Reference no: EM132785793
Unit 19 Electronic Devices and Circuits - Pearson BTEC Level 3 National Foundation Diploma in Engineering
Learning aim: Explore the safe operation and applications of analogue devices and circuits that form the building blocks of commercial circuits
Assignment - Analogue electronic devices and circuits
Task 1 Carry out theoretical and practical investigations into analogue devices and circuits.
You need to investigate:
(a) Diodes and how they are used in a full-wave rectified power supply with voltage regulation
(b) Transistors and how they are used in a stabilised common emitter amplifier
(c) Operational amplifiers and how they are used in an amplifier circuit
You need to provide evidence that you have consistently worked safely in accordance with relevant risk assessments.
To do this you will need to work systematically following the guide below:
(a) Diode circuits
(i) Identify different types of diode and their uses
(ii) Construct a schematic diagram and simulate the operation of a diode as a half-wave rectifier
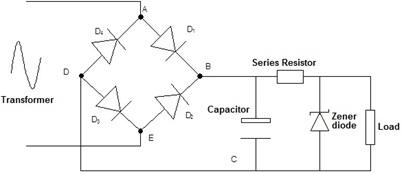
(iii) Develop the circuit schematic and simulation to a full-wave rectifier with capacitor smoothing and Zener diode voltage regulation.
(iv) Build a prototype of your final circuit
(v) Record the output voltage
(vi) Estimate the voltage ripple for different loads
(vii) Compare the results from theory, simulation and measurement
(b) Transistor circuits
(i) Identify different types of transistor and their uses
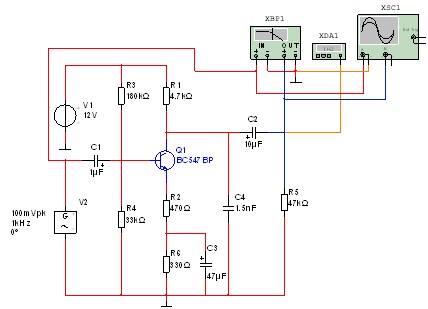
(ii) Construct the schematic circuit of a common emitter amplifier in your ECAD package.
(iii) Use the schematic to simulate the behavior of the circuit with a low voltage sine wave input signal of frequency 1kHz. Adjust the amplitude of the input voltage to give the largest undistorted output voltage.
(iv) Investigate how the voltage gain changes with frequency between 10Hz and 1MHz.
(v) Build a prototype of the final circuit and measure the voltage gain for the same frequency range.
(vi) compare the results from theory, simulation and measurements
(c) Operational amplifier circuits
(i) Identify the pin-out of an operational amplifier and relate it to the schematic diagram
(ii) Simulate inverting and non-inverting amplifier applications of an operational amplifier, noting the effect of resistor values on the voltage gain.
(iii) Construct the schematic diagram of aninverting amplifier with gain of 10
(iv) Simulate the gain at frequencies between 10Hz and 1MHz
(v) Build a prototype circuit and measure the voltage gain over the same range of frequencies
(vi) Compare the results from theory, simulation and measurements.
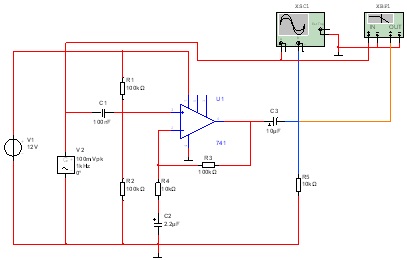
Non-inverting amplifier
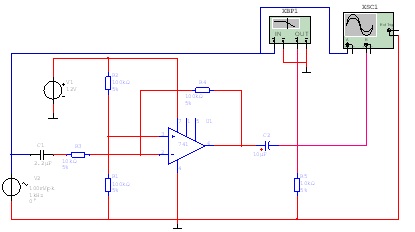
Inverting amplifier
Unit 8 Further Engineering Mathematics - BTEC Level 3 National Extended Diploma in Engineering
Assignment 1: Using sequences and series to solve engineering problems
Scenario:
You have applied for a work placement at a local company as part of your training as a quality control (QC) and in-service Engineer. The company Training Manager has explained that there are a number of roles available that involve applying mathematical skills and knowledge.
