Reference no: EM133096527
Question 1: Consider a gas of N particles, in volume V at absolute temperature T. The parameter b in the volume of one particle, and k is the Boltzmann constant. Here are two differentials of pressure, possibly derived from the equation of state of this substance:
dp = {-Nk/T2/(V - Nb)2]dV + {-2Nk/(V -Nb)}dT}
dp = {-NkT/(V - Nb)2]dV + [Nk/(V -Nb)}dT}
-
One of theme is correct; the other one is impossible. Explain which one is correct, then derive the original equation of state from which the correct differential was derived.
Question 2: A step pn junction diode having Na=1016/cm3 and Nd = 4 x 1018/cm3 values was false
A step pn junction diode having Na=1016/cm3 and Nd = 4 x 1018/cm3 values was fabricated.
T = 300K, applied voltages VA = -3 and 0.4V were respectively applied. ni=1.5x1010/cm3.
a. Check if the low-level injection condition is satisfied when the forward voltage 0.4 V is applied.
b. Calculate how the magnitude of the energy barrier between p- and n-type semiconductors changes when forward and reverse voltages are applied
c. VA = -3 and 0.4V: Calculate the width(W) of the depletion layer in each of these conditions and explain the result.
d. Calculate and plot how the electric field, E(x), changes when forward and reverse voltages are applied.
Question 3: The free energy F of a compressible solid (einstein's elastically coupled oscillators model) has the following form as a function of temperature T and volumen V:
F(T, V) = Fo(V) + ATln(1 - e-E(V)/KBT)
with
F0(V) = B/2V0 (V - V0)2
and E(V) given by:
E(V) = E0 - E1(V- V0)/Vo
and A, B, E0, E1 positive constants.
1. Calculate the presion P, entropy S and internal energy U as a function of T and V. If you can, Express the result with the Bose Function
n(T, V) = (eE(V)KBT -1)-1
2. Estimate, at the lowest not null order on El, the diference in Cp - Cv of the heat capacities.
Question 4: Some student asked me whether the m0 (rest mass of electron) shall be in the denominator in HW1-1 (a), so the question is to prove following.
Δω = ω - ω' = hk2/2(1/me + 1/mh)
Stoke effect of semiconductor
Consider a direct bandgap semiconductor is excited by a laser light with photon energy hw. Since the excitation is weak, most of the carriers will relax to the band edge and recombine to generate PL with photon energy hω'.
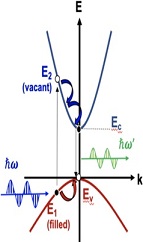
(a) Show that:
Δω = ω - ω' = hk2/2(1/me + 1/mh)
(b) Consider GaN (E0 = 3.45eV) is excited by He-Cd laser (λ = 325 nm). The effective mass of electrons and holes are 0.2m0 and 1.2m0, respectively. What's the allowed k for excitation?
Please express kin the unit of nm-1.
(c) What's the amount of wavelength Stoke shift between excitation source and the PL peak in nm?
Question 5: (a) If a sample of gas is kept in complete thermal isolation from its surroundings, then show that the work done on this system will be W = 1/γ-1 (pfvf - pivi,), where the symbols have their usual meaning