Reference no: EM13957648
PRoblem 1: (1) Two firms have technologies for producing identical paper clips. Assume that all paper clips are sold in boxes containing 100 paper clips. Firm A can produce each box at unit cost of cA = $6 whereas firm B (less efficient) at a unit cost of cB = $8.
(a) Suppose that the aggregate market demand for boxes of paper clips is p = 12 − Q/2, where p is the price per box and Q is the number of boxes sold. Solve for the Nash-Bertrand equilibrium prices p b A and p b B, and the equilibrium profits π b A and π b B. Explain your reasoning!
(b) Answer the previous question assuming that firm A has developed a cheaper production technology so its unit cost is now given by cA = $2.
Problem 2: Consider an infinitely-repeated price competition game between GM and FORD. Each firm can set a high price or a low price in each period t = 0, 1, 2, . . .. The profit of each outcome are given in the following matrix:
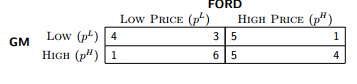
Suppose that each firm adopts a trigger-price strategy under which the firms may be able to implicitly collude on setting the high price. Let ρ (0 < ρ < 1) denote the time discount factor.
(2a) Compute the minimum threshold value of ρ which would ensure that GM sets p H in every period t. Show and explain your derivations
(2b) Compute the minimum threshold value of ρ which would ensure that FORD sets p H in every period t. Show and explain your derivations.
Problem 3:
(3) Aike (Brand A) and Beebok (Brand B) are leading brand names of fitness shoes. The direct demand functions facing each producer are given by qA(pA, pB) = 180 − 2pA + pB and qB(pA, pB) = 120 − 2pB + pA. Assume zero production cost (cA = cB = 0).
(a) Derive the price best-response function of firm A as a function of the price set by firm B, pA = BRA(pB). Show your derivations, and draw the graph associated with this function.
(b) Derive the price best-response function of firm B as a function of the price set by firm A, pB = BRB(pA). Show your derivations, and draw the graph associated with this function.
(c) Solve for the Nash-Bertrand equilibrium prices, hp b A, pb Bi. Then, compute the equilibrium output levels hq b A, qb Bi, the equilibrium profits hπ b A, πb Bi, and aggregate industry profit Πb = π b A + π b B.
(d) Suppose now that the two producers hold secret meetings in which they discuss fixing the price of shoes to a uniform (brand-independent) level of p = pA = pB. Compute the price p which maximizes joint industry profit, πA + πB. Then, compute aggregate industry profit and compare it to the aggregate industry profit made under Bertrand competition which you computed in part (3c).
Problem 4: Ann Arbor and Ypsilanti are very similar cities, because each city has exactly one McDonald’s. Ann Arbor has NA = 200 residents and Ypsilanti has NY = 200 residents. Each resident demands one hamburger. A resident of Ann Arbor who wishes to buy a hamburger in Ypsilanti must bear a transportation cost of TA = $3. Similarly, a resident of Ypsilanti who wishes to buy a hamburger in Ann Arbor must bear a transportation cost of TY = $3.
(4a) Solve for the undercut-proof equilibrium prices p U A and p U Y and profit levels π U A and π U Y assuming that McDonald’s has the technology for producing hamburgers at no cost. Show your derivation.
(4b) Answer the previous question assuming now that McDonald’s in Ann Arbor bears a cost of $1 of producing each hamburger, whereas McDonald’s in Ypsilanti bears a cost of $4 of producing each hamburger. Show your derivation.
|
Develop a linear trend line model for the freshman
: Develop a linear trend line model for the freshman applications data at State University in problem 1.
|
|
What is the probability that it is neither red nor an ace
: You have a regular deck of 52 cards. You remove one card. You look at the card and see that it is the 8 of Clubs. You DO NOT put the 8 of clubs back in the deck. You choose another card at random. Before you look at it,
|
|
Compile a marketing strategy to change consumers
: The overall purpose of the assessment is for you to demonstrate an advanced and integrated understanding of a complex body of knowledge - Explain and analyse nominatedvalue proposition and marketing mix strategy
|
|
Never dispel gains from currency fluctuations
: Although a company would never dispel gains from currency fluctuations, they truly hate accounting for the losses. This is why minimizing risk is so important. It is absolutely necessary to retain a firm's profits from selling a product or providi..
|
|
Two firms have technologies for producing identical paper
: Two firms have technologies for producing identical paper clips. Assume that all paper clips are sold in boxes containing 100 paper clips. Firm A can produce each box at unit cost of cA = $6 whereas firm B (less efficient) at a unit cost of cB = $8.
|
|
What is the probability that addie picked the second box
: Addie, who is blindfolded, selects a box at random and draws one envelope from the box. The envelope contains a $5 bill. What is the probability that Addie picked the second box?
|
|
Legal contract using example from scenario where application
: Jim and Laura Buyer visit the local car dealership because they are interested in buying a new car. The car they currently have is aging and is starting to have mechanical problems. Jim and Laura would share the new car, and use it to go back and ..
|
|
What is the probability that the sum of the two is even
: Possible combinations (1,4), (1,5), (1,6), (2,4), (2,5), (2,6), (3,4), (3,5), and (3,6) for a total of 9 possible combinations.
|
|
Sections from the texas bill of rights
: Pick any of the sections from the Texas Bill of Rights What is the right that is mentioned? What does it mean (in your own words)? Find a Supreme Court case (US or Texas) dealing with the issue brought up by the right you are mentioning. What wer..
|