Reference no: EM138940
Q. 1 (Hawk-Dove) Two animals are fighting over some prey. Each can choose one of two stances: passive or aggressive. Each prefers to be aggressive if its opponent is passive, and prefers to be passive if its opponent is aggressive; given its own choice, each animal prefers the outcome when its opponent is passive to that in which its opponent is aggressive. Formulate this situation as a matrix game and find its Nash equilibria. You are free to assign payoffs for the players, but the numbers you choose should eflect the aforementioned rankings of the outcomes by each player.
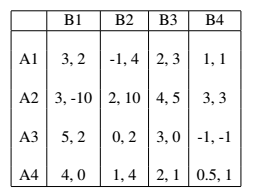
Q.2 Player 1 has the following set of strategies {A1;A2;A3;A4}; player 2’s set of strategies are {B1;B2;B3;B4}. Use the best-response approach to find all Nash equilibria.
Q.3 Two firms compete in a market. The market demand is given by the equation Q = 4-P where Q is the total quantity demanded and P is market price. Suppose firm 1 chooses a price p1 and firm 2 chooses p2. Each firm must choose a price from five possible values: 0, 1, 2 ,3, or 4 (other values are not allowed). The payoffs (profits) of the two firms are calculated by the following rules (so this is a Bertrand model):
If p1 < p2 then firm 1 receives a payoff equal to (4- p1)p1 and firm 2 receives zero payoff.
If p1 > p2 then firm 1 receives zero payoff and firm 2 receives a payoff equal to (4-p2)p2.
If p1 = p2 = p then both firms receive the same payoff (4-p)p/2
(a) Construct the payoff matrix.
(b) Is there any weakly or strictly dominant strategy for either player? If so, find all of them.
(c) Is there any weakly or strictly dominated strategy for either player? If so, find all of them.
(d) Find all of the Nash equilibria using best responses.
Q.4 Consider a variant of the Stag Hunt game. There are 12 hunters. In the following, assume only a minimum of 7 hunters are needed to capture the stag. A captured stag is equally shared only by the hunters who have chosen to hunt the stag. As before, a player gets zero payoff if he chooses Stag but the stag is not caught, and gets a payoff 1 if he chooses Hare regardless of other players’ strategies. Other things equal, a player prefers a larger share of the stag. Find all Nash equilibria for each of the following three cases (so you need to explain why some strategy profiles are Nash equilibria and why the others are not). Note that each case is a different game.
(a) Assume each hunter prefers 1=12 of the stag to a hare.
(b) Assume V /6 > 1 > V/7 , where V is the total value of the stag. In words, each hunter prefers 1/6 of the stag to a hare, but would prefer a hare to 1/7 of the stag.
(c) Assume V/7 >1> V/8 , namely, each hunter prefers 1/7 of the stag to a hare, but would prefer a hare to 1/8 of the stag.
|
Mco-15 course v : human resources management
: MCO-15 Course V : Human Resources Management, 1. “Effective Human Resources Management depends upon sound reward system”. Comment. 2. Discuss the social security measures available to workers in India.
|
|
Prepare a balance sheet
: prepare a Balance Sheet, given details attached below, Acid Test Ratio : 2.5, Current Ratio : 1.5, Net working capital Rs. 10, 00,000, Fixed Assets ?, Share holders fund Rs. 15, 00,000, Stock\ Inventory ?
|
|
Write the t statistic for testing the null hypothesis
: Explain why this model violates the assumption of no perfect collinearity. Write the t statistic for testing the null hypothesis
|
|
Operationalize sustainability
: This is designed to analyze an organization and to help develop a plan for that organization to better Operationalize sustainability in the future. This is the paper you will keep as part of your MBA Portfolio which you could show to current or futur..
|
|
Use the best-response approach to find all nash equilibria
: Player 1 has the following set of strategies {A1;A2;A3;A4}; player 2’s set of strategies are {B1;B2;B3;B4}. Use the best-response approach to find all Nash equilibria.
|
|
Perfectly competitive case
: What will the equilibrium be. How do producer and consumer surplus change from the perfectly competitive case.
|
|
Two deficits are related economically
: Carefully explain how these two deficits are related economically so that changes in one are reflected in changes in the other.
|
|
Results in the social optimum
: What is the social optimum? What specific tax per unit of output of gunk results in the social optimum.
|
|
Output rate to maximize its profits
: If each of the firms sets its own output rate to maximize its profits, assuming that the other firm holds its rate of output constant.
|