The Training Manager has said that they would like to see how you approach solving engineering problems before deciding on the most appropriate role for you. This is the second set of problems that they have provided. The problems are based on matrices, determinants and complex numbers.
Task 1
You have been asked to explore a range of engineering problems that will require you to solve problems based around sequences and series
To do this:
Your tutor will provide you with a set of data for you to use to complete the following activities. You need to:
1 Use your given sequences to answer the questionsuse series A, B and D
|
Series A
|
1, -1, -3, -5, -7 ...
|
|
Series B
|
4, 2, 1, 0.5, 0.25 ...
|
|
Series C
|
6, 7, 8, 9, 10 ...
|
|
Series D
|
4, 5, 7, 10, 14 ...
|
|
Series E
|
1, 10, 100, 1000, 10000 ...
|
|
Series F
|
2, 5, 8, 11, 14 ...
|
|
Series G
|
1, -1, 1, -1, 1 ...
|
|
Series H
|
1, 4, 9, 16, 25 ...
|
(a) Identify which of your given sequences is
(i) an Arithmetic Progression (AP)
(ii) a Geometric Progression (GP)
(iii) neither an AP or a G
(b) Identify for your AP,
(i) the first term (a)
(ii) the common difference (d)
(iii) the 10th term
(iv) the sum of the first 10 terms
(c) Identify for your GP,
(i) the first term (a)
(ii) the common ratio (r)
(iii) the 8th term
(iv) the sum of the first 8 terms
(v) whether the GP is convergent,(give reasons).
(d) Explain why the other sequence is neither an AP or a GP
2 A tunnelling machine drills 500 metres. Use your values from the table to estimate the cost of drilling if the first metre costs £1000 and each extra metre costs £100.
3 A motor has 5 speeds varying from 10 rpm to 160 rpm in a Geometric Progression.
(a) Calculate the common ratio
(b) Make a table of the speeds.
4 A CNC machine centre costs £100,000. Its value depreciates at 1.0% per annum.
(a) What will be its value after 2 years?
(b) How long will it take to have a value of £50,000?
5 Use Pascal's triangle to expand your binomial expression A.
|
A
|
(1+x)3
|
|
B
|
(1-x)3
|
|
C
|
(1+x)4
|
|
D
|
(1-x)4
|
|
E
|
(1+2x)3
|
|
F
|
(1-2x)3
|
6 Use thebinomial theorem to expand the same binomial expression as question 5.
7 Use the binomial theorem to expand your binomial expression up to and including the term in x^3and state the range of values of A for which the expansion is valid.
8 Write the first four terms of a Maclaurin seriesfor f(x)= e^x
9 Use your value of 1 to calculate a value for ? e?^xfrom the first four terms. Compare the answers to questions 7 and 8.
10 You have carried out an experiment to investigate the effect of the length of a pendulum on the time period of oscillation. Theory says that the pendulum should follow the rule T=2π√(L/g)
Where T is the time period (seconds)
L is the length of the pendulum (metre)
G is the acceleration due to gravity (g=9.81m/s2)
Calculate the expected percentage error in the time period calculation if your measurement of length is 1% high.
Assignment 2- Using matrices, determinants and complex numbers to solve engineering problems.
Purpose of this assignment:
Examine how matrices, determinants and complex numbers can be used to solve engineering problems
Scenario:
You have applied for a work placement at a local company as part of your training as a quality control (QC) and in-service Engineer. The company Training Manager has explained that a number of roles available that involve applying mathematical skills and knowledge.
