Reference no: EM1343574
1,1 An experimenter uses an X-ray spectrometer which has a rotating drum scale a pointer to measure angles. A view of this scale is shown.
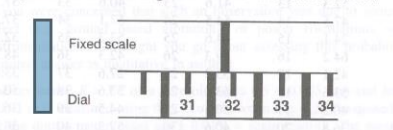
(a) It is expected to measure an X-ray peak which occurs at an angle of around 31.6g. Alter viewing the scale and pointer, with what accuracy will you quote the result?
(b) A preliminary set of measurements are made in which little care is taken in making the measurements (e.g. not always approaching from the smile direction, careless estimation of position etc). Five repeated measurements in degrees are as follows:
30,8, 31.3, 31.8., 31.7, 32.2
Is this acceptable?-if not, why not?
(c) The mechanical linkages in the spectrometer are adjusted to remove 'backlash', and care is taken to always approach the measurement in the same direction. Five repeated measurements in degrees are as follows:
31,2, 31.3, 31,7. 31.6, 31.7
Is this acceptable? If so what is the measured angle of tile peak.
1.2 (a) Using the spectrometer in Problem 1 with a calibration peak which is known to occur at 31,6 ± 0.10, a set of 10 repeated measurements give values in degrees:
30.8. 31.3, 31.2, 31.4, 31.3,
31.4, 30.9, 31.2, 31.1, 31.1
What is the systematic error in the scale setting of the spectrometer?
The correction should he added to or subtracted from the actual scale reading.
(b) The spectrometer is used to determine the position of another peak which is measured at the following angles on repeated measurements in degrees
35.1, 35.3, 34.9, 35.5, 35.1,
35.6. 35.4, 35.5. 34.8, 35.1
What is the value of the corrected peak position?
1.5 The following observations (V) were made using a voltmeter:
15, 18.5, 14.5, 19.5, 18.4. 16.5, 17.3. 15.5, 13.3
For this sample set, calculate the (a) mean value, (b) standard deviation, (c) standard deviation of the mean value. (d) State the value of the quantity, (e) In a subsequent measurement, a value of 11.5 was observed. How likely is this reading to be correct, and not due to a mistake? Justify your answer quantitatively.
1.6 If you are in the apple business and sell bags of 20 apples for $2 with a guarantee that you will replace free of cost any bags that contain a bad apple. how much money will you make selling 2000 bags if your cost of a bag is $1.00. The probability of an apple being bad is 0.006. What is the average number of bad apples per bag?
1.7 A Neutrino Observatory expects to detect 2 solar neutrinos in a 24 hour period. What is the probability of detecting 8 neutrinos over this time period?
If you were concerned that such an observation was due to some spurious effect (e.g. ground based vibrations, or power fluctuations within the instrumentation, how might you go about assessing this probability? 1.The required answer is qualitative in nature).
1.9 The resistance of a semiconductor as a function of temperature varies as R = A exp (E/KT)
where E is an activation energy of 0.71 ± 0.05 eV,
k is Boltzmann's Constant (8.63 x 10-5 eV/K) and T is the absolute temperature in degrees K. If A = 1.3 ± 0.1Ω, what is the value of the resistance R when T = 673 ± 5K? Neglect any error in the definition of k.