Reference no: EM13837426
1. For each of the following economic conditions, place an X in the table to indicate theappropriate range in the Aggregate Supply Curve
|
Condition
|
Keynesian
|
Intermediate
|
Classical
|
|
Unemployment is above the historical average
|
|
|
|
|
The nation's factories are running at capacity
|
|
|
|
|
Any increase in GDP will be accompanied by high inflation
|
|
|
|
|
The nation is suffering through a severe recession
|
|
|
|
|
A mid-point in the business cycle expansion phase
|
|
|
|
|
GDP can increase without an increase in the Price Index
|
|
|
|
2. Many exogenous factors can cause a shift in the Aggregate Supply Curve. For each of the following factors, place an X in the table to indicate how the AS curve would shift.
|
Factor
|
AS shift right (increase in AS)
|
AS shift left (decrease in AS)
|
|
World oil prices increase substantially
|
|
|
|
Environmental Protection Agency enacts broad pollution restrictions
|
|
|
|
Business taxes are reduced
|
|
|
|
Internal combustion engine fuel efficiencies are greatly increased
|
|
|
|
Adverse winter weather persists for months more the normal
|
|
|
|
New restrictions slow immigration
|
|
|
|
Federal minimum wage is increased by 30%
|
|
|
3. Earlier we learned that Demand, which we now call Aggregate Demand, is comprised of 4 components: Consumption (C), Investment (I), Government spending (G), and Net Exports (NE). Any exogenous factor that increases any of the component(s) will also increase Aggregate Demand. For each of the following, place an X to indicate the component affected and an R (increase) or and L (decrease) to show whether the AD curve shifts Right or Left. Consider only the primary effect.
|
Factor
|
C
|
I
|
G
|
NE
|
R or L
|
|
Real interest rate decreases
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Consumers and executives become more confident in the economic future
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The stock market rises
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
China's economic growth slows
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Congress increases spending for in the currentfiscal year
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Tariffs are imposed by many countries to protect domestic employment
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The US Import/Export bank eliminates guarantees for loans to foreign airlines to purchase Boeing aircraft
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Congress enacts tax incentives for firms purchasing new equipment and facilities
|
|
|
|
|
|
4. For each of the following government economic actions, place an X in the table to indicate whether the action is fiscal or monetary policy.
|
Action
|
Monetary
|
Fiscal
|
|
Taxes are increased on the wealthiest 1% of households
|
|
|
|
The Fed purchases Mortgage-backed securities (MBS)
|
|
|
|
The US Treasury borrows money to finance increased government spending
|
|
|
|
The federal government provides a rebate to first time home buyers
|
|
|
|
The President signs and enacts the Affordable Care Act
|
|
|
|
The Fed promises to keep interest rates near zero for an extended time
|
|
|
5. For each of the following government actions, insert the original and shifted AD curve. Insert an arrow to show the shift in the AD curve. Here's an example:
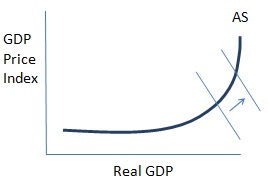
a. While in a steep recession, the federal government enacts a stimulus program of increased spending and reduced taxes. Inflation does not increase.
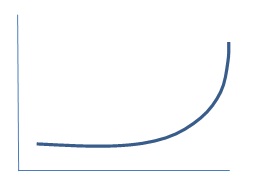
b. In Argentina, the government increases spending in order to win more votes in the upcoming election. Inflation increases substantially but GDP increases slightly (demand pull inflation).
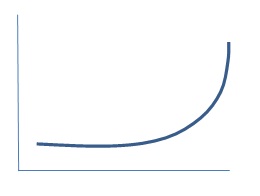
c. The central bank lowers interest rates to near zero, C and I increase modestly and inflation remains below the target rate of 2% annually.
d. A housing market bubble collapses, the economy enters a recession but previously high inflation falls to near zero.