Reference no: EM131105234
Topology Honors Exam 2013
A. Point-set topology
(1) Say that a space Y "separates the points of X" if for any two points a, b in X there exists a continuous function f: X → Y such that f(a) ≠ f(b).
a. Recall that a space X is said to be "totally disconnected" if the connected components of X consist of single points. Let T be the space {t1, t2} with the discrete topology. Prove that X is totally disconnected if and only if T separates points of X.
b. Let R denote the real numbers in the usual topology. Does R separate points of Rn? Does R separate points of the sphere, Sn-1?
c. Prove or disprove: If Y separates the points of X and Y is Hausdorff, then X is Hausdorff.
(2) Suppose that X is a topological space with an infinite number of points. For an integer k ≥ 1, let
Ck(X) = {(x1, ..., xk) : xi ≠ xj whenever i ≠ j},
topologized as a subspace of Xk. Say that "X has the Ck-property" if Ck(X) is path-connected.
a. What does it mean for X to have the C1-property?
b. Prove that R (usual topology) has the Ck-property only for k = 1.
c. For what values of k does S1 have the Ck-property? A space homeomorphic to the letter Y is another very interesting example. Can you say anything about this?
(3) For each of the following parts, X and Y are given subspaces of R2, in the usual topology. Decide if the regions are homeomorphic, and justify your answer. (Start by drawing a picture.)
a. X = {(x, y) | x = 0} ∪ {(x, y) | y = 0} ∪ {(x, y) | y = 1/x}
Y = {(x, y) | x = 0} ∪ {(x, y) | y = 0} ∪ {(x, y) | y = 1/|x|}
b. Let C = {(x, y) | 1 ≤ x2 + y2 ≤ 4}. Then take:
X = C ∪ {(x, 0) | 2 ≤ |x| ≤ 2.5}
Y = C ∪ {(x, 0) | -1 ≤ x ≤ -.5} ∪ {(x, 0) | 2 ≤ x ≤ 2.5}
B. The fundamental group
(1) Define n-dimensional real projective space, RPn, as the quotient of Sn by the relation x ∼ -x and let qn: Sn → RPn be the quotient map. The map qn is a covering map.
a. Sketch an argument that Sn
is simply connected for n > 1. (You may use the Seifert-VanKampen Theorem, as long as you state it carefully.)
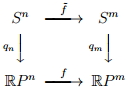
b. Let f: RPn → RPm be a continuous map. Prove that there exists a "lift" f˜ that makes the diagram below commute. Is there more than one choice for f˜? If so, how many?
(2) Let X be the union of an infinite nested family of open path-connected subspaces
U1 ⊆ U2 ⊆ · · · ⊆ Un ⊆ Un+1 ⊆ . . .
Suppose that x0 ∈ U1, and that for each n the induced homomorphism π1(Un, x0) → π1(Un+1, x0) is trivial. Prove that X is simply connected. Hint: An element of π1(X, x0) is represented by a continuous map f: I → X, and I is compact. The sets {Un} are open, so....
(3) Let f: (X, x0) → (Y, y0) be a continuous, basepoint-preserving map, and let f∗: π1(X, x0) → π1 (Y, y0) denote the induced map on fundamental groups.
a. By example, show that if f is injective, f∗ may or may not be injective.
b. By example, show that if f is surjective, f∗ may or may not be surjective.
c. If A ⊆ X is a subspace, we say that A is a "retract" of X if there exists a continuous map r: X → A such that r|A is the identity map of A. Show that if a0 ∈ A ⊆ X and A is a retract of X, then the induced map π1 (A, a0) → π1 (X, a0) is injective. Give an example that is not an isomorphism.
(4) Let f, g : (X, x0) → (Y, y0) be two continuous, basepoint-preserving maps. Suppose that f and g are homotopic, but not necessarily by a basepointpreserving homotopy.
a. Do f and g necessarily induce the same homomorphism on fundamental groups? If not, what can be said about the relationship between the induced maps? Formulate a precise statement and outline the proof.
b. Let X = S1 with the basepoint (1, 0), and let Y be the figure eight, with the basepoint in the middle of the eight. Give an example of two maps f, g: (X, x0) → (Y, y0) that are homotopic, but not homotopic by a basepoint-preserving homotopy.
C. Homology
(1) Let (C∗, dC) and (D∗, dD) be chain complexes, and let f, g: C∗ → D∗ be chain maps. Recall that f and g are said to be "chain homotopic" if for all n there exist maps Hn: Cn → Dn+1 such that f - g = HdC + dDH.
a. Let Cyl(C) be the chain complex whose nth group is Cn ⊕ Cn-1 ⊕ Cn, with differential d (x, y, z) = (dx + y, -dy, dz - y). Verify that Cyl(C) is a chain complex.
b. Prove that if f and g are chain maps from C∗ to D∗, then f and g are chain homotopic if and only if there exists a chain map Cyl (C∗) → D∗ such that H(x, 0, 0) = f(x) and H(0, 0, z) = g(z).
c. Briefly explain the analogy with a homotopy between maps f, g : X → Y of topological spaces.
(2) a. Let Z and Q denote the integers and the rational numbers, respectively. Compute the homology of RP2 with coefficients in Z, with coefficients in Q, and with coefficients in Z/2. Does anything surprise you?
b. If X and Y are spaces, let X ∪ Y denote the disjoint union of X and Y. Prove that
Hn (X ∪ Y; Z) ≅ Hn(X; Z) ⊕ Hn(Y ; Z)
What can you say about the homology groups of X ∨ Y , the one-point union of X and Y ? (Assume that X and Y are polyhedra.)
(3) Consider the following commutative diagram of abelian groups. Assume that the long row and the long column are exact.
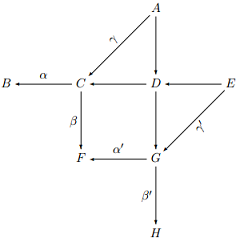
Prove that (ker(α) ∩ ker(β)/im(γ)) ≅ (ker(α') ∩ker(β')/im(γ'))
D. Essay question
You and a high school friend who majored in math at Tychonoff College (TC) are waiting at 30th Street Station for your train home. Your friend notices your topology book, and remarks that TC's topology course was hard to understand. Write a coherent essay describing a topological topic to your friend, appropriately outlining the definitions, theorems, and interesting examples. You will need make decisions about (i) what is important and interesting (be sure to include it), (ii) what is boring and technical (skip over this), and (iii) what is interesting and important but out of reach ("It turns out that...."). It is not unusual for discussion of a mathematical topic to contain a mix of the expected and the surprising.
As with diving or skating, your essay will be judged both on what you attempt and on how well you achieve it. Here are some suggestions, or you can make up your own. If there's something you worked really hard on, and didn't have an opportunity to show, this is your chance!
(1) Compactness. What is it? How should we think of this concept, and why do we care? What are the most important theorems and interesting examples (or non-examples)?
(2) Surfaces. What are they? What are the main theorems? What is surprising, and what is to be expected?
(3) Homology. What is it? How should we think of it and what good is it? What are some computational and conceptual theorems about it?
(4) Fixed point theorems. What are examples? What does one need in order to get such theorems?