaches the minimum average cost.
Use the information provided in Figure 7.4 below to answer the questions that follow.
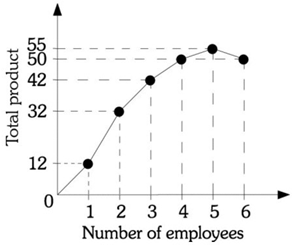
Figure 7.4
13. Refer to Figure 7.4. The marginal product of the second worker is
A)10.
B)16.
C)20.
D)32.
14. Refer to Figure 7.4. The marginal product of the fourth worker is
A)5.
B)8.
C)50.
D)55.
15. Refer to Figure 7.4. The marginal product of the sixth worker is
A)-50.
B)-5.
C)5.
D)8.33.