Reference no: EM133692595
Database Management Systems
Learning Objectives
- Use SQL to create a table manually
- Use SQL to create a copy of a table using a subquery
- Manipulate the structure of existing tables to add, modify, and remove columns and constraints
- Use SQL to do data manipulation (insert, update, and delete rows of data)
- Use SQL to create database views, including updatable views
- Use Procedural Language SQL (PL/SQL) to create triggers, stored procedures, and PL/SQL functions
- Create embedded SQL
Assessment Details: Advanced SQL
Question 1: What type of integrity is enforced when a primary key is declared?
Question 2: Explain why it might be more appropriate to declare an attribute that contains only digits as a character data type instead of a numeric data type.
Question 3: What is a trigger, and what is its purpose? Give an example?
Question 4: The ConstructCo database stores data for a consulting company that tracks all charges to projects. The charges are based on the hours each employee works on each project. The structure and contents of the ConstructCo database are shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: ConstructCo Database
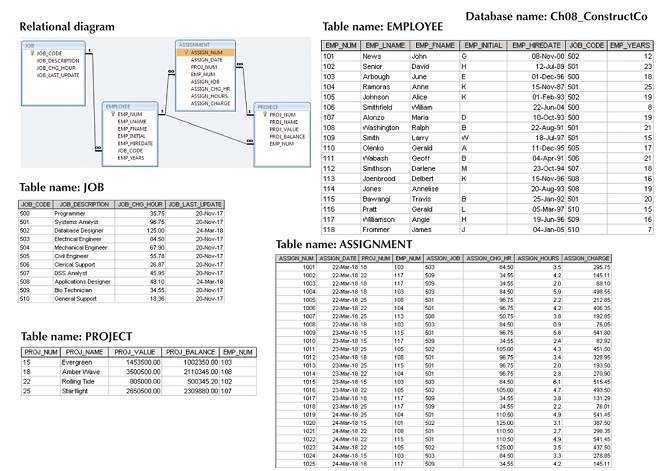
Given the structure and contents of the ConstructCo database shown in Figure 1, use SQL commands to answer following exercises
a. Download the following file from Moodle: Week 8: 08_ConstructCo_MySQL.txt
b. Import the file 08_ConstructCo_MySQL.txt into XAMPP.
c. Write the SQL code that will create only the table structure for a table named EMP_1. This table will be a subset of the EMPLOYEE table. The basic EMP_1 table structure is summarized in the following table. Use EMP_NUM as the primary key. Note that the JOB_CODE is the FK to JOB so be certain to enforce referential integrity. Your code should also prevent null entries in EMP_LNAME and EMP_FNAME.
ATTRIBUTE (FIELD) NAME DATA DECLARATION
EMP_NUM CHAR(3)
EMP_LNAME VARCHAR(15)
EMP_FNAME VARCHAR(15)
EMP_INITIAL CHAR(1)
EMP_HIREDATE DATE
JOB_CODE CHAR(3)
d. Having created the table structure in 4 (c), write the SQL code to enter the first two rows for the table shown in Figure 2. Each row should be inserted individually, without using a subquery. Insert the rows in the order that they are listed in the figure.
Figure 2 The EMP_1 Table
| EMP_NUM |
EMP_LNAME |
EMP_FNAME |
EMP_INITIAL |
EMP_HREDATE |
JOB_CODE |
| 401 |
News |
John |
G |
8-Nov-00 |
502 |
| 102 |
Senior |
Davie |
H |
12-Jul-89 |
501 |
| 103 |
Arbough |
June |
E |
1-Dec-96 |
500 |
| 104 |
Ramoras |
Anne |
K |
15-Nov-87 |
501 |
| 105 |
Johnson |
Alice |
K |
1-Feb-93 |
502 |
| 106 |
Smithfield |
william |
|
22-Jun-04 |
500 |
| 107 |
Alonzo |
Maria |
D |
10-Oct-83 |
500 |
| 108 |
Washington |
Ralph |
B |
22-Aug-81 |
501 |
| 109 |
Smith |
Larry |
w |
18-Jul-97 |
501 |
e. Using the EMPLOYEE table that already exists, use a subquery to insert the remaining rows from the EMPLOYEE table into the EMP_1 table. Remember, your sub- query should only retrieve the columns needed for the EMP_1 table and only the employees shown in the figure.
f. Write the SQL code to change the job code to 501 for the person whose employee number (EMP_NUM) is 107.
g. Write the SQL code to delete the row for William Smithfield, who was hired on June 22, 2004, and whose job code is 500. (Hint: Use logical operators to include all of the information given in this problem.)
h. Write the SQL code to create a copy of EMP_1, including all of its data, and naming the copy EMP_2.
i. Using the EMP_2 table, write the SQL code that will add the attributes EMP_PCT and PROJ_NUM to EMP_2. The EMP_PCT is the bonus percentage to be paid to each employee. The new attribute characteristics are:
EMP_PCT NUMBER(4,2) PROJ_NUM CHAR(3)
Note: If your SQL implementation requires it, you may use DECIMAL(4,2) or NUMERIC(4,2) rather than NUMBER(4,2).
j. Using the EMP_2 table, write the SQL code to change the EMP_PCT value to 3.85 for the person whose employee number (EMP_NUM) is 103.