Reference no: EM133039873
Unit 39 Topics in Number and Matrix Theories - Pearson BTEC Level 5 HND in Engineering (Electrical And Electronic Engineering)
Learning Outcome 1: Use applications of number theory in practical engineering situations
P1 Apply addition and multiplication methods to numbers that are expressed in different base systems
P2 Solve engineering problems using complex number theory
P3 Perform arithmetic operations using the polar and exponential form of complex numbers
Learning Outcome 2: Solve systems of linear equations relevant to engineering applications using matrix methods
P4 Calculate the determinant of a set of given linear equations using a 3x3 matrix
P5 Solve a system of three linear equations using Gaussian elimination
Assignment brief
Purpose of this assignment
Be able to assess trainee's analytical and computational skills in solving engineering problems related to number theory and matrix theory concepts.
Scenario
You work as a technician for a company that specializes on the electrical aspects of the buildings of its clients. As a technician, your specific work focuses on making plans for the electrical installations in a building. With a range of electrical data available, your manager has asked you to do lots of analyses on the different electrical aspects that should be considered in the construction of a building.
Task 1
Question 1. Your manager understands the role of computer in engineering system. Computer data are represented as a string of 1s and 0s called binary number. Binary numbers can be conveniently expressed as octal and hexadecimal numbers. As part of your task, you were asked to add and multiply the hexadecimal and octal numbers below as binary, octal and hexadecimal numbers:
CF916 and 5438 .
To check your solution, you were also asked to use the decimal number system.
2. If the output terminals of a symmetrical T - network are open-circuited (respectively short- circuited), then the open-circuit (respectively short-circuit) impedance is given by
ZOC = ZA + ZB (respectively ZSC = ZA2 + 2ZAZB/ZA + ZB).
It is known that the characteristic impedance Z0 is given by
Z0 = √ZOCZSC .
Given that ZA = 37∠76° Ω and ZB = 28 ∠60° Ω ,
a) solve for the open-circuit impedance ZOC .
b) solve for the short-circuit impedance ZSC , in Cartesian, polar and exponential forms.
c) deduce the value of Z0 using the values of ZOC and ZSC.
Question 3. Your manager has observed that in your electrical analyses, complex numbers played a very important role. Because of the usefulness of de Moivre's Theorem in extracting roots and raising to a certain power of complex number, you were asked to prove that
sin5 θ cos6 θ = 5/512 sinθ + 5/512 sin 3θ - 5/1024 sin 5θ - 5/1024 sin 7θ + 1/1024 sin 9θ + 1/1024 sin11θ
using the theorem.
Task 2 This task provides evidence for LO2
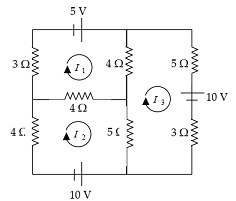
In line with your duty as a technician, your 5 V manager has shown you an electrical circuit as shown at the right. You were asked to analyze it through the system of linear equations below:
11I1 - 4I2 - 4I3 = 5
- 4I1 +13I2 - 5I3 = -10
- 4I1 - 5I2 + 17I3 = -10
1. You were asked to include in your analyses the calculation of the currents I1 , I2 and I3 (all in amperes) using Cramer's rule, Gaussian elimination and inverse matrix method.
2. In establishing the correctness of your computations, you were asked to validate your matrix solutions using appropriate computer software. You were also asked to evaluate the different methods, including the one using the computer software/package, based on their advantages and limitations in solving 3 x 3 systems of linear equations.
Attachment:- Number and Matrix Theories.rar