Reference no: EM132882494
ITECH2301 Network Architecture and Design - Federation University
Assessment Objective
- This assignment provides an opportunity to understand the techniques and protocols used in the layers of TCP/IP network (Internet) model
Learning Outcome 1: Explain the technologies and protocols of physical, data link, network and transport layers.
Learning Outcome 2: Analyse data communication and networking technologies in today's Internet.
Learning Outcome 3: Analyse data communication and networking technologies in today's Internet.
Requirements
1. Fig. 1 illustrates how a message is transmitted from the application layer to the physical layer in the Internet model of a data communication network.
a. With the aid of the diagrams of header formats, explain the main purpose of all fields of the header formats of the transport, network, and data link layers protocols. For example, the main purpose of the source address and destination address of an IP Header is to provide the sender and receiver IP addresses, respectively. Note, for IP header, include IPv4 packet header format only i.e., you do not need to consider IPv6 packet header format.
Using the Wireshark protocol analyser, capture all packets generated in response to your request for the above web page. For a selected pair of the first HTTP request-response lines, write the hex/decimal values of all fields of the header formats of the transport, network and data link layers protocols whatever available in your file captured by Wireshark.
Note, HTTP request packet and response packet are identified by the following ways:
HTTP Request - GET / HTTP/1.1 HTTP Response- HTTP/1.1 200 OK
However, if you use Wi-Fi (WLAN) and are not in monitor mode, Wireshark does not show HTTP protocols. Note, monitor mode is not supported by WinPcap, and thus not by Wireshark or TShark, on Windows (https://wiki.wireshark.org/CaptureSetup/WLAN). In this case, any sorts of packets, such as from the client to the server (e.g., Client Hello) and from the server to the client (Server Hello) will be accepted as request packet and response packets, respectively.
• The application Layer uses the HTTP protocol
• The transport layer uses the TCP (Transmission Control) Protocol
• The network layer uses The IP (Internet) Protocol
• The data link layer of the LANs typically uses the Ethernet protocol
• Protocol Data Units
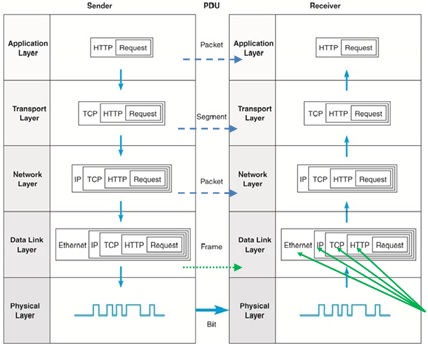
Fig. 1: Message transmission through layers.
2. Signaling (Encoding) and Modulation Techniques
Draw how the bit pattern 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 would be sent using
a. Unipolar signalling
b. Return to zero (RZ) signalling
c. Non return to zero (NRZ) signalling
d. Manchester encoding
e. Amplitude Modulation (AM)
f. Frequency Modulation (FM)
g. Phase Modulation (PM)
N.B. You can draw the bit pattern on papers and insert them as pictures into your document.
Which of the above mentioned signaling (encoding) techniques [refer to 2.1 (a)-(d)] you think is the best? Please justify your answers with some supporting evidence.
3. Answer the following question on media access control:
a. List two examples of controlled access and contention-based media access protocols and their application areas.
4. Briefly describe why you think the Web of Things will change the way people live.
Attachment:- Network Architecture.rar