Reference no: EM13963091
Question 1. Define briefly:
(a) the fault level of a system or unit in a system
(b) base MVA.
State:
(c) the equation for percentage impedance or impedance voltage
(d) the relationship between X% and X pu
(e) the units of X% and X pu
(f) X pu in terms of the fault level. MVA and the base MVA.
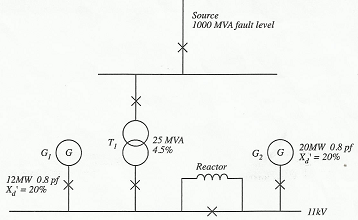
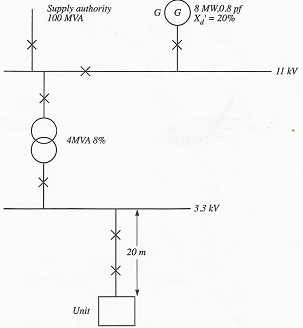
Question 2. Draw the individual and combined impedance (X pu) diagrams to a base of 10 MVA for the units and system shown in FIGURE 1. Determine the system fault MVA and fault currents at the 11 kV and 3.3 kV busbars. Show all working.
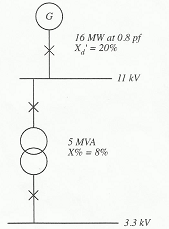
Question 3. For the system shown in FIGURE 2, using a 10 MVA base, calculate the fault MVA levels through each unit and the base "voltage" MVA across each unit for a fault at F. Draw the impedance diagrams showing the fault levels and the base "voltage" MVA across each unit for:
(a) bus section switch B open and A open
(b) bus section switch B closed and A open.
Other circuit breakers are closed.
The generators have the same rating and characteristics.
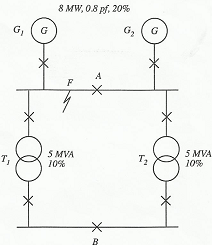
Question 4. FIGURE 3 shows part of an electrical supply system. Draw the impedance diagrams reducing to a single impedance. Calculate the fault MVA levels in each unit for a fault on the left 3.3 kV bus with the bus-section switch B open and A closed. Use a base MVA of 10 and show the fault MVA levels on a diagram. Comment on the result and suggest a method of improving the system to limit the fault MVA through T1 to approximately 5 x FL current. (It is not necessary to recalculate.)
Question 5. Given the relationships:
X pu = MVA base/MVA fault
= (MVA base/MVA rated) x X%/100
fault MVA = √3VIfault
XΩ = V/√3 Ifault
show that (a) Fault MVA = MVA rated/X% x 100
(b) X pu = MVA base V2 x XΩ
and hence calculate the pu impedance of 100 m of 3 single core 415 V cables in trefoil. Take the cable impedance to be 90 microhms per metre. Use a 1 MVA base. Neglect the resistance of the cables.
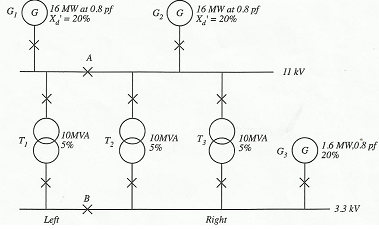
Question 6. (i) For the system shown in FIGURE 4, determine the fault level for a fault on the cable at the 3.3 kV unit shown when the bus section switch is closed. The cable impedance is 90 microhms per metre. Neglect cable resistance and use a base of 10 MVA.
(ii) What would be the effect on the fault level of replacing the unit shown in FIGURE 4 with a running motor?
Question 7. Determine the pu impedance and the reactance of the interbus reactor for the system shown in FIGURE 5, if generator G2 is to be used. The switchgear rating is 500 MVA. Use a 10 MVA base and assume all circuit breakers are closed, except' the 11 kV bus section circuit breaker, and the inter bus reactor is in service.