Reference no: EM131296071
Part I:
Q1. Which of the following does NOT affect potential GDP?
A) the quantity of money B) the quantity of labor employed
C) the quantity of capital and human capital
D) the amount of entrepreneurial talent available
Q2. Moving along the potential GDP line, when the price level changes, the
i. real wage rate stays at the full-employment equilibrium level.
ii. money wage rate changes by the same percentage.
iii. money prices of non-labor resources change by the same percentage.
A) i only B) ii only C) iii only D) i and ii E) i, ii, and iii
Q3. A fall in the real wage rate firms' profits and leads to in the quantity supplied.
A) raises; an increase B) raises; a decrease C) lowers; an increase
D) lowers; a decrease E) does not change; no change
Q4. The aggregate supply curve is a(n) curve because it represents the relationship between price level and the quantity of real GDP supplied, two items that are correlated.
A) upward-sloping; negatively B) downward-sloping; positively
C) upward-sloping; positively D) downward-sloping; negatively
Q5. Moving along the aggregate supply curve, when the price level rises,
A) the quantity supplied does not change because the aggregate supply curve is a vertical line.
B) the quantity supplied increases. C) the quantity supplied decreases.
D) the aggregate demand curve shifts rightward.
E) the aggregate demand curve shifts leftward.
Q6. ) During 2010, a country reports that its price level fell and the money wage rate did not change. These changes led to
A) a higher real wage rate, lower profits, and a decrease in the quantity of real GDP supplied.
B) a higher real wage rate, higher profits, and an increase in the quantity of real GDP supplied.
C) a lower real wage rate, lower profits, and a decrease in the quantity of real GDP supplied.
D) a lower real wage rate, higher profits, and an increase in the quantity of real GDP supplied.
Q7. ) If the price level rises but the money wage rate does not, then firms will hire labor and the quantity of real GDP supplied will .
A) more; increase B) the same amount of; not change
C) less; decrease D) more; not change
E) less; increase
Q8. Which of the following changes aggregate supply and shifts the aggregate supply curve?
i. change in the price level
ii. change in potential GDP
iii. change in the money wage rate
A) i only B) ii only C) iii only
D) ii and iii E) i, ii, and iii
Q9. An increase in the money wage rate and an increase in the money prices of raw materials .
A) shifts the AS curve rightward; shifts the AS curve rightward
B) shifts the AS curve leftward; shifts the AS curve leftward
C) shifts the AS curve rightward; shifts the AS curve leftward
D) shifts the AS curve leftward; shifts the AS curve rightward
E) shifts the AS curve leftward; does not shift the AS curve'
Q10. The aggregate supply curve shifts rightward when
A) potential GDP decreases.
B) the money wage rate falls.
C) income taxes increase.
D) government purchases increase.
E) the money wage rate rises.
Q11.
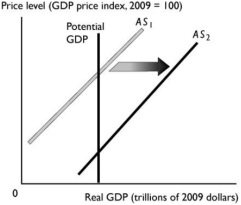
The change reflected in the above figure might be a result of
A) a decrease in the money wage rate. B) a decrease in the real wage rate.
C) an increase in the money wage rate. D) an increase in the real wage rate.
E) a rise in the price level.
Q12.
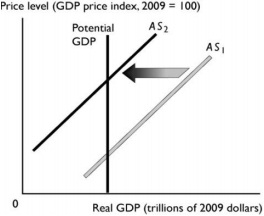
The change reflected in the above figure might be a result of
A) a decrease in the quantity of capital. B) an increase in the quantity of labor.
C) a rise in the money wage rate. D) a fall in the price level
E) a decrease in the money prices of resources other than labor.
Q13. Which of the following produces a movement along the aggregate demand curve and does not shift the aggregate demand curve?
A) a change in foreign incomes B) a change in the price level
C) a change in monetary policy D) a change in expectations about the future
E) a change in government expenditures on goods and services
Q14. A rise in the price level brings a in the buying power of money that consumption expenditures and causes the quantity of real GDP demanded to .
A) rise; decreases; decrease B) fall; decreases; decrease
C) fall; increases; increase D) rise; increases; increase
Q15. Which of the following does NOT shift the aggregate demand curve?
A) a change in the money wage B) a change in expectations about the future
C) a change in monetary policy D) a change in fiscal policy
E) a change in foreign income
Q16. All of the following shift the aggregate demand curve to the right EXCEPT
A) an increase in taxes. B) an expansion of the global economy.
C) an increase in foreign income. D) an increase in government expenditure.
E) an increase in expected future profit
Q17. If firms' expectations about the future become pessimistic so that they think future profits will be lower, then
A) aggregate demand decreases and the AD curve shifts leftward.
B) aggregate demand increases and the AD curve shifts rightward.
C) the quantity of real GDP demanded decreases, and there is a movement up along the AD curve.
