Reference no: EM132359752
Question 1. Both GSM and DECT use GMSK, but with different Gaussian filters (BGT = 0.3 in GSM, BGT = 0.5 in DECT). What are the advantages of having a larger bandwidth time product? Why is the lower one used in GSM?
Question 2. In the EDGE standard (high-speed data in GSM networks), 3Π/8-shifted 8-PSK is used. Sketch transitions in the signal space diagram for this modulation format. What is the ratio between average value and minimum value of the envelope? Why is it that Π/4-shifted 8-PSK cannot be used?
Question 3. Consider two functions:
1 0 < t < T/2
f (t) =
-2 T/2 < t < T (30.23)
and
g(t) = 1 - (t/T) for 0 < t < T.
(a) Find a set of expansion functions, using Gram-Schmidt orthogonalization.
(b) Find points in the signal space diagram for f(t), g(t), and the function that is unity for 0 < t < T.
Question 4. Relate the mean signal energy of 64-QAM to the distance between points in the signal space diagram.
Question 5. Consider a point-to-point radio link between two highly directional antennas in a stationary environment. The antennas have antenna gains of 30 dB, distance attenuation is 150 dB, and the RX has a noise figure of 7 dB. The symbol rate is 20 Msymb/s and Nyquist signaling is used. It can be assumed that the radio link can be treated as an AWGN channel without fading. How much transmit power is required (disregarding power losses at TX and RX ends) for a maximum BER of 10-5:
(a) When using coherently detected BPSK, FSK, differentially detected BPSK, or noncoherently detected FSK?
(b) Derive the exact bit and symbol error probability expressions for coherently detected Gray-coded QPSK. Start by showing that the QPSK signal can be viewed as two antipodal signals in quadrature.
(c) What is the required transmit power if Gray-coded QPSK is used?
(d) What is the penalty in increased BER for using differential detection of Gray-coded QPSK in (c)?
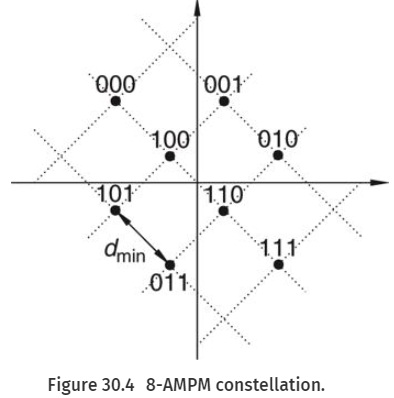
Question 6. Consider the 8-Amplitude Modulation Phase Modulation (8-AMPM) modulation format shown in Figure 30.4. What is the average symbol energy expressed in dmin (all signal alternatives assumed to be equally probable)? What is the nearest neighbor union bound on the BER?
Question 7. Obtain simulated BER results for Gray-coded QPSK and 8-PSK by creating a MATLABTM program. Run simulations for Eb//N0 in the range from 0 to 15 dB. In which region does the nearest neighbor union bound on BER (see Problem 3) appear to be tight?