The Training Manager has said that they would like to see how you approach solving engineering problems before deciding on the most appropriate role for you. This is the second set of problems that they have provided. The problems are based on matrices, determinants and complex numbers.
You have been asked to explore a range of engineering problems that will require you to solve problems involving matrices, determinants and complex numbers.
To do this:
Your tutor will provide you with a set of data for you to use to complete the following activities. You need to:
1 Use your given matrices to solve the problems. Give reasons if the procedure is not possible.
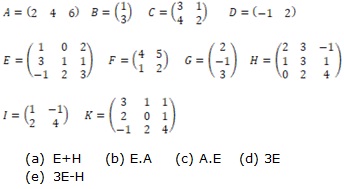
2 Calculate the determinant of each of your given 2x2 and 3x3 matrices
3 Solve your given pair of simultaneous equations (with two variables) using matrix and determinant methods.
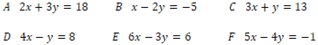
Solve for A and F
4 Solve your given set of simultaneous equations (with three variables) using matrix and determinant methods.
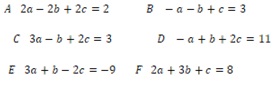
Solve for B, C and D
5 Solve your given pair of complex numbers placing them on an Argand diagram.
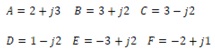
(a) XA+F
(b) YF-A
6 Convert your pair of complex numbers to polar form
7 Complete multiplication and division of your pair of complex numbers in polar form
(a) X A.F
(b) X A/F
8 Convert the answers to rectangular (Cartesian) form
9 The two complex numbers A and F represent two reactance's connected in series.
Calculate the total reactance by finding their sum.
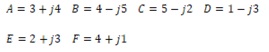
10 The complex numbers A and F represent two force vectors. Place them on an Argand diagram and calculate the difference between them.
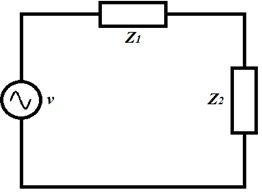
11 Use your given values of A and F to represent the reactances Z1, Z2 (as shown in the circuit diagram).
Calculate the current flowing in the circuit in polar form if the voltage is v = 12∠0° and i = ZTotal.
Assignment 3: Using statistics and probability techniques to solve engineering problems
Purpose of this assignment:
Investigate how statistical and probability techniques can be used to solve engineering problems
Scenario:
You have applied for a work placement at a local company as part of your training as a [enter specific route] Engineer. The company Training Manager has explained that there are a number of roles available that involve applying mathematical skills and knowledge. The Training Manager has said that they would like to see how you approach solving engineering problems before deciding on the most appropriate one for you. The final set of problems that they have provided are based on statistics and probability techniques, which they would like you to solve using the supplied data.
The Training Manager has asked you to use the data for Candidate number [write in candidate number]
1. Use the ungrouped data that you have been supplied with to complete the following:
Use table 1 given below and use your given set number
(a) Arrange the data into equal classes
(b) Determine the frequency distribution
(c) Draw the frequency histogram
(d) Create a cumulative frequency table for the data
(e) Draw the cumulative frequency graph
(f) Use your cumulative frequency graph to determine if the data is normally distributed or not?
(g) Calculate:1)the mean and standard deviation; 2) the upper and lower quartile values; 3) the inter-quartile range for the given data. Use table 2 given below and use your given set number
2. Use the table of measurements of length and force that you have been supplied with to complete the following activities:
(a) Draw a scatter graph for your given data.
Describe what the scatter graph is indicating.
(b) Use the scatter graph to estimate the length for a force of 57N
(c) Calculate the line of regression of extension on force (Y on X)
(d) Calculate the regression coefficient
(e) Explain what the regression coefficient indicates?
(f) Use the equation for the line of regression to predict the length for a force of 57N
(g) Compare the calculated value with the value that you have determined from the scatter graph.
Attachment:- Electronic Devices and Circuits.rar