D) the quantity of real GDP demanded increases, and there is a movement down along the AD curve.
E) the aggregate demand curve does not shift, but potential GDP decreases.
Q18. If a country is trying to recover from a recent recession, it is unlikely their government officials will decide to because it would _ .
A) lower interest rates; decrease aggregate demand
B) raise interest rates; decrease aggregate demand
C) raise interest rates; increase aggregate demand
D) institute a tax cut; increase aggregate demand
E) increase taxes; increase aggregate demand
Q19. A decrease in foreign income exports of U.S.-made goods, so aggregate demand
and the aggregate demand curve shifts .
A) increases; increases; rightward B) decreases; decreases; leftward
C) decreases; increases; rightward D) increases; increases; leftward
Q20. A macroeconomic equilibrium occurs when the
A) quantity of real GDP demanded is greater than the quantity of real GDP supplied.
B) quantity of real GDP demanded is less than the quantity of real GDP supplied.
C) quantity of real GDP demanded equals the quantity of real GDP supplied even if they are not equal to potential GDP.
D) quantity of real GDP demanded equals the quantity of real GDP supplied and both equal potential GDP.
E) None of the above answers is correct
Q21. Starting from a situation of full employment, an increase in aggregate demand creates
and the price level.
A) an inflationary gap; raises B) a recessionary gap; lowers
C) a recessionary gap; raises D) an inflationary gap; lowers
Q22. A recessionary gap occurs when so that real GDP is potential GDP.
A) aggregate supply increases; less than
B) aggregate supply decreases; less than
C) aggregate demand increases; greater than
D) aggregate demand decreases; less than
E) potential GDP decreases; greater than
Use the figure below to answer Q23-24
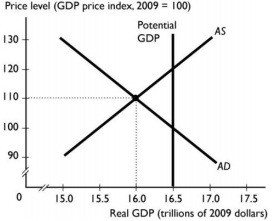
Q23. In the figure above, the economy is at an equilibrium with real GDP of $16 trillion and a price level of 110. At this point there is
A) an inflationary gap. B) a recessionary gap.
C) price stability. D) a full-employment equilibrium.
E) an above full-employment equilibrium
Q24. In the figure above, the economy is at an equilibrium with real GDP of $16 trillion and a price level of 110. As the economy moves toward its ultimate equilibrium, the curve shifts because . (self-correction machanism)
A) aggregate supply; leftward; the money wage rate rises
B) aggregate supply; rightward; the money wage rate falls
C) aggregate demand; rightward; the money wage rate falls
D) aggregate demand; leftward; the money wage rate rises
E) potential GDP; leftward; the money wage rate falls
Q25.A country is on its aggregate production function. If the adult population increases with no change in the country's capital or technology, .
A) the real wage rate will fall, and the aggregate production function will shift upward
B) employment will increase, and the aggregate production function will shift upward
C) the real wage rate will fall, and the economy will move up along its aggregate production function
D) employment will increase, and the economy will move down along its aggregate production function
Q26. An increase in labor productivity _ and .
A) increases the demand for labor; raises the real wage rate
B) decreases the quantity of labor employed; decreases the supply of labor
C) raises the real wage rate; shifts the aggregate production function downward
D) decreases the demand for labor; lowers the real wage rate
Q27. The supply of labor curve has a slope because as the real wage rate rises,
.
A) negative; firms hire fewer workers
B) positive; the opportunity cost of leisure rises
C) positive; the opportunity cost of leisure falls
D) negative; households work more hours
Q28. Economic growth is a sustained expansion of production possibilities, as measured by the increase in over time.
A) real GDP B) population C) inflation D) the price level
Q29. A technological change and a change in the capital stock .
A) shifts the productivity curve; shifts the productivity curve
B) shifts the productivity curve; creates a movement along the productivity curve
C) creates a movement along the productivity curve; shifts the productivity curve
D) does not change the productivity curve; creates a movement along the productivity curve
Q30 . A nation's population was 250 million last year and is 255 million this year. If its real GDP was $8.5 trillion last year and is $8.8 trillion this year, what is its growth rate of real GDP per person?
Part II.
a. Assuming businesses expect to have a higher profit in the near future Explain the effects of this event on real GDP (Y) and the price level (P) in Toughtimes, starting from a position of full employment equilibrium, where P=Y=Y*=YP. (Draw the AD, SRAS, and LRAS curves)
b. Based on the answer from part a, Does an inflationary or recessionary gap exists in the economy? Explain your answer.
c. Explain clearly how the government can do to overcome the problems faced by the economy based on your answer from part b. (Hints: use AD-AS model both in words and graphically.
d. Show the transition from the short rum equilibrium to the long run equilibrium, based on the concept of self-correction mechanism (a change in SRAS) without the Fed or government intervention.